
ImageScope
User’s Guide
MAN-0001, Revision P | 23 September 2015
The Pathology Company

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 20152
ImageScope User’s Guide
This document applies to eSlide Manager Release 12.3 and later.
Copyright Notice
ÌÌ Copyright © 2006-2015 Aperio. All rights reserved. LEICA and the Leica logo are registered trademarks of Leica Microsystems IR GmbH. Aperio is
a registered trademark of Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. in the USA and other countries.
Customer Resources
ÌÌ For the latest information on Leica Biosystems Aperio ePathology products and services, please visit www.LeicaBiosystems.com/ePathology.
Disclaimers
ÌÌ Use normal care in maintaining and using Aperio ePathology servers. Interrupting network connections or turning off the servers while they are
processing data (such as when they are analyzing eSlides or generating an audit report) can result in data loss.
ÌÌ This manual is not a substitute for the detailed operator training provided by Leica Biosystems Imaging or for other advanced instruction. Leica
Biosystems Imaging Field Representatives should be contacted immediately for assistance in the event of any instrument malfunction. Installation
of hardware should only be performed by a certified Leica Biosystems Imaging Service Engineer.
ÌÌ ImageServer is intended for use with eSlides created by scanning glass slides with the scanner. Educators will use Aperio ePathology software to
view and modify eSlides in Composite WebSlide (CWS) format.
Patents
ÌÌ Aperio ePathology products are protected by U.S. Patents: 6,711,283; 6,917,696; 7,035,478; 7,116,440; 7,257,268; 7,428,324; 7,457,446; 7,463,761;
7,502,519; 7,518,652; 7.602.524, 7,646,496; 7,738,688 and licensed under one or more of the following U.S. Patents: 6,101,265; 6,272,235;
6,522,774; 6,775,402; 6,396,941; 6,674,881; 6,226,392; 6,404,906; 6,674,884; and 6,466,690.
Contact Information – Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc.
Headquarters Customer Support General Information
Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc.
1360 Park Center Drive
Vista, CA 92081
USA
Tel: +1 (866) 478-4111 (toll free)
Direct International Tel: +1 (760) 539-1100
US/Canada Tel: +1 (866) 478-3999 (toll free)
Direct International Tel: +1 (760) 539-1150
US/Canada/Worldwide Email:
US/Canada Tel: +1 (866) 478-4111 (toll free)
Direct International Tel: +1 (760) 539-1100
Email: [email protected]
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 3
Customer Service Contacts
Please contact the office for your country for technical assistance.
Australia:
96 Ricketts Road
Mount Waverly, VIC 3149
AUSTRALIA
Tel: 1800 625 286 (toll free)
Between 8:30 AM-5 PM, Monday-Friday, AEST
Email: [email protected]
Austria:
Leica Biosystems Nussloch GmbH
Technical Assistance Center
Heidelberger Strasse 17
Nussloch 69226
GERMANY
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +43 1 486 80 50 50
Email: [email protected]
België/Belgique:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +32 2 790 98 50
Email: [email protected]
Canada:
Tel: +1 866 478- 999 (toll free)
Direct International Tel: +1 760 539 1150
Email: T[email protected]
China:
17F, SML Center No. 610 Xu Jia Hui Road, Huangpu District
Shanghai, PRC PC:200025
CHINA
Tel: +86 4008208932
Fax: +86 21 6384 1389
Email: [email protected]
Remote Care email: [email protected]
Danmark:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +45 44 54 01 01
Email: [email protected]
Deutschland:
Leica Biosystems Nussloch GmbH
Technical Assistance Center
Heidelberger Strasse 17
Nussloch 69226
GERMANY
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +49 6441 29 4555
Email: [email protected]
Eire:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +44 1908 577 650
Email: [email protected]
España:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +34 902 119 094
Email: [email protected]
France:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +33 811 000 664
Email: [email protected]
Italia:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +39 0257 486 509
Email: [email protected]
Japan:
1-29-9 Takadannobaba, Sinjuku-ku
Tokyo 169-0075
JAPAN
Nederland:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +31 70 413 21 00
Email: [email protected]
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 20154
New Zealand:
96 Ricketts Road
Mount Waverly, VIC 3149
AUSTRALIA
Tel: 0800 400 589 (toll free)
Between 8:30 AM-5 PM, Monday-Friday, AEST
Email: [email protected]
Portugal:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +35 1 21 388 9112
Email: [email protected]
Sweden:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +46 8 625 45 45
Email: [email protected]
Switzerland:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +41 71 726 3434
Email: [email protected]
United Kingdom:
Tel: 0080052700527 (toll free)
In-country Tel: +44 1908 577 650
Email: [email protected]
USA:
Tel: +1 866 478 3999 (toll free)
Direct International Tel: +1 760 539 1150
Email: T[email protected]

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 5
1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 10
Intended Use ................................................................................................................................. 10
ImageScope Features ......................................................................................................................10
Types of Files You Can View .............................................................................................................. 11
For More Information ...................................................................................................................... 11
2 Installing ImageScope ................................................................................................... 13
Before You Start .............................................................................................................................13
Installation Requirements .............................................................................................................13
Monitor and System Requirements .................................................................................................13
Security Alerts ...........................................................................................................................13
Installation ...................................................................................................................................13
Modifying or Removing the ImageScope Software .................................................................................14
Starting ImageScope ....................................................................................................................... 14
3 Opening an eSlide .......................................................................................................... 15
About User Permissions ...................................................................................................................15
Opening eSlide Images from eSlide Manager ........................................................................................16
Opening an eSlide Manager eSlide .................................................................................................16
Opening an eSlide Manager eSlide from ImageScope .........................................................................16
Opening an eSlide on Your Workstation or LAN .....................................................................................17
Local Image Support .................................................................................................................... 17
Opening a Recently Viewed Local eSlide ..........................................................................................17
Opening and Viewing Multiple eSlides ................................................................................................17
Managing eSlide Windows ...........................................................................................................18
Keep Open Option ....................................................................................................................... 18
Viewing eSlide Information ...............................................................................................................19
Status Bar ................................................................................................................................. 19
Saving and Opening an Image View .................................................................................................... 20
Closing eSlides ..............................................................................................................................20
4 Viewing an eSlide ........................................................................................................... 21
ImageScope Viewing Window ........................................................................................................... 21
Contents

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 20156
Contents
ImageScope Toolbar Quick Reference ..............................................................................................22
Synchronizing Navigation of Multiple eSlides .......................................................................................24
Smart Synchronization .................................................................................................................24
Moving Around the eSlide Image .......................................................................................................26
Using the Magnifier Window ............................................................................................................27
Changing Viewing Magnification ........................................................................................................27
Viewing with Color Management .......................................................................................................28
Viewing Scalebar, Axes, and Grid ....................................................................................................... 28
Viewing Z-Stack eSlide Images ..........................................................................................................30
Viewing and Navigating a Z-Stack Image .........................................................................................30
Viewing eSlides with IQ ................................................................................................................... 31
IQ Features ................................................................................................................................31
IQ Quick Reference ......................................................................................................................32
5 Rotating Images and Slide Labels ................................................................................ 33
Rotating an Image ..........................................................................................................................33
Rotating a Label .........................................................................................................................34
6 Making Image Adjustments ........................................................................................... 35
Making Image Adjustments ..............................................................................................................35
Saving and Loading Color Settings .................................................................................................. 37
For More Information ......................................................................................................................37
7 Working with Fluorescence eSlides ............................................................................. 38
Applying a Temporary False Color .......................................................................................................38
Adjusting Fluorescence Fused Images .................................................................................................39
Using the Fusion Adjustment Window .............................................................................................39
Viewing All Channel Images .......................................................................................................... 40
Seeing Channel Information .......................................................................................................41
Cycling Channel Displays .............................................................................................................. 41
Adjusting Color ..........................................................................................................................42
Adjusting Brightness, Contrast, and Gamma ......................................................................................42
Intensity Histogram .................................................................................................................43
Adjusting Registration .................................................................................................................44
Fusing Fluorescence Images ..............................................................................................................45
Notes on Creating an AFI .............................................................................................................. 47
8 Image Resolution ........................................................................................................... 48
Setting or Changing Image Resolution ................................................................................................. 48
Computing the Resolution from the Image ............................................................................................ 49

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 7
Contents
9 Working with Annotations ............................................................................................. 51
Using the Annotation Tools ............................................................................................................... 51
Measuring the Distance Between Two Line Annotations ...................................................................... 53
Annotating Z-Stack Images ...........................................................................................................54
Drawing Fixed Size Annotations .....................................................................................................54
Drawing Annotations with a Fixed Aspect Ratio ................................................................................. 54
Moving Annotations ....................................................................................................................55
Editing Free-Form Annotations Created with the Pen or Negative Pen .....................................................55
Completing a Free-Form Shape ...................................................................................................56
Editing a Free-Form Shape .........................................................................................................56
Fixing a Problem Area ..............................................................................................................57
10 Using the Annotations Window .................................................................................... 58
Annotations Summary View Window – Quick eIHC Analysis .....................................................................58
Slide-Specific Processing .............................................................................................................. 58
Using the Annotations Summary View Window .................................................................................59
Enabling and Disabling Pre-processing .............................................................................................61
Incremental Processing ................................................................................................................61
Other Options ............................................................................................................................61
The Annotations – Detailed View Window ...........................................................................................62
Annotations Window Tools ........................................................................................................62
Annotation Length and Area Display ...............................................................................................63
Adding Text to an Annotation ........................................................................................................63
Moving Annotations ....................................................................................................................64
Exporting and Importing Annotation Layers .......................................................................................65
Using Attributes .........................................................................................................................66
Adding and Deleting Attributes ..................................................................................................66
11 Linking Annotations and eSlides ................................................................................. 67
Working with the Link Manager ......................................................................................................... 67
Creating a Link ...............................................................................................................................68
Viewing Links ................................................................................................................................68
Deleting Links ................................................................................................................................69
12 Tracking .......................................................................................................................... 70
Turning on the Tracker .....................................................................................................................70
Viewing a Track .............................................................................................................................71
Playing a Track ...............................................................................................................................72
Appending to a Track .......................................................................................................................72

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 20158
Contents
13 Saving eSlides and Regions ......................................................................................... 73
Copy and Paste an eSlide Image ........................................................................................................73
Taking a Snapshot ..........................................................................................................................73
Emailing a Snapshot .......................................................................................................................73
Receiving a Snapshot Email .......................................................................................................74
Exporting Images ............................................................................................................................74
Extracting a Region ......................................................................................................................... 76
Note on Fluorescent Images ..........................................................................................................77
Saving an Image of a Specific Size .................................................................................................. 78
Extracting an Image of a Predefined Size or Aspect Ratio ..................................................................78
Managing Viewing Applications ..................................................................................................... 78
Compatibility Notes .................................................................................................................78
Defining a Viewing Application ...................................................................................................79
Using the Viewing Application ...................................................................................................79
Deleting Viewing Applications ...................................................................................................79
14 eSlide Conferencing ...................................................................................................... 80
About eSlide Conferencing ...............................................................................................................80
Concepts ..................................................................................................................................80
Starting an eSlide Conference ...........................................................................................................81
Connecting to an eSlide Conferencing Server ....................................................................................81
Opening an Image to Share ...........................................................................................................82
Joining a Conference ................................................................................................................... 83
Viewing Slides in Conference ............................................................................................................ 84
Changing the Conference Leader ........................................................................................................84
Leader Initiates Change in Leadership .............................................................................................84
Follower Initiates Change in Leadership ...........................................................................................85
Conference Creator Re-asserts Leadership ....................................................................................... 85
15 TelePath Live .................................................................................................................. 86
Scanner Compatibility Notes ............................................................................................................. 86
Before You Use TelePath Live ............................................................................................................86
Calibration ................................................................................................................................86
Setting the ImageServerURL ..........................................................................................................86
What Is a Z-Stack? .........................................................................................................................87
Connecting to an Aperio Scanner .......................................................................................................88
Preparing a Slide for TelePath Live .....................................................................................................90
Viewing Live Video from the Scanner ..................................................................................................90
Capturing Z-stacks .......................................................................................................................... 91
Viewing Z-stacks ............................................................................................................................ 94

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 9
Contents
16 Utilities and Diagnostics ............................................................................................... 95
Logging ........................................................................................................................................ 95
Cache Display ................................................................................................................................95
Running Multiple ImageScope Sessions ..............................................................................................96
Tuning Parameters/Statistics ............................................................................................................97
Maximum Cache Size ..................................................................................................................97
Statistics ..................................................................................................................................97
17 ImageScope Options ..................................................................................................... 99
General Options .............................................................................................................................99
Magnification ............................................................................................................................99
Default Gamma Files .................................................................................................................100
Loading a Default Gamma Table File for the Main Image ................................................................100
Loading a Default Gamma Table File for Z-stack Images .................................................................100
Analysis .....................................................................................................................................101
Navigation Options .......................................................................................................................101
Synchronization Option ..............................................................................................................101
Panning Options .......................................................................................................................102
Annotation Options ....................................................................................................................... 102
Annotation Color Options ............................................................................................................102
Fixed Size Annotations ............................................................................................................... 102
Automatically Saving Annotations ................................................................................................103
Tracking Options ..........................................................................................................................103
Performance Options ..................................................................................................................... 104
HTTP Proxy Option ........................................................................................................................105
Report Image Options .................................................................................................................... 105
Color Management Options ............................................................................................................106
Email Settings .............................................................................................................................107
For More Information ....................................................................................................................107
A Keyboard Shortcuts ..................................................................................................... 108
ImageScope Keyboard Shortcuts ...................................................................................................... 108
B Aperio Integrated Color Management .........................................................................111
ICC Profiles ................................................................................................................................. 111
Scanner ICC Profile .................................................................................................................... 111
Display Monitor ICC Profile ......................................................................................................... 111
How ImageScope Uses Color Management ........................................................................................ 112
Index ....................................................................................................................................113
Symbols...............................................................................................................................118

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201510
1
Introduction
This chapter introduces you to ImageScope and indicates where to find information on specific features.
Intended Use
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
ImageScope Features
Although the basic function of ImageScope is to allow you to view eSlides, ImageScope offers much more:
Ì` View eSlides from any workstation on the network, eliminating the delay of physically transporting glass slides.
Ì` Share and discuss eSlides in real-time in multiple remote locations by using eSlide conferencing.
Ì` View multiple eSlides concurrently.
Ì` Apply image adjustments for contrast, brightness, and gamma.
Ì` Analyze entire eSlides or selected regions using algorithms.
Ì` View, annotate, and analyze scanned z-stack images.
Ì` Interface directly to a Aperio scanner through a network connection to view slides “live” and in different focal
planes.
Ì` Rotate eSlide images and labels.
Ì` Use Aperio Integrated Color Management to view eSlides to ensure the eSlides are displayed in accurate color.
Ì` Use the Image Quality (IQ) feature to optimize viewing of an eSlide based on its stain.
Ì` Add and manage various types of eSlide image annotations.
Ì` Interface to the Aperio ePathology ImageServer and eSlide Manager.
Ì` Instantly pan and zoom to any region of the slide.
Ì` Extract a region or selected regions of an eSlide to a file in a choice of formats.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 11
Chapter 1: Introduction
Types of Files You Can View
You can use ImageScope to view:
Ì` ScanScope Virtual Slides – .SVS files created when the Aperio scanner scans glass microscope slides.
Ì` JPEG files – Both .JPG and .JP2 files.
Ì` TIFF and TIF files.
Ì` Aperio fluorescent images (Aperio Fused Image, .afi)
Ì` CWS files – Composite WebSlides
1
.
Ì` Hamamatsu NanoZoomer files – NDPI and .VMS files. Slide label images are not available for these images in
eSlide Manager, ImageScope, Digital Slide Studio, and WebScope, as these images do not contain labels.
Ì` Zeiss Mirax files – .MRXS files. (Note that Mirax images are composite images that consist of a group of .DAT
files.)
Ì` ScanScope image set, .sis file – The ImageScope image view is what you see when one or more eSlides are
viewed in the ImageScope window. ImageScope enables you to save the image view as a ScanScope image set so
that you can open all the slides at once in the future.
Ì` SCN files – Leica Biosystems SCN brightfield and fluorescent images. ImageScope supports multiple region SCN
image files.
For More Information
Here is where to locate information on ImageScope features.
How do I... Go to...
Install ImageScope? “Chapter 2: Installing ImageScope” on page 13
View eSlides? “Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide” on page 15
“Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide” on page 21
Enable or disable clinical viewing mode? “Clinical Viewing Mode” on page 22
Make annotations and link annotations or
eSlides to make a viewing sequence?
“Chapter 9: Working with Annotations” on page 51
“Chapter 11: Linking Annotations and eSlides” on page 67
Use algorithms to analyze eSlides? See the Image Analysis User’s Guide
Work with algorithms and algorithm
macros?
See the Image Analysis User’s Guide
Share slides with others in real time? “Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing” on page 80
Display the image with a grid, scale axes,
or a scalebar?
“Viewing Scalebar, Axes, and Grid” on page 28
Adjust image color, brightness, contrast,
and gamma?
“Chapter 6: Making Image Adjustments” on page 35
“Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides” on page 38
1 A Composite WebSlide, also known as a CWS slide, is a proprietary format created by Bacus Laboratories, Inc (“Bacus”). WebSlide
®
is a
registered trademark of Bacus Laboratories Inc.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201512
Chapter 1: Introduction
How do I... Go to...
Set and view image resolution? “Chapter 8: Image Resolution” on page 48
Track movements through an eSlide? “Chapter 12: Tracking” on page 70
Rotate images and eSlide labels? “Chapter 5: Rotating Images and Slide Labels” on page 33
Save image snapshots, email snapshots,
and extract part of an eSlide?
“Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions” on page 73
View z-stack eSlide images that were
scanned on your Aperio scanner
“Viewing Z-Stack eSlide Images” on page 30
View a specimen in various focal planes
directly on the scanner?
“Chapter 15: TelePath Live” on page 86
View live video from the scanner? “Chapter 15: TelePath Live” on page 86
Fine-tune performance? “Chapter 17: ImageScope Options” on page 99
Debug and troubleshoot? “Chapter 16: Utilities and Diagnostics” on page 95
Use keyboard shortcuts for ImageScope
commands?
“Appendix A: Keyboard Shortcuts” on page 108
Use Aperio Integrated Color Management? ”Viewing with Color Management” on page 28
“Appendix B: Aperio Integrated Color Management” on page 111

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 13
2
Installing ImageScope
This chapter contains information on installing the client software for the ImageScope eSlide viewer.
Before You Start
Review the information in this section prior to installing ImageScope.
Installation Requirements
To successfully install ImageScope, you must first log into Windows as a user with administrative privileges.
Monitor and System Requirements
Because eSlides are, by design, high resolution and information rich, for best results you should use a high-quality LCD
monitor to view them. Make sure the monitor is at the proper viewing height and in a room with appropriate lighting.
Before installing ImageScope, make sure your workstation and monitor meet the minimum requirements discussed in the
Aperio ePathology System Requirements.
Security Alerts
If during installation you see messages from Microsoft or third-party firewall, VPN, or virus software telling you that
the installation has been blocked, you should consult your network administrator for help resolving these issues before
continuing.
Installation
To install ImageScope, follow these steps:
1. Ensure you are logged into Windows as a user with administrative priviledges.
2. Double-click My Computer or open Windows Explorer and navigate to the ImageScope installer file. (This file may
have been downloaded from the www.LeicaBiosystems.com/ePathology web site, may have been provided on CD,
or may reside on your network; contact your network administrator for help if you have trouble finding it.)
If you are installing ImageScope on your DSR (Digital Slide Repository), use DSRInstall; if installing ImageScope on
a user’s workstation, use ClientInstall.
3. Double-click the .exe file to start the installation wizard.
4. Follow the instructions on your screen to accept the terms of the license agreement and install ImageScope.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201514
Chapter 2: Installing ImageScope
Modifying or Removing the ImageScope Software
At any time after ImageScope is installed, you can run the installer again to modify, repair, or remove the ImageScope
software. If ImageScope is already installed, select from the following options on the installer window:
Ì` Modify to change the ImageScope installation by adding or deleting components.
Ì` Repair to reinstall all the components previously installed. This is the option to use if you are upgrading a previous
installation to new software.
Ì` Remove to uninstall the ImageScope software.
Starting ImageScope
To start ImageScope, click Start on the Windows taskbar, point to All Programs > ScanScope, and select ImageScope.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 15
3
Opening an eSlide
This chapter contains information on opening and viewing eSlides in ImageScope.
Connection speeds may affect ImageScope performance when viewing remote images. For best
viewing, we recommend a connection speed of 100 mbps or greater.
Use ImageScope to view:
Ì` Local eSlides – images that reside on your workstation or your local network and are accessible using Microsoft
file sharing (for example, by using Windows Explorer). Some features are not available when viewing local eSlides.
See “Local Image Support” on page 17 for further details.
Ì` Remote eSlides – images that you open directly on an Aperio ePathology ImageServer or that you open using
eSlide Manager.
Because Aperio ePathology eSlides are by design high resolution and information rich, for best results you should use a high
quality monitor to view them. For details about monitor requirements, see the Aperio ePathology System Requirements.
About User Permissions
ImageScope makes use of eSlide Manager security to enforce user permissions when viewing images.
The eSlide Manager administrator uses data groups and user roles to define what data you can see and what you can do
when you see it. Data groups organize data such as eSlides into different groups that can be seen and used by different
users. User roles define the commands you can use and the elements of an eSlide Manager page you can see.
What this means for ImageScope users is that when you open a remote image ImageScope may request that you log in so
eSlide Manager can determine if you have the correct permissions to view the images you want to access. Type the same
user name and password you use to log into eSlide Manager.
This also means that you may be restricted in what you can do with an eSlide. If, for example, you have read-only access
to the data group that contains the eSlide you are viewing, you can use the ImageScope drawing tools to draw annotations
but you won’t be able to save them. If you have questions about your user permissions, contact your eSlide Manager
administrator for assistance.
Some of the features of the eSlide Manager security system you should know about are:
Ì` To keep user information secure, user credentials are encrypted and are never passed in clear text between the
components of the eSlide Manager system.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201516
Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide
Ì` User credentials can time out. If enough time elapses after you log in, you may be asked to log in again.
Ì` Data groups and user permissions are defined in eSlide Manager by the administrator.
Depending on how eSlide Manager is configured, you may be able to log in as Guest to see public images that do not
require user authentication.
Opening eSlide Images from eSlide Manager
You can open a remote eSlide from eSlide Manager or you can open it from ImageScope. (For more details about using
eSlide Manager, see the eSlide Manager Operator’s Guide.)
Opening an eSlide Manager eSlide
To open an eSlide image from eSlide Manager, follow these steps:
1. In eSlide Manager, use the List commands or search feature to find the eSlide you want to view.
2. Click the thumbnail image of the eSlide, or select the check box next to the eSlide and click View Images.
The eSlide opens in ImageScope.
Opening an eSlide Manager eSlide from ImageScope
To open an eSlide image from ImageScope, follow these steps:
1. Go to the ImageScope File menu and select Access Remote Server to connect to eSlide Manager.
2. Enter the name of the server where eSlide Manager resides, and set the Port value to 82.
3. Click Connect.
4. When prompted, enter your eSlide Manager user name and password.
5. When the list of eSlide appears, select either the List or Thumbnail view from the drop-down list at the upper right.
6. Click the ImageScope link below the image.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 17
Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide
Opening an eSlide on Your Workstation or LAN
To open an eSlide that resides on your workstation or local area network:
1. Start ImageScope by clicking Start, pointing to All Programs > ScanScope, and then selecting ImageScope.
2. Go to the File menu and select Open Image (or click on the ImageScope toolbar).
3. On the Open Image window, navigate to the location that contains the image you want to view.
4. Click the name of the eSlide you want to open and click Open.
You may need to change the file type in the Open Image window to see the type of image you want to view. For example, to
view a CWS image, click the file type drop-down list and select Composite WebSlides (*/SlideScan.ini).
Local Image Support
If you open a local image instead of an image in eSlide Manager, Smart sync, Tracking, and IQ are not supported for that
image.
Opening a Recently Viewed Local eSlide
ImageScope displays a list of the last few eSlides that were viewed on the File menu. To open one of these images, go to
the File menu and click one of the eSlides listed at the bottom of the menu.
Opening and Viewing Multiple eSlides
You can open multiple eSlides within ImageScope. To open multiple eSlides in eSlide Manager:
1. In eSlide Manager, use the List commands or search feature to find the eSlide you want to view.
2. Select the check boxes next to the eSlides you want to view, and click View Images:

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201518
Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide
The eSlides open in ImageScope:
You can view all the slides at once or view them separately by selecting Tile Vertical, Tile Horizontal, or
Cascade from the Window menu.
You can move between the opened images by clicking on an image in the filmstrip, which appears in the left pane
of the ImageScope window. If the ImageScope filmstrip is not visible, go to the View menu and select Filmstrip.
See “Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide” on page 21 for more information on viewing images and using the
ImageScope viewing tools.
Managing eSlide Windows
To maximize, minimize/restore, or close the individual eSlide windows within the ImageScope main window, click the slide
icon on the image menu bar and select an action to perform.
Keep Open Option
When you open one or more multiple images from eSlide Manager, any images already open in ImageScope are closed
before displaying the new ones.
To do this: Do this:
Keep an image open in ImageScope
when you open another image from
eSlide Manager.
Select the image in ImageScope, and then go to the Image menu and select
Keep Open.
Do this for each image you want to keep open.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 19
Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide
To do this: Do this:
Close an image Select the image, go to the ImageScope File menu and select Close Image.
Viewing eSlide Information
To view information, such as the image size, location, and compression ratio, about the active eSlide, go to the Image menu
and select Information or click on the toolbar. The following information appears in the Image Information window.
Go to this tab: To view this information:
Information Provides detailed data regarding the eSlide, including the magnification,
image ID, and description. The ICC profile is provided if one is being used. (See
“Appendix B: Aperio Integrated Color Management” on page 111 for
information on ICC profiles and color management.)
If this eSlide was scanned on an Aperio scanner, the time zone of the scan
location and time of the scan appear. The Information tab is always shown.
The other tabs only appear if those elements are associated with the eSlide.
For example, if there is no label image for this eSlide, you do not see the Label
Image tab.
For a z-stack eSlide image, information appears for each layer. The Depth is the
layer separation value that is set during scanning, which is measured in microns
(µm).
For an Aperio Fused Image (AFI), the Information window contains information
on the separate channel images that comprise the AFI image.
Thumbnail A thumbnail image of this eSlide (the area of the glass slide that was scanned).
Label image The eSlide label.
Macro image A macro image of the entire slide.
Status Bar
Information about the active eSlide appears in the status bar at the bottom of the ImageScope window.
The sample status bar above shows the following information:
Ì` 73091 x 62821 = 12.8GB, file = 575MB – The entire eSlide is 73,091 by 62,821 pixels in size. The eSlide’s raw
data is 12.8 gigabytes in size and the compressed size of the eSlide file is 575 megabytes.
Ì` 0, -12950 : 73091 x 62821 – The first two numbers indicate the pixel position of the top, left corner of the display.
The second numbers indicate which part of the image is being viewed.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201520
Chapter 3: Opening an eSlide
Ì` 1815, 37033 – The current pixel position of your cursor.
Ì` Prefetching/progressive rendering – Indicates which performance options are in effect. For information on
performance options, see “Performance Options” on page 104.
Ì` PAN – The current navigation or annotation tool is selected. In this case, panning is selected.
You can turn the status bar off and on by going to the View menu and selecting Status Bar.
Saving and Opening an Image View
An Image View is the entire set of slide images that are open at one time in ImageScope. If you have a group of eSlides that
you want to view together, you can save them as an Image View.
To do this: Do this:
Save an Image View 1. Go to the File menu and select Save Image View(s). The Save Image
View(s) window appears.
The file type for an Image View is ScanScope Image Sets (.sis).
2. Type the name you want to use for the file and click Save.
Opening an Image View
1. Go to the File menu and select Open Image. Locate the .sis file you
saved on your network. You need to select .sis from the Files of type
drop-down list to see the file.
2. Select the .sis file to open and click Open. ImageScope opens the .sis
file with all eSlides in that image view open and in their former pan
and zoom configuration.
Closing eSlides
To do this: Do this:
Closing a single eSlide If you have multiple eSlides open, click the one you want to close in the
filmstrip. If you only have one eSlide open, it is already selected. Go to the File
menu and select Close Image.
Closing all eSlides Go to the File menu and select Close All Images.
If you made any changes to the eSlide (for example, adding an annotation), you are asked if you want to save the changes
before you close the slide. If you want ImageScope to automatically save annotations when you close an image, see
“Automatically Saving Annotations” on page 103 for instructions.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 21
This chapter provides a tour of the ImageScope main window and describes how to use the navigation and
magnification tools.
ImageScope Viewing Window
Toolbar
eSlide label
Zoom slider
Filmstrip
Thumbnail
ImageScope main
window pane
MagnierStatus bar
4
Viewing an eSlide

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201522
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
The main elements of the ImageScope viewing window include:
Ì` Toolbar – You can perform many tasks from the toolbar. See the next section for a quick reference list of the
ImageScope toolbar icons.
Ì` Zoom slider – You can magnify or shrink the current view. See “Zoom Slider” on page 27 for details.
Ì` Focus slider (not shown) – Appears with z-stack eSlide images only. Used to view different focal areas (z-stack
layers) on a z-stack image. See “Viewing Z-Stack eSlide Images” on page 30 for details.
Ì` Filmstrip – Open eSlides appear in the filmstrip. Click a slide in the filmstrip to view it in the main window.
Ì` Label window – If the eSlide has an image of the slide label, it appears in the slide label window.
Ì` Thumbnail window – The thumbnail is a navigation tool that shows the complete eSlide. See “The Thumbnail
Window” on page 26.
Ì` Magnifier window – Enables you to magnify a portion of the eSlide. See “Using the Magnifier Window” on page
27.
You can hide or show these tools from the View menu.
Clinical Viewing Mode
Clinical Viewing mode provides a simple toolbar that contains only the tools used in a clinical environment.
To do this: Do this:
Use the clinical toolbar Go to the View menu and select View Clinical Toolbar.
To provide quick and easy eSlide analysis, only the Summary View of the Annotations window
is available when using clinical viewing mode.
Return to the full toolbar Go to the View menu and select View Standard Toolbar.
ImageScope Toolbar Quick Reference
Here is a quick list of the toolbar buttons.
*These icons are shown in clinical viewing mode.
Tool Action
Go to the Open Image window where you can browse for a local eSlide to open for viewing.
Close the eSlide that is currently being viewed in ImageScope.
Export images of a specified area on the eSlide. You can export the raw eSlide image, the eSlide with annotations,
and the mark-up image. See “Exporting Images” on page 74.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 23
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Tool Action
Create a snapshot image of the current ImageScope window, including any annotations. You can save the image
as a TIFF or JPEG file. See “Taking a Snapshot” on page 73.
Send the snapshot image in an email. See “Emailing a Snapshot” on page 73.
Save an Image View as a .sis file. An Image View includes the entire set of eSlides currently open in ImageScope.
See “Saving and Opening an Image View” on page 20.
Go to the Image Adjustment window, where you can make color and other adjustments to the eSlide currently
being viewed. See “Making Image Adjustments” on page 35.
Go to the Image Information window, which displays information about the eSlide currently being viewed. See
“Viewing eSlide Information” on page 19.
Go to the previous view of the eSlide.
Go to the next view of the eSlide (only enabled if you first used the back arrow to go to a previous view).
*Manually synchronize navigation for all eSlides you are viewing. (Used when multiple eSlides are open in the
ImageScope window.) See “Synchronizing Navigation of Multiple eSlides” on page 24.
*Use smart synchronization for multiple eSlides you are viewing. Corresponding regions in the eSlide images are
synchronized. (Same icon as for manual synchronization, but colored yellow.) (This feature is not available when
viewing local eSlides.) See “Smart Synchronization” on page 24.
Show or hide axes or axes and grid. See “Viewing Scalebar, Axes, and Grid” on page 28.
Show or hide the zoom slider. See “Zoom Slider” in the table on page 27.
Show or hide the eSlide label.
Show or hide the thumbnail window.
Show or hide the magnifier window.
Display on the full monitor screen. (Or turn off if already in full-screen mode.)
*Open the Annotations window where you can create multiple annotation layers and organize and add
descriptions to annotations. See “Chapter 9: Working with Annotations” on page 51.
For customers using Image Analysis, open the Analysis window. For details on using Image Analysis, refer to the
Image Analysis User’s Guide.
Open the Annotation Link Manager window, where you can link annotations or eSlides to create a viewing
sequence. See “Chapter 11: Linking Annotations and eSlides” on page 67.
Go to the previous link (if a previous link exists). See “Viewing Links” on page 68.
Go to the next link (if a next link exists). See “Viewing Links” on page 68.
Move the eSlide by panning different directions. See the “Panning” row in the table on page 26.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201524
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Tool Action
Zoom the selected area of the eSlide. See the “Zoom Navigation” row on page 28.
*Extract a region of an eSlide. See “Exporting Images” on page 74.
*Draw a free-form annotation. See the “Pen” row in the table on page 51.
Draw a free-form annotation to be excluded from analysis. (This creates a negative annotation.) See the “Negative
pen” row on page 52.
*Measure an object on an eSlide. See the “Ruler” row on page 52.
*Draw a rectangular region (or a square if you hold down the Shift key while you draw).
Draw an elliptical annotation (or a circle if you hold down the Shift key while you draw).
*Draw an arrow pointing to an area of interest.
Mark the eSlide image with numeric counters. See the “Counter” row in the table on page 52.
*Select an image for a report. This feature is only useful if you have eSlide Manager Reporting option installed
and the report template you are using uses images.
Measure the distance (µm) between two free-form line annotations. See “Measuring the Distance Between Two
Line Annotations” on page 53.
Copy the selected annotation.
You can paste the annotation in any open eSlide. If you have run analysis on the annotation, only the annotation is
copied (not the analysis results).
Paste the copied annotation region in the active eSlide.
Turn Integrated Color Management on or off. Only useful if the image contains an embedded ICC profile. See
“Viewing with Color Management” on page 28.
*Turn Image Quality (IQ) mode on or off. See “Viewing eSlides with IQ” on page 31. (This feature is not available
when viewing local eSlides.)
*See help information for ImageScope.
Synchronizing Navigation of Multiple eSlides
If you want all open eSlides to respond to the same navigation (for example, panning to the right) when you are viewing
them side by side, go to the ImageScope toolbar and click .
Smart Synchronization
Smart syncronization is only available for remote images opened in ImageScope from eSlide Manager.
Smart synchronization is an extension of the manual synchronization feature discussed above. In addition to synchronizing
navigation between the slides, corresponding regions in the eSlide images are also synchronized.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 25
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Click the icon on the ImageScope toolbar to use smart synchronization.
Smart synchronization compensates for rotation (non-flipped) but not for other factors such as
stretched or missing tissue. In those cases, ImageScope tries to display the same tissue feature in all
tiled images, but not necessarily in exactly the same location.
This feature is useful when the original microscope slides were prepared from the same tissue block but were stained
differently, as shown in the example below. Using smart synchronization, the main features of the slide stay locked in step
as you move around the slides.
You cannot use smart synchronization on images that were flipped vertically or horizontally. Also, you cannot flip an image
while smart synchronization is turned on.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201526
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Moving Around the eSlide Image
ImageScope offers different options for moving around an eSlide.
This feature: Works like this:
Panning
With the Panning tool selected , hold down the mouse button and drag the
cursor across the eSlide.
Panning moves the slide the direction you are dragging. If you want to set
ImageScope to pan in reverse (“pathologist mode”), see“Panning Options” on
page 102.
Autopanning Autopanning enables you to move at high speed over an eSlide.
With the cursor at the center of the main viewing area, click the scroll wheel on
your mouse or right-click and select Autopan from the menu.
When the autopan icon appears , the eSlide starts moving toward your
mouse pointer. The greater the distance between your mouse pointer and the
icon, the faster the scroll.
Scrolling Move your pointer toward any edge of the ImageScope main window. When the
pointer changes to an arrow: , click and hold the mouse button to scroll in that
direction. To stop scrolling, release the mouse button.
The Thumbnail Window The thumbnail window shows the entire eSlide. The small black rectangle
inside the thumbnail represents the area of the eSlide that appears in the main
window. Click the area in the thumbnail window that you want to view, or drag
the rectangle in the thumbnail window to move to another area of the eSlide.
To resize the thumbnail window, clicking and dragging its lower-left corner.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 27
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
This feature: Works like this:
Moving to a specific point on the
eSlide
Go to the Image menu and select Go To. Using the current image size that
appears as a reference, type an X Coordinate (horizontal) and a Y Coordinate
(vertical) in pixels.
Ìy Click Go To: Center to position the point selected by those coordinates in
the center of the current view.
Ìy Click Go To: Corner to position the point selected by those coordinates in
the upper left corner of the current view.
Page panning Use the Shift+Arrow keys to move a page to the right or left, or up or down.
Using the Filmstrip To move between multiple eSlides in ImageScope, click an image from the
filmstrip.
Using the Magnifier Window
Use the magnifier window to show a larger view of a particular portion of the eSlide. To use the Magnifier window:
Ì` Drag the magnifier window on the main window to the area you want to see in more detail.
Ì` Move your mouse pointer to the area that you want to display in the magnifier window.
Ì` Resize the magnifier window by dragging its lower right corner.
The default magnification is twice the resolution of the image in the main window. To change the resolution of the magnifier
window, go to the Tools menu and select Options. For details, see “Magnification” on page 99.
Changing Viewing Magnification
You can change the resolution of the entire main window image.
Use this feature: To do this:
Immediate Maximum Zoom Double-click the image to zoom to the maximum magnification. Double-click again to
return to the previous magnification.
Zoom Slider Adjust the magnification of the image in the main window.
Ìy Click Fit to fit the entire eSlide within the main viewing area.
Ìy Click a magnification level (2X, 4X, etc.).
Ìy Drag the slider up or down to increase or decrease the magnification.
Ìy Click the image in the main window and roll the scroll wheel.
To set the zoom slider magnification to percentages rather than X-magnification levels, go
to the Tools menu and select Options.
Clear the Use “X” magnification rather than “%” check box and click OK.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201528
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Use this feature: To do this:
Zoom keyboard shortcuts Press Ctrl+Minus key to zoom out, and Ctrl+Plus key to zoom in.
Zoom Navigation
To zoom into a particular area of the eSlide, click on the ImageScope toolbar. Click and
drag in the main image window to draw a rectangle to outline the zoom area.
If you are using fixed size annotations, press the Ctrl key while you click on the area you
want to zoom into. See“Fixed Size Annotations” on page 102 for more information.
Viewing with Color Management
Aperio Integrated Color Management controls the optical characteristics of your scanner and your display monitor to ensure
the colors of the eSlides display accurately. For information on Aperio Integrated Color Management, see “Appendix B:
Aperio Integrated Color Management” on page 111.
By default, ImageScope uses the scanner’s source ICC profile embedded in the eSlide and the target ICC profile for your
monitor to make sure the image displays in accurate color. The ICC profile is embedded in the eSlide image during scanning.
The ImageScope toolbar allows you to turn Integrated Color Management on or off:
Ì` Click the icon on the ImageScope toolbar to turn color management on or off.
Ì` If an image has an embedded ICC profile and color management is turned on, the symbol displays at the bottom
of the image. If color management is turned off, the symbol on the image looks like this: .
Viewing Scalebar, Axes, and Grid
You can view a scalebar, scale axes, or a grid on an image in ImageScope. A scalebar shows the scale of an image and is
often used on maps to allow you to estimate the distance between two points.
The units and spacing are adjusted to correspond to the resolution of the image and the current zoom level.
The zero point of the axes is in the center of the window; it is labeled with the current unit (for example, um for microns). If
the resolution of the image is unknown, the units on the axes/grid are p (pixels), kp (kilopixels), or mp (megapixels). This is
the case for photomicrographs and gross images before the resolution is set. The resolution on such images can be entered
explicitly or by measuring a known item with a ruler (see “Chapter 8: Image Resolution” on page 48).

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 29
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
To enable the axes view:
1. Click on the ImageScope toolbar or go to the View menu and select Scalebar/Axes/Grid. The axes markers
appear along the side of the image.
2. Click the down arrow next to to select whether you want to see the axes or the axes plus a grid or a scalebar.
An image with the axes and grid looks like this:
An image with a scalebar looks like this:
3. The icon on the toolbar changes to reflect the fact that the grid is displayed: instead of . To turn the
scalebar/axes/grid off, click the axes/grid icon.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201530
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
Viewing Z-Stack eSlide Images
The Aperio scanner can create multiple digital images of slide tissue scanned at different focal depths, creating a 3D image
that you can visually navigate through much as a microscope user can navigate through different tissue focal depths by
using the microscope objective fine and coarse adjustments. This ability to create a 3D image is called “z-stack scanning.”
ImageScope enables you to view and annotate specific layers of the z-stack image.
This section contains information about z-stack images that were scanned on an Aperio scanner. For
information on z-stack images created from live video, see “Chapter 15: TelePath Live” on page
86.
Viewing and Navigating a Z-Stack Image
ImageScope automatically opens a z-stack image to the best focused layer, as determined by your Aperio scanner when the
slide is scanned. The number of layers and the layer separation (depth, in microns (µm), between the layers) is set during
scanning. For more information on scanning z-stack images, see the Console User’s Guide for your Aperio scanner.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 31
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
When working with z-stack images:
Ì` You can use the Focus slider to view different layers of the z-stack image. The number at the bottom of the slider
represents the current focus point.
Ì` Click to view image information, including information for each z-stack layer.
Ì` Annotations you draw on the z-stack image are stored on the current z-stack layer. See “Annotating Z-Stack
Images” on page 54.
Ì` Results for analysis performed on the z-stack image are stored in the corresponding z-stack layer.
Viewing eSlides with IQ
IQ is only available for remote images opened in ImageScope from eSlide Manager.
Aperio ePathology Image Quality (IQ) technology provides pathologists and other scientists who view eSlides the ability to
customize the view of those slides to boost productivity and visual clarity by digitally adjusting the stain colors, viewing the
individual stain images, and/or re-mixing the stains on the fly while they navigate the image.
IQ allows you to choose what view of the eSlide gives you the best results and makes it easier for you to identify the
features of the slide you are most interested in. IQ is available when you have opened an eSlide in ImageScope from eSlide
Manager.
For details on using IQ, see the IQ Image Quality User’s Guide.
IQ Features
IQ uses color processing—analyzing each pixel of the eSlide image—to identify stains and modify their appearance on the
eSlide. IQ enables you to:
Ì` View just a selected stain as you navigate the eSlide. IQ uses color deconvolution to separate the stains and
present them as you pan or scroll about the image.
Ì` Boost or dilute the displayed concentration (especially useful for overstained or understained slides, or to suit your
personal preference).
Ì` Enhance cellular detail such as nuclei.
Ì` Digitally adjust individual stain colors for visual clarity and personal preferences (for example, darker/lighter, more
or less vibrant, bluer/redder, and so on).

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201532
Chapter 4: Viewing an eSlide
IQ Quick Reference
To turn on IQ for the image in the ImageScope window, click on the toolbar. Click the down-arrow next to the icon
to select the stain set to use to view this eSlide:
The default stain set is optimized for Hematoxylin and Eosin stains.
To use the IQ viewing toolbar and application:
1. With IQ turned on, go to the Image menu and select Quality. The IQ viewing toolbar appears:
2. Click the buttons to view the eSlide using all stains or individual stains.
3. To see the full IQ user interface, click the Details button on the viewing toolbar:
You can use the IQ tabs to define the stains applied to the eSlide, re-mix and re-color those stains, create your own stain
sets, and measure the stains used by your lab. To return to just the viewing toolbar, click View Only.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 33
ImageScope rotation tools allow you to rotate an image. You can also rotate an eSlide label image.
Rotating an Image
The rotation setting is in effect only for the current viewing session and is not saved with the image. However, when you
create a new image by using the Snapshot or Extract Region commands, the new image is saved in the current rotation.
Saving an Image View also saves the current rotation settings so that opening the Image View displays the image with
those rotation settings applied.
Image rotation is not enabled during a TelePath Live session.
To use image rotation:
1. Go to the ImageScope Image menu and select Rotate Image (Ctrl+E).
2. From the rotation toolbar, select the rotation setting you want to use:
Rotate zero degrees
Rotate 90 degrees right
Rotate 180 degrees
Rotate 90 degrees left
Flip vertically
Rotate 90 degrees right and flip vertically
Flip horizontally
Rotate 90 degrees left and flip vertically
5
Rotating Images and Slide
Labels

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201534
Chapter 5: Rotating Images and Slide Labels
Rotating a Label
You can rotate an eSlide label. Open an eSlide in ImageScope and position the cursor on one edge of the slide label.
Double-click an arrow on the side of the label you want on top. When you save the eSlide, the label rotation is saved.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 35
You can modify the color settings of eSlides if particular colors do not show up well on your workstation
monitor. This chapter discusses the different image adjustment settings.
For information on adjusting fluorescence images, see “Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence
eSlides” on page 38.
Image adjustments apply only to the current ImageScope session. Image adjustments do not modify your original eSlide, and
they are not stored with the eSlide. You can save gamma settings to apply to the current eSlide or to apply to other eSlides
later, and you can make a snapshot of the adjusted image if you want to save the adjusted eSlide image. (See“Chapter
13: Saving eSlides and Regions” on page 73 for information on making snapshots.)
Use the image adjustments to:
Ì` Adjust the brightness or contrast for all colors or for just the red, green, or blue channel.
Ì` Modify the color balance (for example, make reds less red and more cyan).
Ì` Adjust color curves for all colors or for just the red, green, or blue channel.
Ì` Save the color adjustments you have made in a gamma table file so they can be re-applied to the same or other
eSlides in future ImageScope sessions.
Ì` Make image adjustments to the entire eSlide or to live video Z-stack images.
Making Image Adjustments
Follow the instructions below to make color adjustments to your eSlide images using the brightness and contrast, color
balance, color curves adjustment.
To make image adjustments, go to the Image menu and select Adjustments.
Here are some general tips for making image adjustments:
Ì` To modify the appearance of an entire eSlide, select Main Image. To modify just the current live video Z-stack
images, select Z-stack Images. Note that the Z-stack Images option is for live video z-stack images created with
TelePath Live.
Ì` Click and hold the Compare button to temporarily return the image to the original settings. Release the button to
revert back to the changed settings.
Ì` Click the Reset button to return all colors to the original default settings.
6
Making Image Adjustments

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201536
Chapter 6: Making Image Adjustments
To make this
adjustment:
Do this:
Brightness and
Contrast
Go to the Brightness/Contrast tab.
1. Select the Red, Green, or Blue square to adjust
the brightness or contrast for those specific
color channels. Select Gray to adjust all color
channels
2. Drag the sliders to decrease or increase the
brightness or contrast levels or type a number
in the Brightness or Contrast box. A negative
number to decreases the level, and a positive
number to increases the level.
Color Balance
Go to the Color Balance tab:
1. Drag the sliders to adjust the color balance in
the red, green, and blue channels. Or type a
number in the color boxes. A negative number
moves the balance to the left, and a positive
number to moves it to the right.
2. Select the Keep brightness constant
check box to adjust all color channels as one
channel’s intensity is adjusted. To adjust the
intensity of each color independently, clear this
check box.
Color Curves
Go to the Color Curves tab:
1. Select the Red, Green, or Blue square to adjust
the brightness or contrast for those specific
color channels. Select Gray to adjust all color
channels.
2. Edit the curve by clicking the pencil tool to
draw a free-form shape, or select the points
tool to create and drag points.
In this example, we selected the red channel, then
created and dragged a point down to change the
red channel curve. The In and Out boxes indicate
the current cursor position on the curve.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 37
Chapter 6: Making Image Adjustments
Saving and Loading Color Settings
You can save the image adjustments, and load them to apply to other eSlide images.
To save the color adjustment settings: 1. Click the Save button that appears in the upper right corner of the Color
Adjustments window.
2. Navigate to the directory where you want to save the gamma table file, type
a file name, and click Save.
3. Click OK to exit the Image Adjustments window.
To load color adjustment settings 1. Click Load.
2. Navigate to the saved gamma table file, and click Open.
3. Click OK to exit the Image Adjustments window.
For More Information
Ì` For information on z-stack images created with TelePath Live, see “Chapter 15: TelePath Live” on page 86.
Ì` For information on loading color settings to be used every time ImageScope opens, see “General Options” on page
99.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201538
This chapter discusses how to view and adjust fluorescence eSlide images.
Images from the Aperio FL are grayscale images that are pseudo-colored during the scanning process.
ImageScope offers a full range of fluorescence features:
Ì` Temporarily apply a false color to a fluorescence image (this is not needed for fluorescence eSlides created by the
Aperio FL)
Ì` For a fused image:
Ìy Change the display color for each channel image
Ìy Adjust brightness, contrast, and gamma (viewing the results on the image and on a histogram display)
Ìy Adjust registration between channels
Ì` Fuse multiple fluorescence channel images into a fused image (automatically done for images acquired with the
Aperio FL)
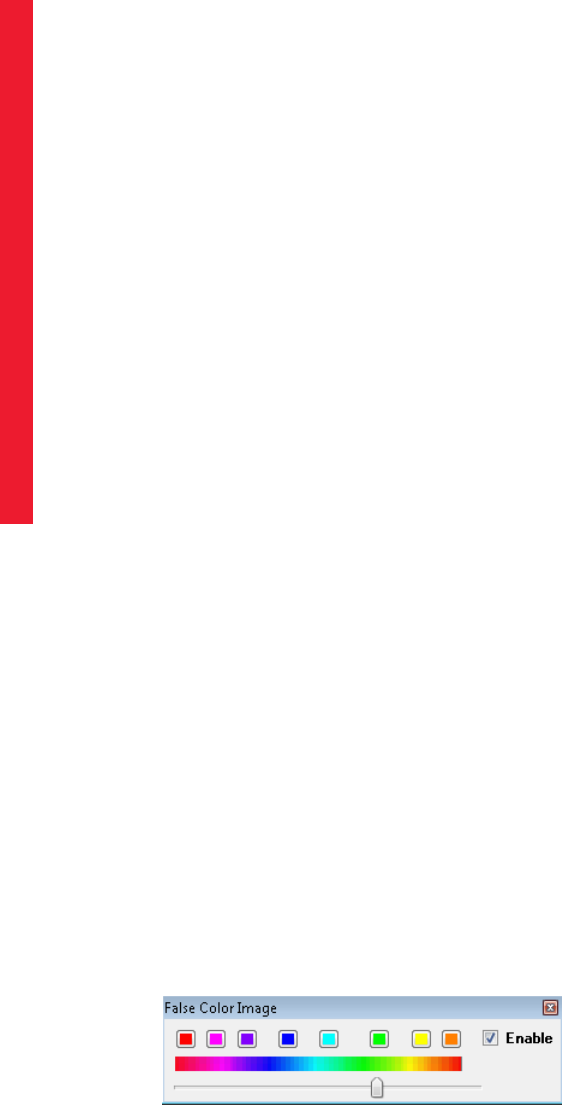
Applying a Temporary False Color
If you are using a grayscale fluorescence image and want to display it in color:
1. Open the image in ImageScope.
2. Go to the Image menu and select False Color. The False Color window displays:
3. Select a color by clicking a color box or using the color slider.
4. Select the Enable check box to see the image in the color you have selected. To view the image without the false
color, clear the Enable check box.
Applying a false color in this way does not permanently change the display color for the image—this adjustment applies
only to the current ImageScope viewing session.
7
Working with Fluorescence
eSlides

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 39
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
Adjusting Fluorescence Fused Images
Fluorescence images are displayed in ImageScope using the color, brightness, contrast, and registration settings made in
the scanner Console when the scan was made.
Any changes you make on the Image Fusion Adjustments window are saved with the image so that they apply the next time
you open the image in ImageScope.
To use the Image Fusion Adjustments window:
1. Open an Aperio Fused Image (AFI) in ImageScope. The usual way to do this is from eSlide Manager. Note that the
AFI is indicated by the symbol in the eSlide Manager eSlide list.
2. Go to the ImageScope Image menu and select Fusion Adjustments (only available if viewing an AFI) to open the
Image Fusion Adjustments window:
The fused image is at the top, and the individual channels that make up that image appear below the fused image.
Using the Fusion Adjustment Window
You can enable features by clicking the symbols on the Image Fusion Adjustments window (see the following sections for
details on using each of these tools):
If at least one channel is hidden, this button cycles between the channels, showing different combinations.
Show/hide color pane.
Show/hide brightness, contrast, gamma adjustment pane.
Show/hide registration pane.
Show the channel images that make up the AFI.
On each secondary pane, click to reset the image to the original image settings (at the time the image was scanned). If
the fused image is selected, this button resets all channels.
Before using one of the options at the bottom of the window, select a channel so that the changes you make apply to that
channel image.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201540
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
After opening a tool pane, click to close the pane to exit back to the main Image Fusion Adjustments window.
Viewing All Channel Images
eSlide Manager displays only the AFI and not the channel images that comprise the AFI for fluorescence images that were
created by scanning a glass slide on a Aperio FL.
If you need to view the channel images that comprise an AFI, you can do so by using ImageScope.
1. Open the AFI in ImageScope by clicking its thumbnail on the eSlide Manager page. You see the AFI in the main
ImageScope window along with the Image Fusion Adjustment window:
2. To view all of the channel images that make up the AFI, click the channel tile icon on the Image Fusion
Adjustment window. All of the channel images are tiled in ImageScope.
3. You can make channel adjustments, as described below.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 41
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
To make this adjustment: Do this:
Hide a channel
To hide a channel, click the eye symbol: next to it. (To add it back to the
display, click again.)
Hide a channel color Click the color box next to a channel to turn off the false color for that channel
(that is, to display it in grayscale). To turn the false color on, click the color box
again.
Hide all color To remove all color, click the color box next to the AFI.
Seeing Channel Information
Point to a color box to see information about that channel.
Cycling Channel Displays
To cycle the display among the channels:
1. Hide a channel by clicking the eye symbol: next to it.
2. Click the button to cycle among different combinations of channels.
In this example, the FITC channel is hidden (this also turns off the AFI fused
image, because all channels must be on to see the fused image):
Clicking the button cycles the display to a new combination of channels
(TRITC and FTIC).
Clicking the button again cycles the display to another combination of
channels. To turn off cycling, manually turn on all channels by clicking the
next to hidden channels.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201542
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
Adjusting Color
To change false colors, on the Image Fusion Adjustments window, click . Select a channel, and then click a color box to
select the color used to display that channel. You can also use the color slider.
Click to invert color intensity in the display—the brightest pixels in the selected color become dark and the darkest
pixels become bright. When a channel is inverted, a small inversion symbol appears next to the color box for the channel.
For example:
Adjusting Brightness, Contrast, and Gamma
To adjust brightness, contrast, and gamma, click . You can change these settings to eliminate background noise, boost
a weak signal, assign a histogram stretch, and so on. These settings affect the appearance of the fused image and channel
images, but do not affect the actual pixel data in the image files.
Ì` Brightness – Adjusts the overall intensity of every pixel. Use this setting to brighten dark images or darken bright
images.
Ì` Contrast – Makes the dark pixels darker and the light pixels lighter.
Ì` Gamma – Changes the midtones of your image. This is a nonlinear adjustment that can make faint objects more
intense without saturating bright objects. At the same time, medium-intensity objects can be made fainter without
dimming the bright objects.
A typical way to use these settings is to first adjust the contrast to stretch the intensity of the image and then, if the image
is too bright or dark, adjust the gamma.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 43
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
The best way to see the effect of the settings is just to try them on your image to see what improves the image.
Select a channel (or the fused image) and select the settings you want to use. You can make these changes with color
turned on or off. Any adjustments you make are immediately visible in the image in the ImageScope window.
Ì` To see an intensity histogram of the current view of the image, click . (See “The Intensity Histogram” below.)
Ì` To turn automatic contrast settings for the image thumbnail on or off, click (“Th” stands for “thumbnail”).
Automatic contrast for thumbnails is on by default to boost contrast, as thumbnails tend to be very dark.
Brightness, contrast, and gamma settings are applied to the thumbnail only if Auto Contrast is off.
If this setting is not beneficial to the visual quality of your particular image, turn it off. This setting is also used
by eSlide Manager when displaying thumbnails, so turning it off in ImageScope also affects thumbnail display in
eSlide Manager or any other Aperio ePathology application that displays thumbnail images. Once turned off, the
setting stays off for this image until you turn it on again.
Ì` To compare the new settings against the original, click .
Intensity Histogram
To see a histogram of the current image view, click the button.
The histogram plots the number of pixels at each intensity. By looking at the left of the histogram you can see how many
pixels are in the darkest intensity; the right of the histogram shows how many pixels are in the lightest intensity.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201544
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
The black line shows a transfer function that relates input to output. You might also know this line as the tone curve. In an
unadjusted image, this line is a straight line from zero to maximum intensity. As you change settings, the line changes to
reflect your adjustments.
The Low Clip and High Clip sliders allow you to set thresholds. For example, the Low Clip slider sets a lower threshold
point—if any pixels fall below that value they are forced to zero. This is often used to eliminate noise (the “noisy” pixels
that do not convey real information are forced to black). The High Clip slider sets an upper threshold point—if any pixels fall
above that value they are forced to the maximum value (white).
For example, in the image shown above, we adjusted the gamma on the DAPI channel to lighten the midtones.
Adjusting Registration
Fluorescence images acquired on the Aperio FL using the quad multi-bandpass filter cube should be perfectly registered.
Images acquired using single-bandpass filter cubes or images imported from other sources may require registration changes
so that the channels are aligned correctly.
To see the registration pane, click on the Image Fusion Adjustments window.
Select the channel you want to register. (In the example above, DAPI is selected.)
Ì` Use the arrows to move the image pixel by pixel in the X or Y axis. The arrows closest to the center of the arrow
strip move the image by one pixel, the next arrows move it by 10, and the arrows at the end of the arrow strip
move it by 100 pixels.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 45
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
Ì` Click the 0 at the center of the arrow strip to move the image back to its original position on that axis.
Ì` The colored box in the middle of the display shows the position of the image relative to its original position.
The box starts in the center and moves as you use the arrows. The color of the border of the box tells you which
channel you are working with. (In the example above, the blue border is the same color used for the channel DAPI,
so we know we are working with that channel.)
Ì` The movement of the image in the X/Y axes is shown in the X and Y boxes.
Fusing Fluorescence Images
The scanner creates a multi-layer “fused” image made up of the individual channel images. However, you can also use
ImageScope to create your own fused image or create one from individual channel images you received from another
source.
Our example shows opening images in eSlide Manager.
1. Log into eSlide Manager and select All eSlides (As List) from the eSlides menu.
2. Select the check boxes next to the channel images you want to use to create a fused image and click View
Images.
ImageScope opens each of the selected images:
In this example, we have three images, one for each type of fluorochrome used to stain the slide: DAPI, FITC, and
TRITC.
If you want ImageScope to keep each of these images open after it creates the fused image, click the first image to
select it, go to the Image menu, and select Keep Open (or type Ctrl+K). Repeat for the other images.
3. On the ImageScope menu bar, go to the Image menu and select Fuse Images.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201546
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
4. On the Remote Image List Box, select all channel images that comprise the fluorescence scan:
This window does not ask you for a file name or description if you opened the images directly from your local
workstation or network location as ImageScope automatically assigns a file name based on the base file name of
the channels when working with local images.
5. Type a file name to use for the AFI file and, optionally, a description.
If the channel images belong to more than one eSlide, this window asks you to choose which eSlide to add the
fused image to.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 47
Chapter 7: Working with Fluorescence eSlides
6. Click Fuse Selected Images. This creates an AFI. ImageScope opens the AFI and displays it in the main window:
When you close ImageScope and return to eSlide Manager, you see the AFI listed in the eSlide list:
The AFI is indicated by the symbol.
Notes on Creating an AFI
When you are manually fusing channel images into an AFI, note that all of the channel image files and the new AFI file must
reside in the same network/server directory, and this directory must be in the ImageServer’s root directory as defined by the
ImagServer’s -dir option in the ImageServer configuration file.
If you want the new AFI to reside and be visible in eSlide Manager, you must open the individual channel images from
within eSlide Manager, and then fuse them in ImageScope.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201548
8
Image Resolution
This chapter discusses how to see the resolution of an image and, if it is not known, how to set it.
For eSlides created by scanning microscope slides on an Aperio scanner, the resolution of the image is known and is stored
in the image file. The resolution is used to display the magnification in the zoom slider, to compute ruler values, and to
compute the length and area of annotation regions.
The resolution may not be known for other types of images you are working with.
To view and set an image’s resolution:
1. Go to the Image menu and select Resolution. The Image Resolution window displays:
If the resolution of the image is stored within the image file, Current Image Resolution and Apparent
Magnification contains values—if the resolution is not known, these boxes will be empty.
Setting or Changing Image Resolution
When you change the resolution, you affect the way an image is viewed, but do not change the image
file or information stored in it.
Because the resolution is used to display the magnification in the zoom slider, to compute ruler values,
and to compute the length and width of annotations, these values change when you change the
resolution.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 49
Chapter 8: Image Resolution
You can use the options on this window to change or set the image resolution:
Ì` Use Resolution Specified in Image File – If the resolution is stored in the image file (for example, it was
created by scanning a glass slide on an Aperio scanner), select this option to reset the resolution to the value
stored in the file.
Ì` Manually Enter Image Resolution (or Magnification) – If you know the resolution for the image, select this
option and type the image resolution and apparent magnification values in the boxes at the top of the window.
Ì` Compute from Currently Selected Annotation Ruler – You can determine the resolution of the image from an
object of known size in the scanned image. See the next section.
Computing the Resolution from the Image
If you select the Compute from Currently Selected Annotation Ruler option in the Image Resolution window, you can
use an object of known size in the image to calibrate the image resolution.
For example, in the following image a scale is part of the picture:

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201550
Chapter 8: Image Resolution
1. Draw an annotation ruler across the scale, which in this case shows a length of 5 centimeters.
2. Go to the Image menu and select Resolution. The Image Resolution window now has a place for you to enter the
length of the ruler:
3. On the Image Resolution window, select Compute from Currently Selected Annotation Ruler and enter the
length of the ruler in microns. In this case, enter a value of 50000 (5 cm = 50000 microns). If you want to delete the
ruler after calibration, select the Delete Ruler after Resolution Computed check box.
Now all values measured by rulers will be accurately calibrated to this scale, such as the second ruler shown above which
measures a length of 31mm across the specimen.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 51
9
Working with Annotations
Use annotations to mark areas of interest on an eSlide and to define areas to analyze. This chapter provides
information on adding annotations to your eSlides, and managing annotations in the Annotations window.
Using the Annotation Tools
To add an annotation to an eSlide, select the appropriate drawing tool on the ImageScope toolbar, or right-click in the image
and select a drawing tool from the menu.
Notes about annotations:
Ì` When annotating eSlide images you have opened from eSlide Manager, remember to save
your annotations as you work.
Ì` To draw an annotation that extends past the viewable area in the ImageScope window, drag
the annotation drawing tool toward the edge of the imageScope window. The eSlide image
moves with your pointer, allowing to allow you to continue drawing.
Button
Name
(Keyboard
Shortcut)
Description
Pen
(F2)
Click and drag to draw a free-form shape to indicate an area of interest or to enclose
an area to analyze.
You can redraw or finish an incomplete free-form annotation if needed. For more
information, see “Editing Free-Form Annotations Created with the Pen or Negative
Pen” on page 55.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201552
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Negative pen
(F3)
Click and drag to draw a free-form shape around an area you want to exclude from
analysis.
In this example, the rectangle indicates the region to
analyze. The negative pen is used to draw an area to
exclude from analysis.
You can redraw or finish an incomplete free-form annotation if needed. For more
information, see “Editing Free-Form Annotations Created with the Pen or Negative
Pen” on page 55.
Ruler
(F4)
Click and drag to measure an object on the eSlide.
The unit of measure adjusts to the current resolution. For example, a line that appears
in microns at 20x may appear in millimeters at 2x.
The ruler tool may not work on images that were not created by the Aperio scanner.
Rectangle
(F5)
Click and drag to draw a rectangle. To draw a square, press and hold the Shift key as
you draw.
Ellipsis
(F6)
Click and drag to draw an ellipsis. To draw a circle, press and hold the Shift key as you
draw.
Arrow
(F7)
Click and drag to draw an arrow.
Counter
(F9)
Click to mark the eSlide image with a numbered annotation, as
shown in the example. Counters are numbered automatically in the
order they were placed.
Counter are stored in the annotation layer, along with their x/y
coordinates.
Each annotation layer can contain a separate set of counters.
Report region Click the area of the image to include in a report. You can only create one report image
per report. To draw an area of a fixed size, press the Ctrl key while you draw. See
“Report Image Options” on page 105 for information on setting the fixed size of a
report image.
The eSlide Manager report template you are using determines whether images are
included in reports.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 53
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Distance
measurement
Enables you to measure the distance (in microns) between two free-hand line
annotations. For more information, see “Measuring the Distance Between Two Line
Annotations” on page 53.
Copy Annotations
(Ctrl+C)
Paste Annotations
(Ctrl+V)
Select the annotation you want to copy, and click the Copy Annotations button .
Click the Paste Annotations button , and then click to place the annotation in the
eSlide image.
If you have run analysis on the annotations, the annotation is copied, but not the
analysis results.
Measuring the Distance Between Two Line Annotations
Use the Distance Measurement tool to measure the distance (in microns) between two free-hand line annotations. The
measurement lines are placed so that they measure the distance between the relevant parts of each line.
Follow these steps to use the Distance Measurement tool:
1. Select the first annotation and click .
2. Select the second annotation to create an initial set of measurements set at equidistant points.
3. When the Distance Measurement Tuning window appears, you can change the number of measurement lines or
accept the default number (8) by clicking OK.
Measurement lines are placed equidistantly within the relevant area, as shown in the example below:
The measurements are stored in the Annotation layer.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201554
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Annotating Z-Stack Images
Before you draw annotations on a z-stack image, adjust the Focus slider or select an existing annotation region so that the
desired z-stack layer is active. Although annotations are visible from all z-stack layers, annotations are stored on the z-stack
layer on which they are drawn.
The following example of the Layer Regions area of the Annotations – Detailed View window shows the z-stack layers.
The Z (um) column indicates the z-stack layer (the Focus setting) for the corresponding region where you drew the
annotation.
If you select a region from the Layer Regions table, ImageScope automatically displays the z-stack layer that corresponds to
the selected region.
Drawing Fixed Size Annotations
If you have defined a fixed size for annotations, press and hold the Ctrl key while you draw the annotation to use that size.
(You can use a fixed size with the rectangle, ellipse, arrow, report image, and ruler.)
See “Fixed Size Annotations” on page 102 and “Report Image Options” on page 105 for information on setting a fixed
size for annotations.
Drawing Annotations with a Fixed Aspect Ratio
To draw an annotation that uses the same aspect ratio as the fixed size you defined, press the Shift+Ctrl keys while you
draw the annotation. For example, if you specify a fixed annotation size of 400 pixels wide and 300 pixels high, when you
press Shift+Ctrl and draw an annotation, it always has a ratio of 400 to 300 (4:3), regardless of its size.
You can also use the Shift+Ctrl keys to extract a region of a specific aspect ratio. See “Extracting an Image of a Predefined
Size or Aspect Ratio” on page 78.
To set a fixed size (and aspect ratio) for annotations, see“Fixed Size Annotations” on page 102.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 55
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Moving Annotations
To move one or more annotations on the eSlide image, do the following:
Move the selected annotation Press and hold the Ctrl key while you drag the annotation to a new location.
Move all annotations simultaneously Press and hold the Ctrl+Shift keys while dragging the selected annotation to a
new location. All annotations move along with the one you are dragging. This
is useful if you import annotations from a similar eSlide, and slight variations
require some adjustments.
This feature moves all annotations in all layers except for Z-stacks and markup
images.
Editing Free-Form Annotations Created with the Pen or Negative Pen
This feature enables you to edit the shape of free-form annotations that are created with the pen or negative pen tools. You
can change the shape of an existing annotation, or finish an incomplete annotation.
You cannot edit an annotation if you have run analysis on it.
Tips for editing annotations:
Ìy Start and finish your edits in a problem-free area of the annotation. See “Fixing a Problem Area”
on page 57 for an example.
Ìy Drag the pointer in a slow and smooth manner when redrawing annotations.
Ìy When you are redrawing an annotation, you can move back and forth over the same area until you
release the left-mouse button.
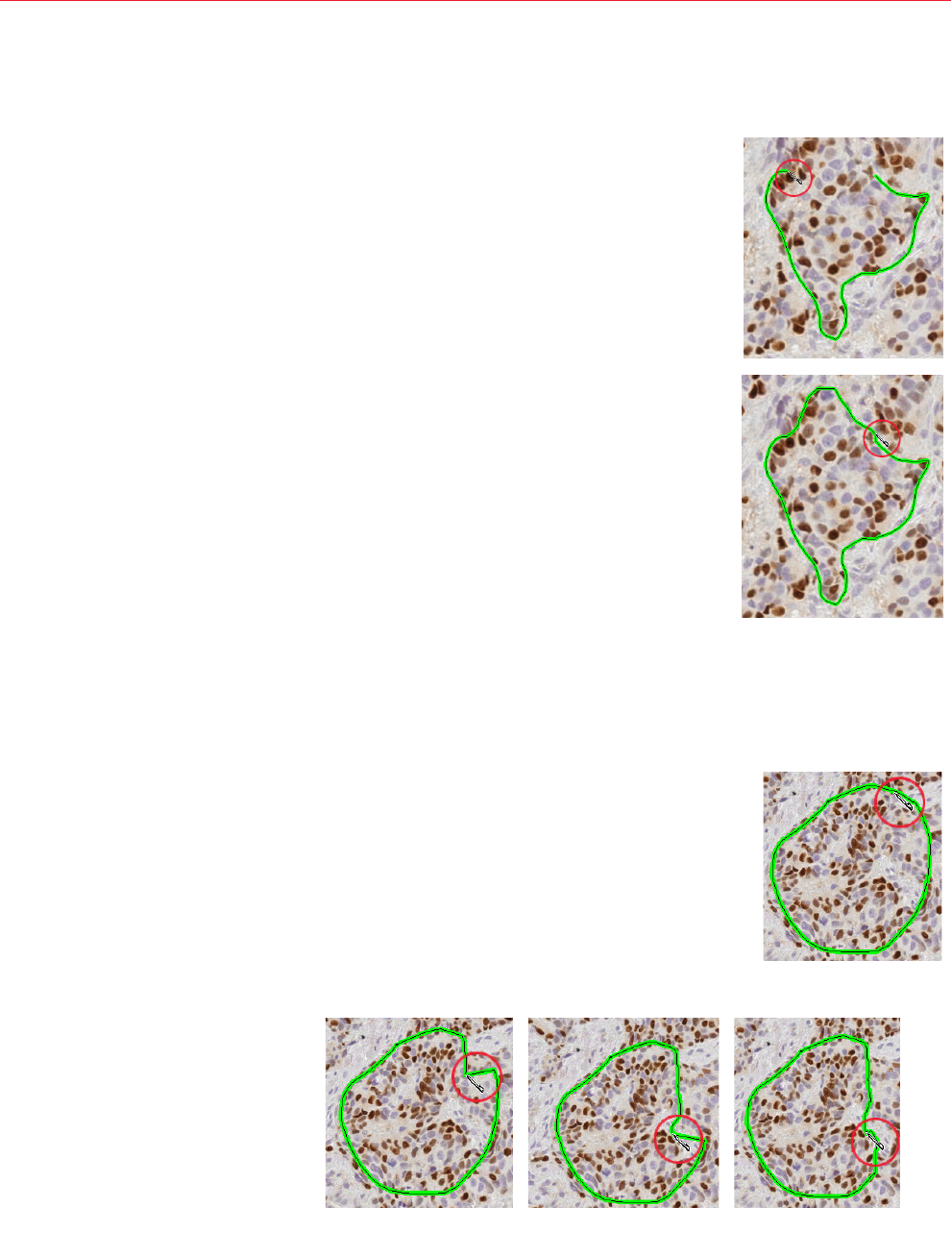
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201556
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Completing a Free-Form Shape
This example shows how to complete an annotation by connecting the two ends.
1. With the annotation selected, place the Pen tool at an open end of the shape.
2. Hold down the left mouse button and slowly drag the line until the two ends are
connected.
3. When you are finished editing the annotation, release the mouse button.
Editing a Free-Form Shape
This example shows how to change the shape of an existing annotation.
1. With the annotation selected, position the Pen tool where you want to start the
edit.
2. Hold down the left mouse button and slowly drag the line to change the shape, as shown below.
3. When you are finished editing the annotation, release the mouse button.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 57
Chapter 9: Working with Annotations
Fixing a Problem Area
In this example, there is an unwanted loop in the annotation shape. To fix this problem, follow these steps.
1. With the annotation selected, place the Pen tool to one side of the area you want to
fix, as shown here.
2. Hold down the left mouse button and slowly drag the line to adjust the shape.
3. When you are finished editing the annotation, release the mouse button.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201558
10
Using the Annotations
Window
Annotations are organized in the Annotations window in layers. Annotation layers also store algorithm analysis results. The
ImageScope Annotations window contains the annotations associated with the image.
You can use the Annotations window in one of two modes:
Ì` Summary View – Designed for use with the eIHC product to provide one-step annotation and analysis for IHC
eSlides. This view can also be used for quick analysis of any type.
Ì` Detailed View – Complete details on all annotations are available and you can add annotation attributes, text
labels, and so on.
See the Aperio Image Analysis User’s Guide for information on using the Annotations Summary Window and on performing
image analysis.
Annotations Summary View Window – Quick eIHC Analysis
The ImageScope detailed Annotations window provides a general solution for image analysis and handling annotations.
However, a more streamlined version of the Annotations window is also available—the Annotations summary view. The
Annotations summary view was specifically developed for analyzing IHC eSlides and makes the process quicker and simpler
by fitting into a pathologist’s or researcher’s standard workflow.
Slide-Specific Processing
The key to the eIHC workflow is slide-specific processing, which defines how an eSlide is processed based on its stain and
type of tissue (body site). Slide-specific processing can define what algorithm is used to analyze that type of slide, how
analysis results are displayed and how to interpret those results (alternatively, manual scoring can be set up for the slide),
and what comments are available for use by the pathologist or researcher viewing the slide. The slide-specific configuration
for each stain/body site combination is defined by the eSlide Manager administrator. Once slide-specific processing is set
up, viewing, annotating, and analyzing an eSlide becomes a quick process.
The summary view of the Annotations window is designed specifically for working with IHC eSlides to provide a quick way
to mark tumor regions and analyze them in one simple step.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 59
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
Using the Annotations Summary View Window
To open the Annotations window in summary view:
1. Identify an eSlide in eSlide Manager for which stain/body site slide-specific processing is defined.
2. From the eSlide Manager page, open the eSlide in ImageScope by clicking its thumbnail. The Annotations window
in summary view displays. (If the window does not look like this, click the Summary button to access the summary
view.)
The appropriate algorithm for this type of slide is listed in the drop-down box. You can select another algorithm from the list.
Note that if you are in clinical viewing mode, the summary view Annotations window is the only view you can see. From this
window you can draw annotations to identify areas to analyze and run the analysis:
1. With the algorithm that you want to use shown in the drop-down list, use the ImageScope pen or rectangle
drawing tools to draw the areas of the eSlide you want to analyze.
2. To navigate between annotations, use the numbered buttons or arrow keys. (As you draw annotations with the
analysis algorithm shown in the drop-down box, the buttons at the top of the window display a number for each
annotation.)
Ì` Click a numbered button to center the corresponding annotation in the ImageScope window.
Ì` Move between the annotations by using the arrow keys.
Ì` To delete the selected annotation click . To delete all annotations, click .

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201560
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
Ì` To hide the selected annotation on the ImageScope window, click .
Ì` To save the annotations to eSlide Manager, click .
3. To analyze the current eSlide with the algorithm shown in the drop-down box:
a. Select the annotation drawn around the area you want to analyze and select Selected Annotation. (Or, if you
want to analyze the entire area shown in the ImageScope window, select Current Screen.)
b. Click Run Analysis. As the analysis runs, you see progress information:
When the analysis is complete, you see the results:

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 61
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
Enabling and Disabling Pre-processing
When using the Annotations window in summary view, you can temporarily turn off pre-processing region finding for
algorithms that support that feature (for example, if you want to select possible tumor areas yourself to analyze rather than
allowing the algorithm to do it for you).
To disable pre-processing, open the Annotations window in summary view and click the pre-processing button:
To turn pre-processing on again, click the button again. Note that this button is only enabled when you are using an
algorithm that supports pre-processing.
Incremental Processing
The eIHC analysis applications are incremental algorithms, which means that as you add new regions and click Run
Analysis on the Annotations window, only the new regions are analyzed, which can save a great deal of time. Any time you
click Run Analysis again, all analysis results are updated.
Incremental processing is useful when a pathologist draws a single region and analyzes it, and after reviewing the analysis
results wants to select additional regions and analyze them as well. The pathologist can add more annotation regions as
needed or delete annotation regions and the analysis results will be updated accordingly.
If you delete a region, ImageScope automatically re-runs the analysis to update the summary analysis results that included
that region. However, adding regions may make the analysis results incorrect until you re-run the analysis.
Other Options
Ì` To see a report image you have selected, select Report Image from the drop-down list.
Ì` To create an annotation that is not used for analysis (for example, a ruler or arrow), select Annotations from the
drop-down list before drawing.
Ì` If the algorithm you are using supports result plots and they are enabled, the summary view window automatically
opens all plots in separate windows when the analysis is done.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201562
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
The Annotations – Detailed View Window
To open the Annotations window go to the View menu and select Annotations.
The following Annotations window shows an eSlide with two annotations layers: “Dr. Bradley” and “Dr. Garcia.” (If your
window does not look like this, click the Details button to return the Annotations window to the detailed view.)
The Annotations window in Detailed View contains the following sections:
Ì` Layers – lists all layers for this eSlide.
Ì` Layer Attributes – enables you to add and delete attributes for a layer. See “Using Attributes” on page 66 for
more information.
Ì` Layer Regions – enables you to add and delete attributes for an annotation. You can use the Layer Regions to
delete or move an annotation. This area also shows the length and area for the different annotation regions. If
the resolution of the image is known, the length and area are displayed in microns. If not, the length and area are
displayed in pixels.
Annotations Window Tools
Use the following tools to work with layers, layer attributes, and layer regions.
This tool: Is located here: And enables you to:
Annotations window toolbar Arrange the Annotations window panes horizontally.
Annotations window toolbar Arrange the Annotations window panes vertically.
Annotations window toolbar Make Annotations window transparent.
Annotations window toolbar Save all annotations with the eSlide.
Annotations window toolbar Import annotations from a previously exported annotation file.
Annotations window toolbar Export the current annotations to an annotation file. Saved as XML with
the same name as the eSlide file.
Layers pane Change the color of the annotations in the selected layer. (This box shows
the current color for the layer annotations.)
You can also change the default color for each annotation layer. For more
information, see “Annotation Color Options” on page 102.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 63
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
This tool: Is located here: And enables you to:
Layers pane Hide or show the annotations on the selected layer in the ImageScope
main window.
Layer Attributes pane
Layer Regions pane
Export the contents of the pane to a text file.
Layer Attributes Pane Display algorithm result plots.
Layer Attributes pane
Layer Regions pane
Export the contents of the pane as an Excel spreadsheet.
Layers pane
Layer Attributes pane
Layer Regions pane
Add:
New layer (if on the Layers pane)
New layer attribute (if on the Layer Attributes pane)
New annotation attribute (if on the Layer Regions pane)
Layer Attributes pane
Layer Regions pane
Delete:
Layer attribute (if on the Layer Attributes pane)
Annotation attribute (if on the Layer Regions pane)
Layers pane
Layer Regions pane
Delete:
Selected layer (if on the Layers pane)
Selected annotation (if on the Layer Regions pane)
Layers pane Delete all layers.
Annotation Length and Area Display
ImageScope measures and displays length and area for annotation regions. If the resolution of the image is known, length
and area are displayed in microns; if not, they are displayed in pixels.
Adding Text to an Annotation
To add a text note that appears with an annotation in ImageScope.
1. In the Layers pane, select the layer that contains the annotation for which you want to add a note.
2. Click the annotation in the Layer Regions pane.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201564
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
3. Type the note into the Text column.
The note appears next to the annotation, as shown below.
Moving Annotations
You can move a single annotation or all annotations.
To move: Do this:
One annotation With the annotation selected on the ImageScope window, press and hold the
Ctrl key, then drag the annotation to a new location.
All annotations You can move all annotations at the same time. For example, if you import
annotations from a similar eSlide, slight variations in the new slide might
require adjusting the position of the imported annotations.
On the ImageScope main window, press and hold the Ctrl and Shift keys, and
drag an annotation to a new location. All annotations move with the one you are
dragging.
All annotations in all layers will be moved except for Z-stacks and markup
images.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 65
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
Exporting and Importing Annotation Layers
ImageScope provides several ways to export and import information and annotations. You can also copy annotation layer
information, and paste it into Word or Excel.
Algorithm analysis results are stored in an annotation layer so you may want to export that information into a text file to
include it in a report or to chart the information in a spreadsheet program.
You can also export annotations to be used on other eSlides. For example, if working with several very similar eSlides, you
may find the same annotations apply to all of them.
To use this import or export
feature:
Do this:
Import or export annotations to the
active eSlide
Ìy Export all annotations – on the Layers pane, click . Specify a name
and location for the .xml file created.
Ìy Import an annotation file – on the Layers pane click . Navigate to the
location of a previously exported annotations file.
Export text from Annotations Window
Panes to a tab-delimited text file
This allows you to import the data into
a spreadsheet program.
Ìy Export the text of the Layer Attributes pane – on the Layer Attributes
pane, click . Specify the name and location of the text file to be created.
Ìy Export the text of the Layer Regions pane – on the Regions Attributes
pane, click . Specify the name and location of the text file to be created.
Export text from Annotations
Window panes to a Microsoft Excel
Spreadsheet
Ìy Export text from the Layer Attributes pane – on the Layer Attributes
pane, click . Specify the name and location of the new Excel (.xls) file.
Ìy Export the text from the Layer Regions pane – on the Layer Regions
pane, click . Specify the name and location of the spreadsheet .xls file
to be created.
Note: The numeric data is exported to Excel as text. Excel displays a note for
each cell indicating that the numbers are in text format—you can click on the
note to opt to transform the text to numeric format.
Copy and Paste Layer Attributes or
Layer Region information
Select one or more cells from the Layer Attributes or Layer Region grids, and
press Ctrl+C to copy the information to the Windows clipboard. Press Ctrl+V to
paste the information into Word or Excel.
Note that the column headings are automatically copied over with the cell
information.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201566
Chapter 10: Using the Annotations Window
Using Attributes
Attributes are text fields that describe the layer or annotation. Several attributes are already defined. For example, the
Layers pane and the Layer Regions pane both contain a Description attribute. You can type in this column to include
comments or a descriptions.
When multiple entries are defined for an attribute, you can sort the entries alphabetically by clicking the attribute title. In
the following example, Case# was clicked to sort the list of annotations by case number:
Adding and Deleting Attributes
Attributes are text fields that describe the layer or annotation. Several attributes are already defined. For example, the
Layers pane and the Layer Regions pane both contain a Description attribute. By typing text in this column, you can include
comments or a description of the layer or annotation
To add new attributes (for example, slide routing information, test results, etc.) or delete attributes, do the following:
To add a new layer attribute: With the appropriate layer selected in the Layers pane:
Ìy Add a new layer attribute – go to the Layer Attributes pane
and click . Enter the name of the attribute in the window that
appears. The new attribute appears as a new row in the Attributes
list.
Ìy Add a new annotation attribute – go to the Layer Regions
pane and click . Enter the name of the attribute in the window
that appears. The attribute appears as a new column in the Layer
Regions table.
To delete a layer attribute or a layer region
attribute:
With the appropriate layer selected in the Layers pane, select the
attribute you want to delete from the Layer Attributes pane or the Layer
Regions pane, and click .

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 67
11
Linking Annotations and
eSlides
Creating a viewing sequence by linking eSlides and/or annotated regions is a powerful way to organize and
present information.
Here are two sample uses of linking annotations and eSlides:
Ì` Create a path of views through a slide or group of slides that takes the viewer on a tour of highlighted features.
Ì` Create a hierarchy of images, perhaps from gross specimen down through blocks and then to slides.
Links have the following characteristics:
Ì` Links can be associated with a region in an eSlide or with the entire image.
Ì` Links have direction. If you traverse a link in the forward direction, you can follow the same link back.
Ì` You can create any number of links into or out of a region or image.
Ì` If there is more than one link to or from the currently selected annotation or slide, then the Link Manager window
will open so that you can select a link.
Ì` You cannot create links for layers, only for eSlides or annotations.
Working with the Link Manager
To start the Link Manager, go to the View menu and select Annotation Links Manager.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201568
Chapter 11: Linking Annotations and eSlides
On the left side of the Link Manager window is a tree view of all eSlides open in ImageScope. The next level represents
annotation layers, and the final level is annotations in that layer. For example, the first slide above, Ex3_40X.svs, contains
two layers, “Dr. Bradley” and “Dr. Garcia.” The “Dr. Bradley” layer contains three annotations, “TB5/5/06,” “TB5/12/06,”
and “TB5/12/06.”
Click + to expand the lists, and click – to collapse them.
When you click a node in the tree, any links for that node appear in the list on the right.
Creating a Link
To create a link:
1. In the left pane of the Link Manager window, drag a node and drop it onto another node.
For example, we dragged the first annotation on the Dr. Bradley layer onto the second annotation to create a link:
The symbol indicates that the link is a forward link. The symbol indicates the link is a backward link.
Viewing Links
The link navigation icons and commands are only enabled if a link exists. For example, if no previous
link exists, you cannot use the Previous Annotation Link command.
You can follow links either on the main ImageScope window or from within the Link Manager window. You do not need to
open the Link Manager window to follow links.
If no annotation is selected, the viewing tools follow slide-level links; if there is more than one link to or from the selected
annotation or slide, then the Link Manager window opens so that you can select a link.
ImageScope displays the target of the link in its main window. If the target is an eSlide, then it is fitted into the main
window; if it is an annotation, then the annotation is centered and zoomed.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 69
Chapter 11: Linking Annotations and eSlides
To follow links in the main ImageScope
window:
1. Open an eSlide that contains links.
2. To go to the next link, go to the View menu and select Next
Annotation Link, or press Shift+F8, or click the icon on the
ImageScope toolbar.
3. To go to a previous link, go to the View menu and select Previous
Annotation Link, or press Shift+F7, or click the icon on the
ImageScope toolbar.
To follow links in the Link Manager window: 1. Open an eSlide that contains links.
2. Go to the View menu and select Annotation Link Manager to
open the Link Manager.
3. Click on the node for which links have been created and click in
the right pane of the Link Manager window to follow the link.
Deleting Links
To delete a single link: In the Link Manager window, select a link in the right pane of the window
and click .
To delete all links:
In the Link Manager window, click .

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201570
12
Tracking
The tracker tool enables you to record your movements through an eSlide and to save that record (known
as a track) with the image as an annotation layer.
Tracking is only available for remote images opened in ImageScope from eSlide Manager.
Typical uses for the tracker tool are:
Ì` Histologists and pathologists might use this tool as reminder of which sections of the eSlide were visited.
Ì` The saved track might be useful for quality assurances purposes by providing permanent evidence of what sections
of the eSlide were viewed.
Ì` The saved track could be used for educational purposes to provide students a tour of the eSlide.
Turning on the Tracker
To turn on the Tracker:
1. Go to the View menu and select Tracker. The tracker tool displays:
You can move this tool anywhere on your monitor display, even off the ImageScope window.
2. To start recording your movements, click the red record button :

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 71
Chapter 12: Tracking
When the recording begins, the thumbnail image turns gray. Each section of the image you move to is highlighted
in the thumbnail. The intensity of the highlight shows the resolution at which that part of the image was viewed.
You can change the size of the thumbnail by dragging the lower left corner of the thumbnail window.
Tips:
Ì` If you do not want to see your progress mapped on the thumbnail, clear the Map check box on the tracker tool. To
show or hide mapping, type Ctrl+M. You can also set the default value of this check box. See “Tracking Options” on
page 103.
Ì` Click on the tracker tool to move through the image to areas you have not viewed, working left to right, and
top to bottom. Using this button, you can systematically view the entire slide.
Ì` To stop recording, click on the tracker tool.
Viewing a Track
To view a track, go to the View menu and select Annotations.
Each track associated with this eSlide is listed in the Layers pane of the Annotations window. To see information on each
track, click a Track in the Layers pane.
Tips:
Ì` A + symbol after the Track name indicates the track recording is complete.
Ì` An * after the Track name indicates the track recording is still in progress.
Ì` An indented track indicates that the track is appended to the track above it. (See “Appending to a Track” on page
72 for information on appending.)
Ì` The Layer Attributes pane shows when the selected track was recorded.
Ì` The Layer Regions pane gives information on each stage of the recording. The first region of the track is the path
that connects the center of all the views in the session. The other regions in the track are rectangles corresponding
to each view in the session.
Ì` To see a track in the main ImageScope window, select the track in the Annotations window and click the eye icon
at the top of the Layers pane.
Ì` As with any annotation layer, you can change the name of the track (for example instead of “Track 1+” you can
name the track “Dr. David”) by clicking it and typing in a new name.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201572
Chapter 12: Tracking
Playing a Track
To play the current track:
1. Click on the tracker tool.
To play a track made in the past:
1. Open an eSlide.
2. Go to the View menu and select Annotations to open the Annotations - Detailed View window. Select the track
you want to play by clicking it in the Layers pane of the Annotations window.
3. Click on the tracker tool.
Tips:
While playing a track, use the tracker tool buttons to affect the playback:
Stop playing or recording the track.
Go to first view in the track
Go to the last view in the track
Go to the next view in the track
Go to the previous view in the track
As you play the track, the Annotations window updates to show your location in the Layer Regions pane.
Appending to a Track
You can either start a new recording or append to a previous one. If a track already exists for this eSlide, when you click the
record button, a message appears asking if you want to append the new track to the selected track.
To start a new recording, click No; to append to the previous track, click Yes.
If more than one track is created for the eSlide, to append to a specific track, open the Annotations window and select that
track in the Layers pane before clicking the record button.
When a track is appended, the recording starts off as if all the views in the parent track have been viewed.
See “Viewing a Track” on page 71 for an example of an appended track.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 73
13
Saving eSlides and Regions
This chapter discusses several different ways to save images of eSlides.
Copy and Paste an eSlide Image
To copy the viewable area of the eSlide image, including any annotations, go to the Edit menu and select Copy. You can
paste the image from the clipboard into an image or word, such as Microsoft Paint, Adobe Photoshop, or Microsoft Word.
Taking a Snapshot
To save the viewable area of the eSlide image as a JPEG or TIFF image file, follow these steps.
1. Navigate to the area of the eSlide you want to capture so that it appears in the main ImageScope window.
2. Go to the File menu and select Save Snapshot or click on the toolbar.
3. In the Save Snapshot window, specify the location and name of the file, as well as the file type (JPEG or TIFF).
You can open and view the file from Windows Explorer or from within ImageScope.
If you make a snapshot of an image that has an embedded ICC profile, and Integrated Color
Management is turned on in ImageScope, then ImageScope transforms the image using the monitor
ICC profile. If Integrated Color Management is turned off, then ImageScope embeds the ICC profile
from the scanner.
See “Viewing with Color Management” on page 28 for more information on color management.
Emailing a Snapshot
You can email the entire image displayed in the ImageScope window, or you can email snapshots of individual regions of
the image.
To email a snapshot:
1. To draw attention to specific areas of the eSlide, use the ImageScope rectangle drawing tool to mark those areas.
2. Go to the File menu and select Email Snapshot.
If you have not defined email settings for ImageScope, the SMTP Server tab of the ImageScope options appears.
You must complete this information to continue. See “Email Settings” on page 107.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201574
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
3. When the Mail Snapshot window appears, complete the email information by typing the recipient’s email address
in the To field, and completing the Subject and Note fields.
4. In the Select Snapshot section, select from the following options:
Ì` Send current image view to send only the current viewable area of the image.
Ì` Send Regions in currently selected Annotation Layer to include regions in the selected annotation layer.
Ì` Delete Annotation Layer After Snapshot Mailed to delete the rectangle annotations after sending the
email.
5. Click Mail.
Receiving a Snapshot Email
The ImageScope snapshot email includes the text you entered and JPEG files of the full ImageScope screen image and any
annotations you selected for the email. The snapshot images are extracted at the same resolution used when the annotation
was made.
Exporting Images
Use this feature to export image files of a defined area of the eSlide image. You can export three versions of the same area,
as shown below:
Original Image Annotated Image Markup Image
Images are exported as TIFF files, and are saved at the current viewing magnification.
To export images:
1. Click on the toolbar.
2. Click and drag a rectangle on the image to capture the area you want to export.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 75
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
The Export Images window appears showing the area you specified, as shown below.
3. Select the check boxes next to the images you want to export:
Ì` Original Image – does not include annotations or markups.
Ì` Annotated Image – includes any annotations in the selected area.
Ì` Markup Image – includes any annotations and analysis markup areas.
4. Click to specify the name and location of the exported image. The name you enter for the Original Image is
used to name the annotated and markup image versions.
5. Click OK to create the images.
If the original image has an embedded ICC profile, and Integrated Color Management is turned on in
ImageScope, then ImageScope applies the color profile to the image before creating the TIFF files.
See “Viewing with Color Management” on page 28 for more information on color management.
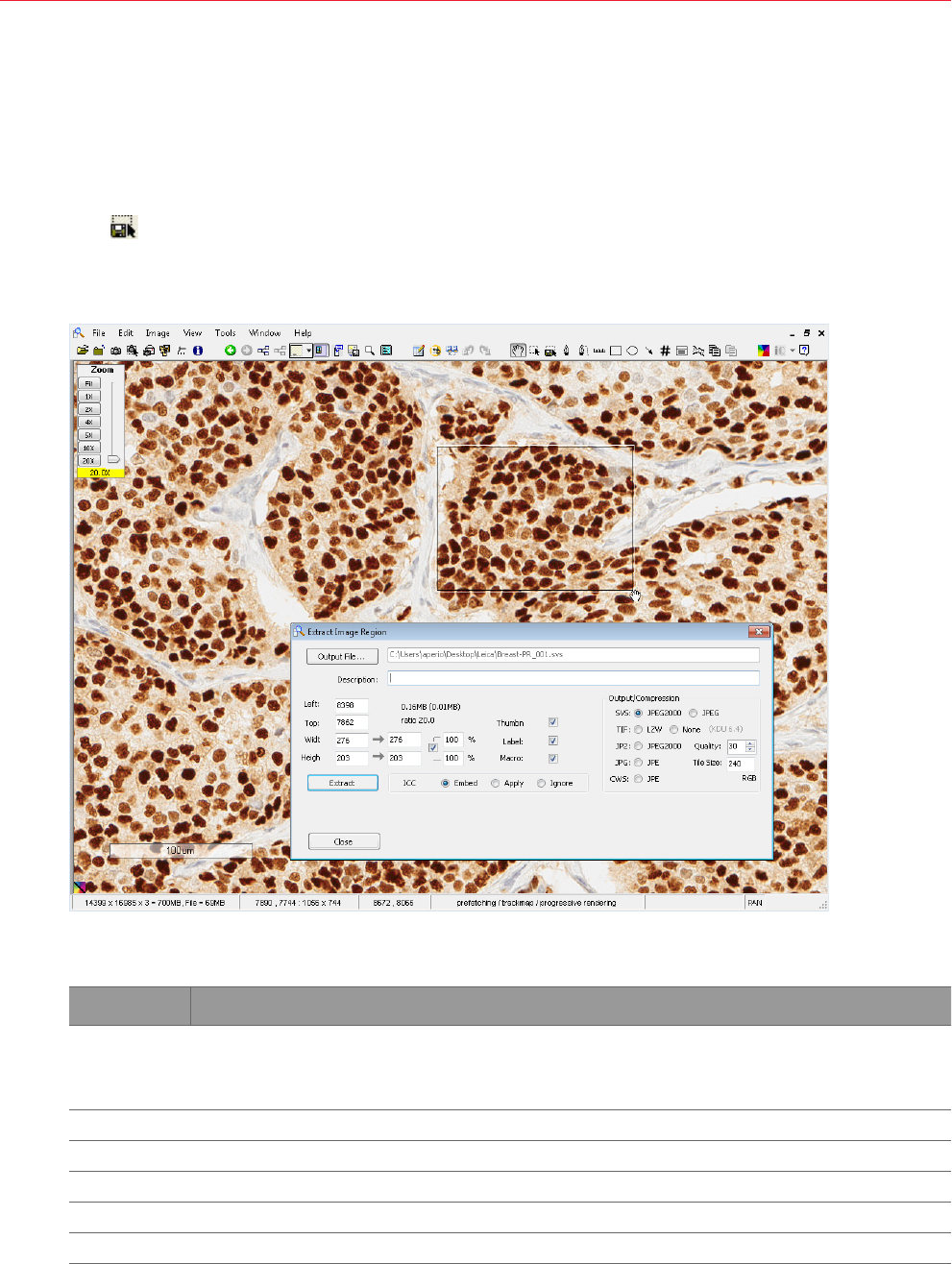
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201576
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
Extracting a Region
You can extract selected regions of an eSlide in different formats and open the extracted region in another application.
When you extract a region, you can define the exact size of the new image or use a predefined fixed size, which may be
useful when preparing images for presentations or publication (see“Saving an Image of a Specific Size” on page 78 ).
To extract a region:
1. Click on the toolbar.
2. Click and drag a rectangle on the screen to capture the area. When you release the mouse button, the Extract
Image Region window appears.
3. Select from the following options:
Option Description
Output File Location and name of the of the extracted file. If you do not use the Output File button, the new
file is created in the same location as the original eSlide, using the same name with a number
appended.
Description Your title for the extracted region.
Left Left pixel co-ordinate of the original image.
Top Top pixel co-ordinate of the original image.
Width Width of the extracted image in pixels.
Height Height of the extracted image in pixels.
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 77
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
Option Description
Thumbnail Attach the thumbnail of the exported image.
Label Attach the label image from the original scan if it exists.
Macro Attach the macro image from the original if it exists.
Tile Size Determines the organization of the data within the extracted image. For large SVS and TIFF files,
a tile size of 240 or 256 is optimal to enable fast access to the image.
To extract images for use with a third-party program that doesn’t support blocked TIFF files, you
can set the tile size to zero to create a “stripped” image. Stripped TIFF files are supported by all
software that processes TIFF files, but there is reduced performance for large images. JPEG files
are always stripped (tile size is always zero).
Output/
Compression
The file formats and compression options available for the saved image:
Ìy SVS file format using JPEG2000 or JPEG compression
Ìy JP2 file format using JPEG2000 compression
Ìy TIF file format using LZW or no compression
Ìy JPG file format using JPEG compression
Ìy CWS file format using JPEG compression
Nx16 to 3x8 If you are using an Aperio fluorescent image (Aperio Fused Image, .afi file), this check box
appears. Select this check box to create a single 3-channel, 8-bit RGB image file in the specified
file format. See “Note on Fluorescent Images” below for more information.
ICC Profile If this image has an embedded ICC profile, you can select whether it is embedded, applied,
ignored in the extracted image. For information on Aperio ePathology color management, see
“Appendix B: Aperio Integrated Color Management” on page 111.
4. Choose the options you require and click Extract.
A progress bar shows the status of the extraction. When the extraction is complete, additional buttons are
available for viewing the image.
5. Click the View button that appears at the bottom of the Extract Image Region window to open the extracted
image in ImageScope. (For information on the Launch button, see “Compatibility Notes” on page 78.)
Note on Fluorescent Images
Multi-channel eSlides produced by the Aperio FL consist of two or more 10-bit monochrome images in the .svs file
format (one for each fluorochrome on the slide), as well as a composite file (.afi, for Aperio Fused Image). When you use
the extraction, conversion, and compression features in ImageScope on multi-channel images, you obtain individual
monochrome images plus a new .afi file of the size and file format selected during the process. Extracted monochrome
channel images have the original pseudo-color enabled by default when opened in ImageScope.
If you are creating the extracted files in the same directory as the input files, ImageScope creates a unique file name for
the new files. (For example, if the original files are 223.afi, 223_DAPI.svs, and so on, ImageScope creates new files named
223_001.afi, 223_DAPI_001.svs, and so on.) Make sure the channel .svs files are in the same directory as the .afi file
because the .afi file references them.
ImageScope allows you to create a single 8-bit RGB file from the channel images, which can be useful for sending an image
for publication. To do this, use the Nx16 to 3x8 check box at the bottom right. The label of this check box differs depending

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201578
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
on the characteristics of the channel files that make up the image. For example, if your original slide used four fluorescent
dyes (and therefore four .svs files were created by the scan), the label will say 4x16 to 3x8. (By default, Aperio fluorescent
images are 10 bit, but the files are saved using 16 bits.) 3 x 8 refers to the output format, a three-channel, 8-bit RGB file.
If this check box is not selected (default), the image extraction results in new monochrome files. If the check box is selected,
ImageScope converts the channel images to a single RGB file (in the format you selected in the Output/Compression area of
the window).
Saving an Image of a Specific Size
To create an image of a specific size:
1. Follow the steps above to capture the area you want to extract.
2. When the Extract Image Region window displays, adjust the size of the saved file by changing the settings in the
Width and Height boxes, located in the left area of the window.
Tips:
Ì` The first column of numbers after Width and Height is the number of pixels of the original extracted image. The
second column is the output dimensions, initially set the same as the original values.
Ì` The percentages show the ratio between the original dimensions and the output dimensions. The check mark in the
box causes both the width and height to be adjusted proportionally.
Ì` You can change the percentages to make an image smaller. If you are extracting a number of images, using the
same percentage for them all ensures they all have the same resolution. You can adjust the percentage to greater
than 100 to make the image larger.
Ì` Instead of changing the percentages, you can define a specific output dimension by typing the exact number of
pixels you want for the height and width in the second width and height columns.
Extracting an Image of a Predefined Size or Aspect Ratio
If you have predefined a fixed size (see “Fixed Size Annotations” on page 102), to extract an image in the predefined size,
hold down the Ctrl key while you click the extract tool on the toolbar.
To extract an image using the same aspect ratio of the predefined size (but not necessarily the same size), hold down the
Shift and Ctrl keys while you use the extract tool to draw the region to extract.
Managing Viewing Applications
You can define applications other than ImageScope for viewing extracted regions. Doing so defines what viewing
application ImageScope launches from the Extract Image Region window, but you can also open the extracted file outside of
ImageScope using any compatible image viewing software (see the next section).
Compatibility Notes
Be aware that the viewing application you define may not be able to open an image of the type you’ve extracted. For
example, Internet Explorer cannot open TIFF files, but can open JPEG files. If you click Launch and the application cannot
open the extracted file, an error message appears from the application indicating it cannot open this type of file.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 79
Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions
Also, the viewing application you define may not be able to handle a file as large as your extracted file. Some applications
have a limit on the size of file they can open and work with. Some third-party programs cannot handle TIFF files, which use
any form of compression. When in doubt, you can specify None for compression of TIFF files. However, if the region is large,
using no compression results in a very large file.
Defining a Viewing Application
To define a viewing application:
1. Follow the instructions above to capture and extract a region of an eSlide.
2. Click the drop-down box next to the Launch button and select Define Application.
If no applications are defined, this list is empty except for this selection. If applications are defined, they display in
alphabetical order.
3. When the Define Applications window appears, type a description of the application (for example, Photoshop) in
the Application Name text box.
4. Click Browse to navigate to the location of the application executable file and select that file.
5. Click Add to add this application to the list of ImageScope viewing applications, and then click Done.
Using the Viewing Application
To view an extracted region with a viewing application (after one is defined):
1. Follow the steps above to extract a region.
2. Click the drop-down box next to the Launch button and select a viewing application.
3. Click the Launch button. (If no applications are defined, the Launch button is disabled.)
Deleting Viewing Applications
To delete applications previously defined:
1. Follow the steps above to extract a region.
2. Click the drop-down box next to the Launch button and select Define Application.
3. When the Define Applications window appears, click the Application Name drop-down box and select the
application you want to delete from the list of ImageScope viewing applications. The Add button now changes to a
Delete button.
4. Click Delete to delete the application from the list of ImageScope viewing applications, and then click Done. (This
does not delete the application from your disk, but only from the list of ImageScope viewing applications.)

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201580
14
eSlide Conferencing
eSlide conferencing makes it possible for several participants to view the same eSlide from multiple,
remote locations. This section discusses how to use the eSlide conferencing feature of ImageScope.
About eSlide Conferencing
ImageScope eSlide conferencing not only allows multiple people to view the same eSlide at the same time, but also
provides the following features:
Ì` Synchronized viewing so all participants see the same region of the eSlide at the same time
Ì` Real-time annotation sharing
Ì` Leader/follower roles and the ability to change those roles
All conference participants must have ImageScope installed on their workstations. (Download the latest free ImageScope
software from www.LeicaBiosystems.com/ePathology.)
Concepts
Ì` The person hosting the conference is called the leader. This is usually the person who created the conference.
Ì` Participants who join the conference are called followers. Followers can see the eSlide the leader opens on the
ImageScope viewer along with any annotations the leader makes.
Ì` Conferencing requires that all parties have access to a common DSC server and a common ImageServer or network
share where images are stored.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 81
Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing
Starting an eSlide Conference
1. Log into eSlide Manager and open an eSlide.
2. Go to the View menu and click Digital Slide Conferencing. The following window displays:
Connecting to an eSlide Conferencing Server
1. On the Digital Slide Conferencing window, click DSC Server. The following window appears:
2. Type the following information:
Ìy Server Name – The example shows a DSC server running at dsc.scanscope.com. Type the name of the server
that is running the DSC service on your network. Usually this is on your DSR, a dedicated server, or it may be
on your workstation.
Ìy Port – Type the number of the port that has been configured for DSC. This is usually 80, but can be set to
another port.
Ìy Email Address and Password are not required.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201582
Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing
Ìy Screen Name – Type the name you want to use as the leader of the conference. You are identified by this
name in the conference participant list.
3. Click Login. The status changes to Connected and the Create Conference button is enabled.
If you set up the DSC server on your workstation, verify your workstation is accessible to
others. See your network administrator if necessary to ensure the correct ports are open,
firewall permissions are set appropriately.
Creating a Conference
1. Click the Create Conference button, and then enter the name of your conference:
2. Enter any name you wish and click OK.
You are notified that you are the conference leader. The baton next to your name indicates that you are the
conference leader.
3. To display your mouse cursor in the participants’ view, select the Show Mouse check box.
The conference is now created.
Opening an Image to Share
The conference leader may open one or more eSlides to share in the conference. Because all participants must have access
to the images too, the leader must open images on an ImageServer using the Access Remote Server command or directly
from eSlide Manager. (You cannot share images in an eSlide conference if they are only on your workstation.)
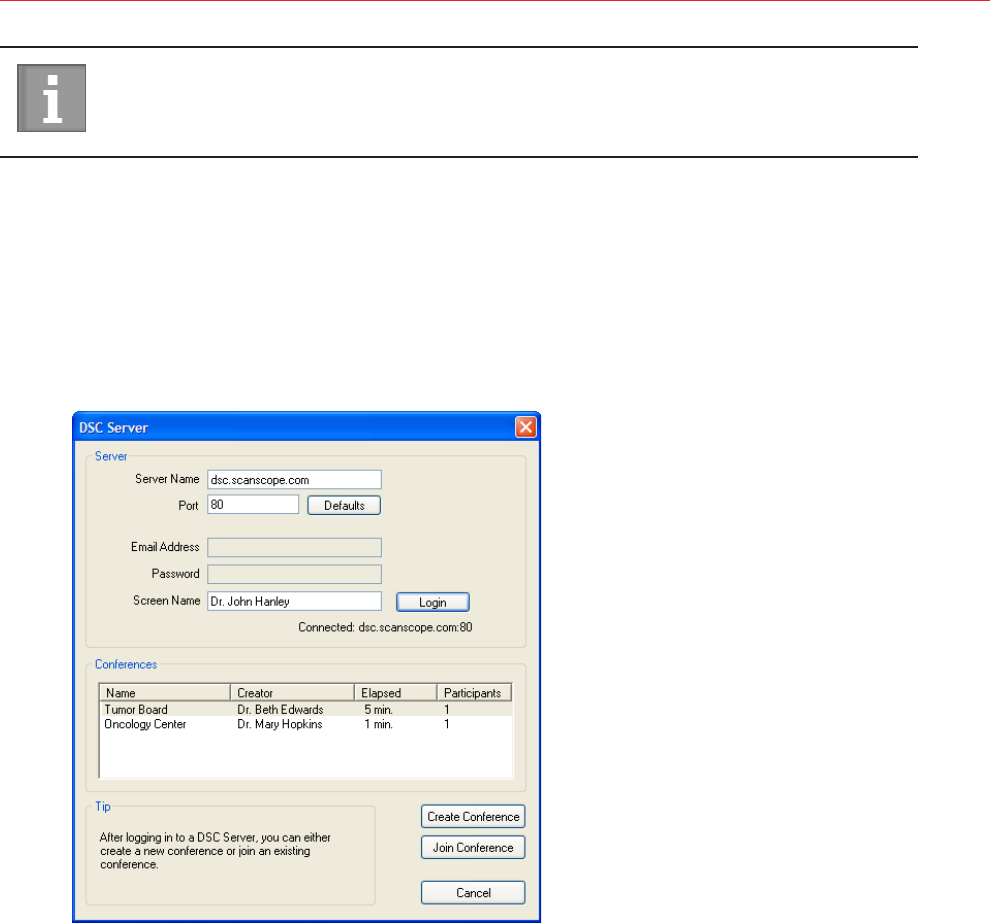
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 83
Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing
The leader can open and move between multiple images during the conference using the
ImageScope filmstrip.
Joining a Conference
Once a conference is created, participants may join.
1. Log into eSlide Manager and open any eSlide by clicking an eSlide thumbnail on the eSlide Manager page.
2. Follow the instructions in “Connecting to an eSlide Conferencing Server” on page 81 to connect to the DSC
server. The following window displays listing any conferences running on that server:
Type the screen name you want to display to the other conference participants.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201584
Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing
3. In the Conferences section, select the conference you want to join and click Join Conference. The Digital Slide
Conferencing window displays, listing you as a participant:
In the ImageScope window you now see the eSlide the conference leader has opened to share.
Viewing Slides in Conference
The conference leader is in charge of the conference:
Ì` As the leader zooms and pans the eSlide, the participant’s view matches the view of the leader. The leader’s mouse
position is visible as a pointer on each participant’s monitor if the leader selected the Show Mouse check box.
Ì` Each participant may have a different screen size or window layout. Each window is kept centered following the
leader’s actions, but the image is adapted to the participant’s window configuration and monitor resolution.
Ì` Only the leader can add annotations, which are visible to all participants.
Changing the Conference Leader
There may be times when either the leader or one of the followers wishes to change the conference leader. For example,
one of the followers may want to point to something on the eSlide or the leader may leave the conference before it is
finished.
If the leader of the conference exits the conference before it is finished, the next person who
joined automatically becomes the leader.
When conference leadership changes, a message appears to alert the participants.
Leader Initiates Change in Leadership
If the leader wishes to assign leadership to another participant, select a follower in the list of participants and click Assign.
The new leader receives the message that leadership has changed.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 85
Chapter 14: eSlide Conferencing
Follower Initiates Change in Leadership
If a follower wants to become the conference leader:
1. On the Digital Slide Conferencing window, select the Request check box.
The DSC server maintains a list of all participants who want to become the leader. An hourglass displays next to
the names of followers waiting to become the leader.
2. To assign the leadership to the next waiting participant, click Relinquish.
The requester is notified that he or she has leadership.
Conference Creator Re-asserts Leadership
If the person who created the conference wants to become leader again, on the Digital Slide Conference window, click
Grab.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201586
15
TelePath Live
TelePath Live, also known as Remote Revisit, provides a way to connect to your scanner remotely.
This chapter provides information and instructions on using TelePath Live to capture z-stack images
from live video. For information on viewing z-stack eSlide images scanned on the Aperio scanner, see
“Chapter 4: Viewing Z-Stack eSlide Images” on page 30.
By using TelePath Live to directly connect to your scanner, you can:
Ì` View a live video feed from the scanner from a remote location.
Ì` Capture Z-stacks and view specimens in multiple focal planes.
Ì` Perform a scan directly from ImageScope.
Scanner Compatibility Notes
Ì` For scanners that contain an AutoLoader—a slide must be on the slide tray to use the Z-stack feature. You cannot
capture Z-stacks from slides in an AutoLoader.
Ì` Some older scanner models cannot use the TelePath Live feature; contact Leica Biosystems Imaging Technical
Services if you have questions about whether your scanner can use TelePath Live.
Ì` Aperio CS scanners support TelePath Live from all five slide positions in the slide tray.
Before You Use TelePath Live
There are some things you should do and know before you use TelePath Live.
Calibration
Your scanner is calibrated at the factory. However, if while using TelePath Live you find that the Live window does not line
up with your cursor position in the ImageScope main window, you should calibrate it again.
For information on calibrating the scanner in preparation for using TelePath Live, please see the TelePath Live (Remote
Revisit) Setup Application Note.
Setting the ImageServerURL
In order for the Console program View Slide button to display images in ImageScope that can be used for TelePath Live, the
ImageServerURL parameter needs to be set up with your ImageServer name.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 87
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
To set up ImageServerURL:
1. Start the scanner Console program by clicking Start > All Programs > ScanScope > Console.
2. Open the Configure window. (See your Console User’s Guide for specific instructions.)
3. Click the ScanScope Properties tab.
4. In the Name field, type: ImageServerURL and click Get.
5. Verify that the name of your ImageServer displays in the Value field.
a. If the ImageServer name is correct, you are done.
b. If the ImageServer name is not correct or is blank, type the correct name of the ImageServer into the Value
box and click Update.
6. Click Close to exit the Configure window. After you exit the Console, your change to ImageServerURL will take
effect the next time you start the Console again.
Here is a little more information about why you need to set this parameter:
When ImageServerURL is set to a valid ImageServer machine name, ImageScope opens the eSlide by passing the
imageID directly to ImageServer. ImageServer uses the database to locate the eSlide. You can tell that you are in the
database mode if you see a number beginning with the @ symbol in the title bar of ImageScope.
You must use ImageServer in this database mode to save captured Z-stacks into the database. If ImageServerURL is not
set, Z-stacks your capture in ImageScope will not be saved in the database when you open the eSlide using the View
Slide button in the Console.
What Is a Z-Stack?
A Z-stack is a three-dimensional image that allows you to view a specimen by moving up and down in the focal planes. This
is especially useful for viewing “thick” specimens.
Z-stack images are cataloged in the ImageServer database, and linked to the original image as an annotation. One of the
reasons for using the TelePath Live feature is to capture and view Z-stack images. See “Capturing Z-stacks” on page 91
for more information.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201588
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
Connecting to an Aperio Scanner
1. Go to the ImageScope View menu and select TelePath Live. The following window displays:
2. Click Configure to define which scanner to connect to. The following window displays:
3. Type the name of the scanner and its port (usually 3333).
4. Define the ImageServer by typing the host name and port number. If you are using an Aperio CS or T3 scanner, this
is the same name and port number as your scanner.
Note that the name of your ImageServer host is typically the same as the ImageServerURL setting (see ”Setting the
ImageServerURL” on page 86) unless you access the ImageServer from outside a firewall, in which case it may
be different—contact your network administrator for assistance.
5. Click OK.
6. On the TelePath Live window, click Connect.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 89
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
Troubleshooting Tips: If you are unable to connect to the scanner, contact your network
administrator to verify the following conditions are true for your network:
y Port 3333 is open and directed to the scanner controller.
y Port 82 is open and directed to the ImageServer.
8. Log in using your eSlide Manager user name and password.
After a few seconds, a window appears showing slides that are loaded in the tray. You are now connected to a
scanner.
The blue dot indicates the slide you are working on. You can click any displayed slide to select that slide.
If the window has no slides displayed, click the Refresh Snapshots button to load macro slide images.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201590
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
Preparing a Slide for TelePath Live
There are two ways to prepare a slide for use with the TelePath Live window:
1. Scan a slide on the scanner and click the View Slide button in the Console. When ImageScope opens, you can
begin placing Z-stack images on the eSlide from the ImageScope TelePath Live window.
2. Use the Revisit Quick Scan or Revisit Hi-Res Scan buttons on the ImageScope TelePath Live window. (See
“Capturing Z-stacks” on page 91.)
Viewing Live Video from the Scanner
Connect to the scanner and open the ImageScope TelePath Live window as discussed in “Connecting to an Aperio Scanner”
on page 88.
After a scan is performed, click around on an eSlide in the TelePath Live window and see a live video feed from the scanner
showing the tissue in the Live window.
When using TelePath Live, coarse and fine focus sliders provide fine-resolution focusing, allowing you to fine-tune the focus:
The right slider’s range is 10% of the entire focus range provided by the left slider, centered on the value of the left slider.
For example, if the left slider is set at 50, the right slider’s range is 50 – 5% of the focus range to 50 + 5% of the focus
range.
Use the slider on the left to get the image roughly into focus. Then use the slider on the right to fine-tune the focus.
Ì` Adjust the size of the Live window by using the Camera Mode drop-down list to select a window size:

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 91
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
Ì` If you locate an area of interest, click the Capture Z-Stack button on the TelePath Live window to capture a
Z-stack (3-dimensional) image of that area. (See the next section.)
Capturing Z-stacks
1. Open the TelePath Live window and connect to a scanner as discussed in “Connecting to an Aperio Scanner” on
page 88.
The blue dot indicates the currently selected slide. Click on any other slide if you want to use it instead.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201592
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
2. Select your Z-stack options:
Ì` Depth – The total number of microns in the Z-stack.
Ì` Frame Count – The number of individual snapshots taken. The limit is 50.
Ì` Camera Mode – The width and height of the Z-stack snapshots. These are limited by the available modes of
the area camera.
3. If you did not open ImageScope by clicking the View Slide button in the Console program, you may need to scan
the slide:
Ì` Clicking the Revisit Quick Scan button on the TelePath Live window performs a high-resolution macro scan
of the slide, generally used when time is short. The slide is scanned at 5x.
Ì` Clicking the Revisit Hi-Res Scan button on the TelePath Live window is the same as pressing the green
button on the scanner. Only the currently selected slide is be scanned, and it is scanned at the currently
selected magnification.
Whether the slide was scanned from the Console or from the TelePath Live window, when the slide is scanned
its image displays in the ImageScope main window along with a Live window that shows the video feed from the
scanner.
4. Click the image in the ImageScope main window. A yellow rectangle displays showing the area of the image
displayed in the Live window. This also selects the area to perform a Z-stack capture. To move the selection
rectangle, click another location in the main image.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 93
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
5. To capture a Z-stack from the selected slide, click the Capture Z-Stack button.
When you see the message “Opening Z-stack” on the TelePath Live window, the Z-stack has been captured and a
green rectangle displays overlaid on top of the yellow rectangle in the ImageScope main window.
Click elsewhere in the image to move the yellow selection rectangle away from the Z-stack image. The green
rectangle showing the location of the Z-stack.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201594
Chapter 15: TelePath Live
Viewing Z-stacks
Once you have captured a Z-stack image, you will see that the Live window now contains a coarse and fine focus tool:
To focus through the stack, simply slide the focus bar up and down.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 95
16
Utilities and Diagnostics
The utilities discussed in this section are primarily used for troubleshooting. Leica Biosystems Imaging
Service representatives may ask you to use these utilities to pinpoint an issue.
Logging
If requested to do so by Leica Biosystems Imaging Services, enable logging by going to the Tools menu and selecting
Logging. This creates a file named viewport.log where text messages on ImageScope actions are logged.
If you are having a problem, Technical Support typically asks you to:
1. Turn logging on.
2. Run until you encounter the problem again.
3. Then email Technical Support the viewport.log file.
You should then turn logging off (by again going to the Tools menu and selecting Logging) as logging affects system
performance.
Cache Display
Because eSlides are typically much larger than can be loaded into memory all at once, ImageScope keeps portions of the
eSlide in computer memory so it can display them quickly. It prefetches data for the eSlide from disk or from a remote
server, determining which portions of the image to fetch by anticipating where the user is going to go next.
Enable the cache display by pressing the Shift+Ctrl+M keys. (Press Shift+Ctrl+M keys again to turn it off.)
The cache display shows which parts of the eSlide are loaded into ImageScope’s cache memory. The darker the area, the
higher the resolution of the part of the image that is loaded.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201596
Chapter 16: Utilities and Diagnostics
Below is an image of the ImageScope screen showing the cache displays:
Running Multiple ImageScope Sessions
ImageScope normally allows only one instance of itself to run. (If ImageScope is open and you try to start it again, the
first copy of ImageScope closes.) There may be special occasions when troubleshooting a problem or testing eSlide
Conferencing, for example, when you want to run more than one copy of ImageScope at a time.
To run multiple copies of ImageScope:
1. Click Start and select Run.
2. Click Browse on the Browse window and navigate to the ImageScope.exe file on your workstation. (The default
location is: C:\Program Files\ScanScope\ImageScope.)
3. Click Open.
The Run window now contains the path to the ImageScope.exe file.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 97
Chapter 16: Utilities and Diagnostics
4. At the end of the path specification, type a space and the characters /M (outside of the quotation marks) as shown
below:
5. Click OK. One copy of ImageScope has now started. Repeat this procedure again to open a second copy of
ImageScope.
Tuning Parameters/Statistics
To see how ImageScope is making use of memory and caching:
1. Go to the Tools menu and select Advanced. The following window displays:
Maximum Cache Size
Ì` Cache Limit – Limits the amount of memory that is allocated for image caching. If you set this to zero, then
ImageScope will use up to 75% of your system’s memory as needed. You should typically leave this set to zero. If
you want to set the cache limit to a specific size, enter the number of megabytes. For example, 128 sets the cache
limit to 128 megabytes. This is the only value on this screen that you can change (except for resetting the statistics
to zero).
Statistics
The following fields change as you view and pan images. ImageScope only reports these values if an eSlide is open. You can
reset them to zero by clicking Reset (unless noted otherwise below).
Ì` Available Mem – Total amount of physical memory not in use on your system. The Reset button does not affect
this value.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 201598
Chapter 16: Utilities and Diagnostics
Ì` Total Mem – Total amount of memory installed on your system. The Reset button does not affect this value.
Ì` Cache Max – Amount of cache memory used in megabytes.
Ì` Cache Used – Current amount of memory cache used in megabytes.
Ì` Cache Used HWM – High water mark for memory cache in megabytes.
Ì` Cache Buffers – Current number of buffers stored in cache.
Ì` Cache Buffers HWM – High water mark for buffers stored in cache.
Ì` Cache Searches – Number of cache searches.
Ì` Cache Hits – Ratio of cache hits to cache searches.
Ì` Cache Hits % – Ratio of cache hits to cache searches.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 99
17
ImageScope Options
Use the Options command to set and review ImageScope settings and preferences.
To access the ImageScope settings, go to the Tools menu and select Options. The Options window appears. Click each tab
to view or change the associated options.
General Options
The general options are organized into three areas: Magnification, Default Gamma Files, and Analysis.
Magnification
The magnification options are:
Ì` Initial Magnification – Specify the initial magnification for images as they are opened. This can be a percentage
from 1 to 100 or you can specify 0 to fit the entire eSlide in the main window display.
Ì` Maximum Magnification – Specifies how far you can zoom into the image. Note that setting this value to
greater than 100% does not increase the resolution of the image—it is enlarging the pixels of the existing image.
Ì` Magnifier Magnification – Specifies the ratio between the main window and the magnifier window. For
instance, if this value is set to 3, and you are viewing the main image at 50% zoom, then the magnifier window
displays 150% zoom. See “Using the Magnifier Window” on page 27 for information on the magnifier window.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015100
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Ì` Normalize magnification levels – Normalizes images to the same microns per pixel. Because of different optic
and camera components, the microns per pixel of images created by the Aperio ScanScope family of scanners may
be different than the microns per pixel for images created by non-ScanScope scanners such as the Versa scanner.
This can result in objects within the images created by the different scanners appearing to be different sizes even
if in reality they are the same size. To ensure all images are normalized to the same microns per pixel, this option is
on by default. You can turn off this option if you want to view your image at its original resolution.
Ì` Use “X” magnification rather than “%” – Adjusts the Zoom slider from displaying magnification in percentages
to displaying them as “2x,” 4x,” and so on. See “Zoom Slider” on page 27 for examples of the Zoom slider in
both modes.
Default Gamma Files
Adjusting the display of an eSlide does not affect the original eSlide, but only its appearance during the current ImageScope
session. You can save these adjustments in a gamma table file to be re-applied in a later session to one or more eSlides.
(See “Saving and Loading Color Settings” on page 37 for information on creating gamma table files.)
The Default Gamma File sections on the General tab allow you to load specific gamma table files every time you start up
ImageScope. This can be useful if you know you need to compensate for a particular monitor, for example (although a better
long-term solution is to calibrate the monitor so it does not have a color bias).
Loading a Default Gamma Table File for the Main Image
To load a default gamma table file that is applied to all images opened in the main ImageScope window:
1. On the General tab, select the Automatically load default gamma file(s) check box.
2. Use the browse button in the Default Gamma File Location text box to search for the gamma table file you want
to use. The Select default gamma file window appears.
3. To protect the selected gamma table file from being modified, select the Open as read-only check box on the
Select default gamma file window.
4. Select the gamma table file you want to use and click Open.
Loading a Default Gamma Table File for Z-stack Images
To load the default gamma table file to be applied only to Z-stack images:
1. Select the Automatically load default gamma file(s) check box.
2. Use the browse button in the Default Gamma File Location – for Z-stack Images text box to search for the
gamma table file you want to use.
3. To protect the selected gamma table file from being modified, select the Open as read-only check box.
4. Select the gamma table file you want to use and click Open.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 101
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Analysis
When you run an algorithm to analyze an eSlide, you can request a visual representation of the analysis in addition to the
quantitative data. (See the Image Analysis User’s Guide more information.) This visual representation is called a markup
image.
Ì` To instruct ImageScope to always generate a markup image by default (this setting can be overridden when you
perform the analysis), select the Generate Markup Images check box.
Ì` To specify the location of the markup file, click the browse button and navigate to the location where you want to
store this data. (This location is used for analyses performed on local eSlides. Remote analyses store the markup
image only in the eSlide Manager database.)
Navigation Options
The ImageScope navigation options affect image panning and multiple image synchronization.
Synchronization Option
When you have multiple eSlides open in ImageScope and they are all visible at the same time, you can click or
(yellow) on the toolbar to synchronize navigation among the open images. If the image navigation is synchronized and you
pan or zoom the first image, the other images will show the same behavior. The synchronization option defines the behavior
of that synchronization:
Ì` Both Pan & Zoom – Synchronizes both panning and zooming.
Ì` Pan Only – Synchronizes panning only.
Ì` Zoom Only – Synchronizes zooming only.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015102
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Panning Options
The following panning options are available:
Ì` Scroll Speed – Specifies how fast the image scrolls when holding down the mouse button near the edge of an
image.
Ì` Pan Speed – Specifies how fast the image pans when clicking and dragging the image.
Ì` Reverse panning direction (“Pathologist” mode) – Select this check box to pan in reverse. With this option
enabled, as you click and drag to the left, the image moves to the right.
Annotation Options
The Annotations tab of the Options window allows you to select annotation options.
Annotation Color Options
Each annotation layer displays annotations in a different color. The Default Annotation Colors section allows you to select
the color used for each layer.
1. Click the colored box above the annotation layer for which you want to change the color.
2. From the color selection window, select a color from the palette shown or click Define Custom Colors to define
your own color.
3. Click OK.
If you use more than five annotation layers, the new layers re-use the colors defined for the first five layers. For example,
layer 6 will use the color defined for layer 1 and layer 7 will use the color defined for layer 2.
Fixed Size Annotations
The Fixed Size Regions options on the Annotations tab set a fixed size for drawn annotations that is used when you press
the Ctrl key while you draw. These settings are also used to extract a region of fixed size and to zoom to a region of fixed
size.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 103
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Ì` Width and Height – these values define the size of rectangles or circles. For example, to always draw a square
of 200 pixels by 200 pixels when you press the Ctrl key while using the Rectangle tool, type 200 into the Width and
Height boxes.
Ì` Length – This value is used for the ruler and arrow annotations.
See “Report Image Options” on page 105 for information on setting the fixed size of a report image.
Automatically Saving Annotations
The Automatically Save Annotation Changes check box saves annotations and changes to annotations when you exit
ImageScope without prompting for a confirmation.
If this option is enabled, but you have also selected Don’t Save Recorded Tracks on the Tracking options tab, tracks will
not be saved when you exit even though other annotations are.
Tracking Options
The Tracking tab contains options that affect tracking. For example, you can enable tracking every time you open an eSlide
in ImageScope. For information on tracking, see “Chapter 12: Tracking” on page 70.
The options on this tab include:
Ì` Automatically Start Tracking on Open – Always begin recording when you open an eSlide. If a track already
exists for the eSlide, opening the slide starts appending a track to the original track.
Ì` Don’t Save Recorded Tracks – Disable saving the track with the eSlide.
Ì` Automatically Display Track Map – Enables track mapping by default. This also selects the Map check box on
the Tracker tool.
Ì` Minimum Resolution – Specifies the minimum resolution of a view which is mapped. This defines the lowest
resolution at which a region of the image is viewed.
Ì` Minimum Magnification – Specifies the minimum magnification of a view which is mapped. This defines the
lowest magnification at which a region of the image is viewed.
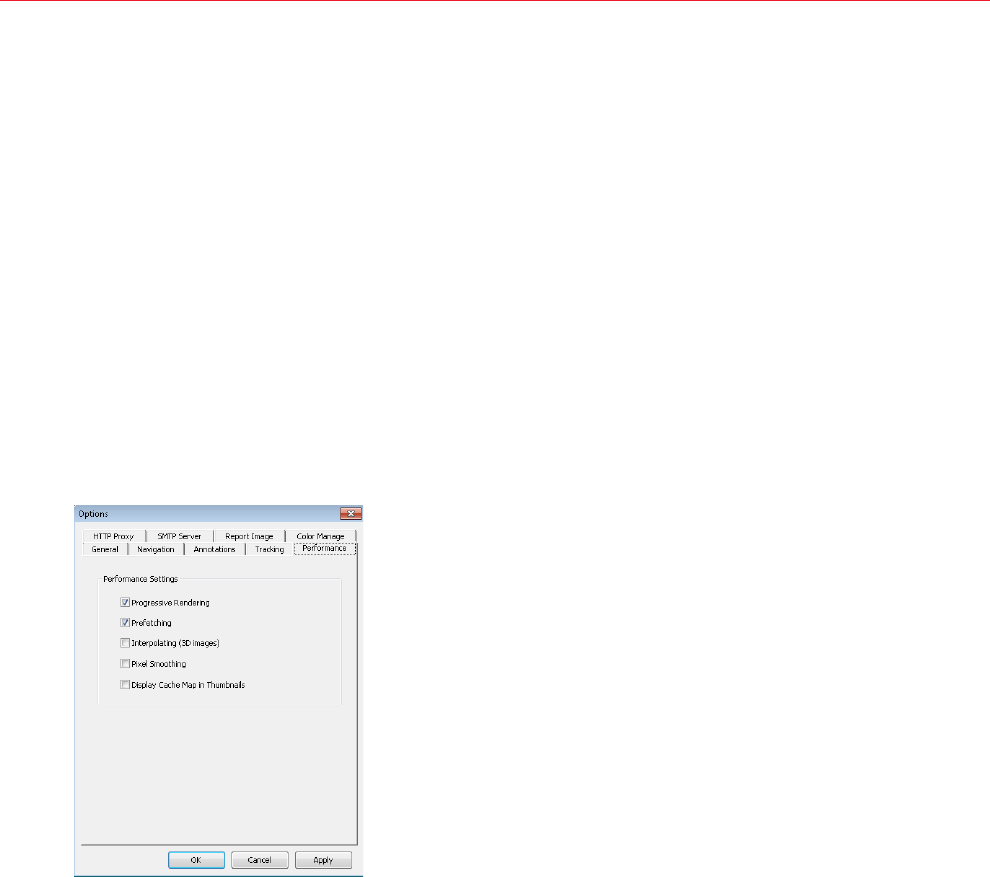
ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015104
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Ì` Region Granularity – Divides the image into granules when deciding which section of the image is glass and
which is tissue. By changing the granularity, you affect the glass/tissue distinction. Slide the control to the left to
decrease the granule size and to the right to increase granule size. Smaller granules generally mean that less of
the image will be classified as glass, while larger granules mean more will be classified as glass. You can see its
effect if a tracking map is shown in the thumbnail as you move this slider.
Ì` White Sensitivity – Displays your progress through tissue, not glass. This setting helps define which is tissue and
which is glass. This slider adjusts the “whiteness” of detected glass. Dragging it to the left increases sensitivity,
causing less of the slide to be classified as glass, and dragging it to the right decreases the sensitivity, causing
more of the slide to be classified as glass. You can see its effect if a tracking map is shown in the thumbnail as you
move this slider.
Performance Options
The Performance tab contains settings that allow you to balance display speed with image quality. These settings are
provided because eSlides are usually too large to fit into memory all at once; therefore, some decisions have to be made
about how ImageScope will act when swapping data in and out of memory from disk.
Ì` Progressive Rendering – When enabled, ImageScope renders image views in low resolution first, and then
increasingly improves the image (by de-pixilating it) as it reads more image data from the disk or retrieves it from
a remote server. With this feature disabled, ImageScope does not render an image view until the entire view has
been loaded into memory.
Ì` Prefetching – When enabled, ImageScope anticipates your next view requests and loads those sections of the
image into memory. By anticipating where you will move next in the image and loading that information into
memory, ImageScope speeds up the image display.
Ì` Interpolating (3D images) – Displays a weighted average of the two neighboring Z-stack views for a Z-level.
Ì` Pixel Smoothing – Uses a high fidelity (but slower) scaling routine.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 105
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
HTTP Proxy Option
Some networks require that all HTTP traffic be routed through an HTTP proxy server. If you are using ImageScope inside a
network that uses an HTTP proxy server, you need to define the proxy server to ImageScope.
Your network administrator can provide the settings you need for the server name, server port, user name, and password.
Not all proxy servers require a user name and password.
If you have already created Windows proxy settings on your workstation, select the Use Windows Proxy Server Settings
check box to use those settings.
Report Image Options
The Report Image tab allows you to select a combination of fixed or user selectable sizes and resolutions. The Fixed Region
Size parameters define the size of the report image rectangle if you press the Ctrl key while selecting the image area.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015106
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
eSlide Manager Reporting is an optional upgrade that create attractive reports with a few clicks of
the mouse. The report image feature is used with this product if you are using report templates that
contain images.
Color Management Options
Aperio Integrated Color Management considers the optical characteristics of your scanner and your display monitor to
ensure eSlide color is displayed accurately. For information on color management and ICC profiles, see “Appendix B:
Aperio Integrated Color Management” on page 111.
You can view the target monitor ICC profile or choose a new monitor:

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 107
Chapter 17: ImageScope Options
Email Settings
To use the ImageScope email snapshot feature, you must define email settings on the SMTP Server tab. The first time you
use the email snapshot feature without these settings defined, ImageScope displays this tab.
For information on how to email a snapshot of the eSlide displayed in ImageScope, see“Emailing a Snapshot” on page 73.
This window defines the information required for ImageScope to send email. For additional information about these settings,
contact your IT department.
Ì` Server Name – Name of the server that hosts your email service.
Ì` Server Port – Port on your email server used to transfer email.
Ì` Use SSL – Select this check box if your email server uses SSL to secure email.
Ì` User ID/Password – If your email server requires authentication, then enter your user name and password.
Ì` eMail Address – Type the email address from which snapshots will be emailed
Ì` Send Test eMail – If you want to verify that the settings are correct, click Send Test eMail. A message displays
if the test email was successful, and the person at the email address specified will receive an email titled “Test
Email” that says “Successful!”
For More Information
For more on the ImageScope settings, see:
Ì` “Chapter 16: Utilities and Diagnostics” on page 95.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015108
A
Keyboard Shortcuts
This section contains a quick reference list of keyboard shortcuts you can use with ImageScope.
ImageScope Keyboard Shortcuts
Key Sequence Command
Toolbar
Icon
Action
Arrow key None Nudge image
Ctrl + Plus key None Zoom in
Ctrl + Minus key None Zoom out
Ctrl Press while drawing an annotation to draw the annotation
in a predefined size.
Ctrl+A Image > Adjustments Displays the Image Adjustments window where you can
make image adjustments to the main image or to the
Z-stack image, as well as load and save adjustments.
Ctrl+B None Enables/disables integrated color management
Ctrl+C Edit > Copy If an annotation is selected, copies the selected annotation
and enables you to paste it on the eSlide image.
Edit > Copy If no annotation is selected, copies the current view of the
eSlide image and places it on the Windows clipboard.
Ctrl+D View > Digital Slide
Conferencing Window
Opens the Digital Slide Conferencing window where you
can create or join an eSlide conference.
Ctrl+E Image > Rotate Image Opens image rotation toolbar
Ctrl+F None Turns image prefetching on/off.
Ctrl+F4 File > Close Image Closes the image currently open in ImageScope.
Ctrl+G View > Analysis Runs an algorithm analysis on a local or remote eSlide.
Ctrl+I Tools > Options >
Performance
Turns interpolating on/off (used for viewing 3D images).
Ctrl+J Tools > Options >
Performance
Turns progressive rendering on/off.
Ctrl+K Image > Keep Open Turns Keep Open option on/off.
Ctrl+L Tools > Logging Turns logging on/off.
Ctrl+M None Shows/hides track map

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 109
Appendix A: Keyboard Shortcuts
Key Sequence Command
Toolbar
Icon
Action
Ctrl+Shift+M None Shows/hides cache map.
Ctrl+N View > Annotations
Window
Opens the Annotations window where you can work with
annotation layers for the current image.
Ctrl+O File > Open Image Displays the Open Image window where you can browse for
a local image file to open.
Ctrl+P Tools > Options Opens the Options window to set general, navigation,
annotation, performance, and HTTP proxy options.
Ctrl+Q Image > Quality Turns IQ on/off.
Ctrl+R File > Access Remote
Server
Connects to an Aperio ePathology ImageServer where you
can select an image to view.
Ctrl+S Tools > Options >
Performance
Turns pixel smoothing on/off.
Ctrl+Shift Moves all annotations.
Ctrl+T View > Thumbnail Shows/hides the thumbnail window.
F1 Help > Help Opens ImageScope help.
F2 None Activates the Pen annotation tool.
F3 None Activates the Negative pen annotation tool.
F4 None Activates the Ruler annotation tool.
F5 None Activates the Rectangle annotation tool.
F6 None Activates the Ellipsis annotation tool.
F7 None Activates the Arrow annotation tool.
F8 View > Annotation Link
Manager
Opens the Annotation Link Manager window, where you
can link slide annotations in a specific viewing order.
F9 None Activates the Counter annotation tool.
F11 View > Full Screen View ImageScope on your entire monitor screen.
Shift None Press while drawing annotations: ellipse becomes a circle;
rectangle becomes a square.
Shift+Arrow None Moves one screen at a time.
Shift+Ctrl None Press while drawing an annotation or using the extract
region tool to create a region of the same aspect ratio as
the predefined fixed annotation size.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015110
Appendix A: Keyboard Shortcuts
Key Sequence Command
Toolbar
Icon
Action
Shift+F7 View > Previous
Annotation Link
If annotation links have been set using the Annotation
Link Manager, this moves to the previous annotation in the
viewing sequence.
Shift+F8 View > Next Annotation
Link
If annotation links have been set using the Annotation Link
Manager, this moves to the next annotation in the viewing
sequence.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 111
B
Aperio Integrated Color
Management
Aperio Integrated Color Management considers the optical characteristics of your scanner and your
display monitor to ensure the colors of the eSlides are displayed accurately.
A challenge for any provider of applications or devices that work with images is to ensure that the end result (in the case of
Leica Biosystems Imaging, viewing an eSlide created by scanning a microscope slide) provides a true representation of the
color of the original glass slide from which the eSlide was made.
Every image capturing device will transform the image color due to the particular characteristics of that device.
Fortunately, there is a way to take those characteristics into account to ensure that all along the path the image travels,
from creation to display, color accuracy is maintained. As of Release 9, Leica Biosystems Imaging provides Integrated
Color Management that works with the international-standard ICC color management specification to maintain image color
accuracy.
ICC Profiles
The ICC (International Color Consortium) is a body that maintains a specification defining a color management system that
ensures the color of images moved among applications, devices, and operating systems is maintained accurately.
The ICC defines a format for ICC Profiles, which describes the color attributes of a particular device.
Scanner ICC Profile
In order to describe the behavior of image capture devices such as an Aperio scanner, the devices must be calibrated to a
standard color space, which creates an ICC profile. At the Leica Biosystems Imaging facility, an ICC profile is created for
your scanner. The scanner’s ICC profile is called the source profile. This profile is stored as a standalone file in \ScanScope\
Profiles on the scanner workstation.
As you scan glass slides, the ICC profile for your scanner is also embedded in the resulting eSlide file.
The embedded profile tells ICC-aware applications, such as ImageScope and WebViewer, the color-transformation
completed by the scanner. This allows the Aperio Integrated Color Management to transform the eSlide to its original color.
Display Monitor ICC Profile
The scanner’s ICC profile is not the only component of the integrated color management equation. The monitor you use to
view the eSlide also has characteristics that affect color display. Your monitor may have shipped with drivers that contain an
ICC profile for the monitor. Or, you can create a new monitor profile by using an external calibration tool. As the monitor is
the final device in the image transformation chain, its profile is called the target profile.

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015112
Appendix B: Aperio Integrated Color Management
If a monitor ICC profile exists, the Aperio ICC-aware applications will use it with the scanner’s ICC profile to display the
eSlide color accurately.
How ImageScope Uses Color Management
ImageScope is an ICC-aware application, which means that for any eSlide containing an embedded ICC profile it uses the
embedded scanner ICC profile and your monitor ICC profile to ensure eSlides are displayed with accurate color.
For information on how ImageScope uses color management with various ImageScope features, see:
Ì` “Viewing with Color Management” on page 28
Ì` “Chapter 13: Saving eSlides and Regions” on page 73
Ì` “Color Management Options” on page 106

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 113
Symbols
3D images. Seez-stack images, scanned
A
AFI (Aperio Fused Image) 39
Analysis button 23
annotations
copy and paste 24, 53
distance measurement 53
drawing
editing free-form shapes 55
ellipsis 52
fixed size 54
grid, exporting 65
layers
attributes 66
exporting 65
grid, exporting 65
importing 65
z-stack images 54
linking 67
notes for working with 51
panning while drawing 51
redrawing freeform 55
saving 51
viewing length and area 62, 63
z-stack images 54
Annotations window
detailed view 58
plots 61
pre-processing 61
summary view 58
Aperio Integrated Color Management 111
arrow tool 52
autopanning 26
axes and grid 28
B
best focused layer, z-stack 30
brightfield image adjustment. Seeimage adjustments
C
cache
display 95
settings 97
change annotation 55
changing color defaults 102
clinical viewing mode 22
closing eSlides 20
color adjustments. Seeimage adjustments
color balance 36
color management 106, 111
ICC profiles 111
conferencing. SeeeSlide conferencing
connecting to scanner 88
copy and paste annotations 24
copy annotations 53
counter annotation button 24
Counter tool 52
CWS files 11
D
deleting regions 61
diagnostics 95
distance measurement button 24
Distance Measurement Tuning window 53
DSR 13
Index

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015114
Index
E
edit annotation 55
ellipsis tool 52
email settings 107
email snapshot image 23, 73
eSlide conferencing 80
changing leader 84
creating 82
joining 83
viewing slides 84
eSlides
closing 20
information about 19
opening local 17
opening recent 17
viewing multiple 17
windows, managing 18
Excel spreadsheet, export annotation text 65
export images, three versions 74
export layer attributes text 65
export regions attribute text 65
export to Microsoft Excel 65
extracted regions 76
fixed aspect ratio 78
options 76
predefined size 78
saving specific size 78
selecting 76
viewing applications 78
extraction tool 74, 76
F
false color 38
applying temporary 38
features 10
file types supported 11
filmstrip 18, 27
fluorescence image 38
adjustments 42
adjustments, tips 42
AFI 39
adjusting 39
brightness, adjusting 42
channel
cycling display 41
registering 44
viewing information 41
color
adjusting 42
inverting 42
contrast, adjusting 42
creating RGB image 77
extracting 77
false color 38
fused image 39
fusing an image 45
gamma, adjusting 42
histogram
high clip 44
intensity thresholds 44
low clip 44
tone curve 44
transfer function 44
thumbnail, automatic contrast 43
viewing channel images 40
Focus slider, z-stack images 31
free-form shape annotation
draw 51
edit 55
fused image
adjusting. See fluorescence image; See fluorescence
image
creating 45
H
histogram 43
HTTP proxy option 105
I
IHC analysis 58
image adjustments 35
fluorescence images 39
main image 35
Z-stacks 35
image analysis
result plots 61
image information 19
image resolution 48

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 115
Index
L
label rotation 34
Layer Attributes pane
copy and paste 65
export to Microsoft Excel 65
export to text file 65
Layer Regions pane
copy and paste 65
export text file 65
export to Microsoft Excel 65
z-stack image layers 54
linking annotations 67
Link Manager 67
links
creating 68
deleting 69
viewing 68
local image support 17
logging activities 95
M
magnification
options 99
magnification levels, normalize 100
magnifier window 27
changing default resolution 27
magnification settings 99
resizing 27
main image gamma settings 100
markup image 101
measure distance annotation 53
measure distance button 24
microns per pixel, normalize 100
Microsoft Excel, export annotation text 65
MRXS files 11
multiple ImageScopes 96
N
navigating 26
options 101
panning 26
z-stack images, scanned 30
NDPI files 11
computing 49
setting/changing 49
image rotation 33
ImageScope
disabling pre-processing 61
features 10
image view 11
installing 13
starting 14
toolbar, quick reference 22
window
filmstrip 18
magnifier window 27
quick reference 21
status bar 19
thumbnail window 26
ImageScope options
analysis 101
annotation 102
default gamma files 100
general 99
HTTP proxy 105
integrated color management 106
magnification 99
navigation 101
performance 104
tracking 103
ImageServerURL 86
image view 11, 20
saving 20
Image view
opening 20
installing 13
integrated color management 28
Intended Use 10
interpolating 104
IQ 31
J
JPEG files 11
K
keyboard shortcuts 108

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015116
Index
save image 23
send in email 23, 73
spreadsheet, export annotation text 65
starting ImageScope 14
status bar 19
symbols 118
synchronization options 101
system requirements 13
T
tab-delimited file, export to 65
TelePath Live
calibration 86
connecting to scanner 88
ImageServerURL 87
live video 90
prerequisites 86
thumbnail window 26
TIFF files 11
toolbar quick reference 22
tracking 70
appending to a track 72
options 103
tips 71
viewing track 71, 72
U
updating analyses 61
user permissions 15
utilities 95
V
viewing
live video 90
track 72
with color management 28
VMS files 11
W
Windows proxy server settings 105
X
X-coordinate navigation 27
negative pen tool
editing annotations 55
using 52
normalize scanned images 100
O
opening eSlides 17
P
page panning 27
panning 26
options 102
panning while annotating 51
Pen tool
editing annotations 55
using 51
performance options 104
prefetching images 95, 104
pre-processing 61
progressive rendering 104
pseudo-color. See false color
R
Rectangle tool 52
redraw annotation 55
registering channels 44
Report Region tool 52
reverse panning 102
rotating
images and labels 33
Ruler tool 52
S
saving
image view 20
saving image to clipboard 73
scalebar 28
security 15
SlideDat.ini files 11
slide-specific processing 58
snapshot
creating 73

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015 117
Index
Y
Y-coordinate navigation 27
Z
zoom, immediate
28
zoom navigation 28
z-stack images
opening 19
z-stack images, scanned
annotating 54
best focused layer 30
Focus slider 31
viewing 30
Z-stacks, TelePath Live
calibrating 86
capturing 91
configuring 88
gamma settings 100
viewing 94

ImageScope User’s Guide, Revision P © Leica Biosystems Imaging, Inc. 2015118
Symbols
ÌÌ The following symbols may appear on your product label or in this user’s guide:
Manufacturer
Date of manufacture (year - month - day)
European Union Authorized Representative
In vitro diagnostic device
Serial number
Relative humidity range
Storage temperature range
Electronic and electrical equipment waste disposal
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert you to the presence of important operating
and maintenance (servicing) instructions.
Le point d’exclamation dans un triangle équilatéral vise à avertir l’utilisateur qu’il s’agit d’instructions d’utilisation
et d’entretien importantes.
The lightning flash with arrowhead symbol within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert you to the presence of
uninsulated “dangerous voltage” within the product’s enclosure that may be of sufficient magnitude to constitute a
risk of electric shock to persons.
Le symbole de l’éclair avec la pointe de flèche dans un triangle équilatéral vise à avertir l’utilisateur que le boîtier
du produit présente une « tension dangereuse » non isolée d’une amplitude suffisante pour constituer un risque
d’électrocution.
The flat surface with waves symbol within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert you to the presence of hot
surfaces which could cause burn damage.
Le symbole d’une surface plane et de vagues dans un triangle équilatéral vise à avertir l’utilisateur de la présence
de surfaces chaudes qui peuvent causer des brûlures.
The UV lamp within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert you to the presence of UV light within the
product’s enclosure that may be of sufficient magnitude to constitute a risk to the operator.
La lampe UV dans un triangle équilatéral vise à avertir l’utilisateur de la présence de rayonnement
UV dans le boîtier du produit qui peut être d’une amplitude suffisante pour constituer un risque pour
l’utilisateur.

www.LeicaBiosystems.com/ePathology
