
BY ORDER OF THE
SECRETARY OF THE AIR FORCE
DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE
MANUAL 36-2100
7 APRIL 2021
Incorporating Change 1, 14 August 2024
Personnel
MILITARY UTILIZATION AND
CLASSIFICATION
COMPLIANCE WITH THIS PUBLICATION IS MANDATORY
ACCESSIBILITY: Publications and forms are available for downloading or ordering on the
e-Publishing website at www.e-Publishing.af.mil.
RELEASABILITY: There are no releasability restrictions on this publication.
OPR: AF/A1P Certified by: SAF/MR
Supersedes: AFI36-2101, 25 June 2013
AFI36-2105, 25 May 2018
AFI36-2107, 22 October 2018
AFI36-2616, 9 October 2018
AFI36-2626, 20 November 2018
AFRCI36-2102, 26 March 2018
Pages: 197
This Air Force Manual (AFMAN) implements Title 10 United States Code (USC) Section 12303,
Ready Reserve: members not assigned to, or participating satisfactorily in, units and 10 USC §
10148, Ready Reserve: failure to satisfactorily perform prescribed training and Air Force Policy
Directives (AFPD) 36-21, Utilization and Classification of Air Force Military Personnel, and
AFPD 36-26, Total Force Development and Management, for administering the provisions of
Department of Defense Instruction (DoDI) 1200.18, The United States Property and Fiscal Officer
(USPFO) Program, DoDI 1200.18, The United States Property and Fiscal Officer (USPFO)
Program, DoDI 1205.18, Full Time Support (FTS) to the Reserve Components, DoDI 1235.09,
Management of the Standby Reserve, DoDI 1235.13, Administration and Management of the
Individual Ready Reserve (IRR) and the Inactive National Guard (ING), DoDI 1300.28, Military
Service by Transgender Persons and Persons with Gender Dysphoria, DoDI 1322.06,
Fellowships, Scholarships, Training with Industry (TWI), and Grants for DoD Personnel and
DoDI 6000.13, Accession and Retention Policies, Programs, and Incentives for Military Health
Professions Officers (HPOs). This manual applies to civilian and uniformed members of the
Regular Air Force (RegAF), Air Force Reserve (AFR), and the Air National Guard (ANG). This
manual requires the collection and or maintenance of information protected by the Privacy Act of

2 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
1974 authorized by 10 USC § 9013, Secretary of the Air Force, and Executive Order 9397,
Numbering System for Federal Accounts Relating to Individual Persons, as amended (E.O 13478).
The applicable System of Records Notice(s) F036 AF PC C, Military Personnel Records System
is available at: https://dpcld.defense.gov/privacy/SORNS.aspx. Ensure that all records created
as a result of processes prescribed in this publication are maintained in accordance with Air Force
Instruction (AFI) 33-322, Records Management and Information Governance Program, and
disposed of in accordance with Air Force Records Information Management System Records
Disposition Schedule. Refer recommended changes and questions about this publication to the
Office of Primary Responsibility (OPR), using Air Force Form 847, Recommendation for Change
of Publication; route Air Force Form (AF Form) 847 from the field through the appropriate
functional chain of command. This AFMAN may be supplemented at any level; all Major
Command (MAJCOM)-level supplements must be approved by the Human Resource Management
Strategic Board prior to certification and approval. The authorities to waive wing/unit level
requirements in this publication are identified with a Tier (“T-0, T-1, T-2, T-3”) number following
the compliance statement. See DAFI 33-360, Publications and Forms Management, for a
description of the authorities associated with the Tier numbers. Submit requests for waivers
through the chain of command to the appropriate Tier waiver approval authority, or alternately, to
the requestor’s commander for non-tiered compliance items. This manual has been reviewed by
the Per Diem, Travel and Transportation Allowance Committee in accordance with DoDI 5154.31,
Volume 5, Commercial Travel Management: the Per Diem, Travel and Transportation Allowance
Committee (PDTATAC), as PDTATAC Case RR19008 (Note: Any conflict between this manual
and the Joint Travel Regulations (JTR), is resolved based on the JTR, and not this manual.) The
use of the name or mark of any specific manufacturer, commercial product, commodity, or service
in this publication does not imply endorsement by the Air Force. Compliance with Attachment
2 in this publication is mandatory.
SUMMARY OF CHANGES
Interim Change 1 deletes Chapter 3, Applying for Flying Training, Air Battle Manager, and
Astronaut Programs and Attachments 6, NASA Qualifying Degree Fields, Attachment 7,
Synopsis of Nasa Medical Standards, and 8, Application for Astronaut Duty (NASA Sample See
Paragraph 3.4.1.). This policy is now published in DAFMAN 36-2137, Applying for Flying
Training, Air Battle Manager, and Astronaut Programs. A margin bar (|) indicates newly
revised matter.
Chapter 1—OVERVIEW 6
1.1. Overview. ................................................................................................................. 6
1.2. General Guidance. ................................................................................................... 6
1.3. Roles and Responsibilities. ...................................................................................... 6
Chapter 2—CLASSIFYING MILITARY PERSONNEL (OFFICER AND ENLISTED) 8
2.1. Classification Overview, Concept, Responsibilities, and Structure. ........................ 8
Table 2.1. Enlisted AFSC Explained. ....................................................................................... 10
Table 2.2. Officer AFSC Explained. ......................................................................................... 11
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 3
2.2. Initial Classification. ................................................................................................ 17
Table 2.3. Initial Determination of Control AFSC. .................................................................. 23
2.3. Classification Actions at Base of Assignment. ........................................................ 24
Table 2.4. Waiver Authority for Mandatory Classification Requirements—Officers (See
paragraph 1.3.7). ...................................................................................................... 28
Table 2.5. Waiver Authority For Mandatory Classification Requirements—Enlisted
Personnel (See paragraph 2.3.7). ............................................................................. 29
Table 2.6. Processing of All Classification Waiver Requests (Except Enlisted On-the-Job-
Training, Time-in-Training for AFSC Upgrade) (Note 1). ...................................... 31
Table 2.7. Processing of On-the-Job-Training, Time-in-Training Waiver Requests for AFSC
Upgrade for Enlisted RegAF, ANG, and AFR Airmen (See Note). ........................ 33
Table 2.8. Criteria for Awarding Officer Rated AFSCs (see Note 1). ...................................... 48
Table 2.9. Criteria for Awarding Officer AFSCs, SDIs and RIs Other Than Rated AFSCs
(See Note 1). ............................................................................................................ 49
Table 2.10. Classifying Students—Officers. .............................................................................. 51
Table 2.11. Criteria for Awarding Enlisted AFSCs, SDIs, RIs or CEM Codes. ......................... 52
Table 2.12. Grade and Skill-Level Authorizations for Use in Establishing Manpower
Positions. .................................................................................................................. 54
Table 2.13. Determining the Control AFSC (CAFSC) for Enlisted Personnel in Training
Status. ....................................................................................................................... 55
Table 2.14. Determining CAFSC as a Result of Assigning or Withdrawing Awarded CEMs,
AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs. ............................................................................................... 56
2.4. Downgrading and Withdrawing AFSC. ................................................................... 57
Table 2.15. Downgrading Enlisted AFSCs for Lack of Recent Performance (see Note). .......... 58
Table 2.16. Downgrading AFSCs as a Result of Demotion. ...................................................... 59
Table 2.17. Processing Downgrade and Withdrawal and/or Disqualification Actions. .............. 69
Chapter 3—DELETED 71
3.1. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 71
3.2. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 71
3.3. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 73
3.4. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 75
3.5. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 76
Table 3.1. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 77
Table 3.2. DELETED. .............................................................................................................. 77
4 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 4—ACTIVE DUTY SERVICE COMMITMENTS AND RESERVE SERVICE
COMMITMENTS 78
4.1. Overview. ................................................................................................................. 78
4.2. Program Processes. .................................................................................................. 80
4.3. ADSC Procedures. ................................................................................................... 82
4.4. ANG Reserve Service Commitments. ..................................................................... 86
4.5. Reserve Service Commitments (RSCs) (General). .................................................. 86
Table 4.1. Line, Chaplain, Judge Advocate General Officer, and All Enlisted RSCs (T-1). ... 90
Table 4.2. Health Profession Officer and Enlisted Education/Training (T-1). ......................... 93
Chapter 5—TECHNICAL TRAINING PROGRAMS REQUIREMENTS 96
5.1. Technical Training Requirements Purpose and Responsibilities. ............................ 96
5.2. HQ Air Force Technical Training Programs............................................................ 103
5.3. HQ Air Force Technical Training Tasking Documents. .......................................... 104
Table 5.1. Program Guidance Letters, Program Requirements Documents Programs and
Users. ....................................................................................................................... 106
5.4. Capacity Assessment and Constraints. .................................................................... 107
5.5. Technical Training Requirements Working Groups. ............................................... 108
Table 5.2. Training Flow Management Working Group Organization. ................................... 108
Table 5.3. Officer Initial Skills Working Group Organization. ................................................ 108
Table 5.4. Mission Readiness Training Program Working Group Organization. ..................... 109
5.6. Program Guidance Letter Changes (Adjustments and Quota Management). .......... 109
5.7. Mission Readiness Training Program. ..................................................................... 110
Table 5.5. Quota Type Breakdown (Mission Readiness Training Program). ........................... 114
5.8. Metrics Submissions. ............................................................................................... 117
Chapter 6—AIRMAN RETRAINING PROGRAM 118
6.1. Officer Crossflow and Reclassification Programs. .................................................. 118
6.2. Enlisted Retraining Program Elements. ................................................................... 124
6.3. Enlisted Retraining Program Processes. .................................................................. 125
6.4. Enlisted Retraining Administrative Actions. ........................................................... 128
Table 6.1. Eligibility for Voluntary and Involuntary Retraining. ............................................. 130
6.5. Enlisted Retraining Programs. ................................................................................. 133
6.6. AFR Retraining Program. ........................................................................................ 135
6.7. ANG Retraining Program. ....................................................................................... 144
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 5
Attachment 1—GLOSSARY OF REFERENCES AND SUPPORTING INFORMATION 150
Attachment 2—OFFICER AND ENLISTED ADSCS AND HEALTH PROFESSIONS
OFFICER ADSCS 170
Attachment 3—SERVICE COMMITMENTS (ANG ONLY) 186
Attachment 4—PREVIOUS AND CURRENT ACTIVE DUTY SERVICE COMMITMENT
REASON CODES WITH CLEAR TEXT TITLES 192
Attachment 5—SERVICE COMMITMENT STATEMENTS OF AGREEMENT 194
Attachment 6—DELETED 195
Attachment 7—DELETED 196
Attachment 8—DELETED 197

6 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 1
OVERVIEW
1.1. Overview. This publication provides one document for all guidance, procedures, programs
and responsibilities pertaining to the military classification system; applying for flying training;
Air Battle Manager (ABM) Training; and astronaut programs; active duty service commitments;
AF technical training management and utilization; officer crossflow; and initial skills training
reclassification program.
1.1.1. Chapter 2 pertains to the military classification system outlining overall
responsibilities which identify duties and tasks for every position for accomplishing the Air
Force mission. The classification system also provides concise award, upgrade and retention
criteria for career progression.
1.1.2. DELETED.
1.1.3. Chapter 4 pertains to active duty service commitments (ADSCs) and reserve service
commitments (RSCs) which assures the Air Force and the taxpayers receive an appropriate
return on their investment of money and/or time in training, education, and bonuses. It outlines
those incurring events that require commitments to assure open communication to Air Force
members regarding obligated service.
1.1.4. Chapter 5 pertains to technical training program requirements which defines the roles,
responsibilities, programs, and procedures necessary for Air Force and applicable non-Air
Force technical training management across the planning, programming, budgeting and
execution cycle to ensure maximum utilization in support of the Air Force mission.
1.1.5. Chapter 6 pertains to the Airman retraining program outlining a process that addresses
career-field imbalances across the Air Force. The program is designed to bring imbalanced
career-fields back into authorized funded end-strength.
1.2. General Guidance.
1.2.1. The term ‘components’ used throughout this publication applies to all parts of the total
Air Force, unless the text of this publication specifies that the provisions being discussed apply
only to one or two of the RegAF, ANG, or AFR.
1.2.2. All references to “days” refer to calendar days unless otherwise stated.
1.3. Roles and Responsibilities.
1.3.1. Vice Chief of Staff (AF/CV) will approve and disapprove medical exceptions to policy.
(T-1).
1.3.2. Secretary of the Air Force Manpower and Reserve Affairs (SAF/MR) will establish
ADSC policies and is the waiver authority for ADSC disputes that are not adjudicated at AFPC
(see paragraph 4.3.9). (T-1).
1.3.3. Secretary of the Air Force Personnel Council (SAFPC or SAF/MRBP) is the authority
for ADSC waiver requests that are submitted in conjunction with a separation or retirement
request (see paragraph 4.3.7.). Waiver requests are submitted as a part of the member’s
request to separate or retire through the appropriate virtual application as outlined in AFI 36-

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 7
3206, Administrative Discharge Procedures for Commissioned Officers, or AFI 36-3208,
Administrative Separation of Airmen.
1.3.4. The Deputy Chief of Staff, Personnel, Manpower and Services (AF/A1) will:
1.3.4.1. Review and approve Air Force classification policy for clarity, propriety, and
accuracy. (T-1).
1.3.4.2. Work with Air Staff agencies to determine if new or revised classification policies
are needed to effectively and efficiently manage manpower requirements and human
resources. (T-1).
1.3.4.3. DELETED.
1.3.4.4. DELETED.
1.3.4.5. DELETED.
1.3.5. AFRC/CC will:
1.3.5.1. DELETED.
1.3.5.2. Approve and disapprove age and Total Federal Commissioned Service (TFCS)
exception to policy (ETP) for all AFR applicants. (T-1).
1.3.5.3. Approve all ineligibility factor ETPs for all AFR applicants. (T-1).
1.3.6. Director, Air National Guard (NGB/CF) will:
1.3.6.1. DELETED.
1.3.6.2. Approve and disapprove age and TFCS ETP for all ANG applicants. (T-1).
1.3.6.3. Approve all ineligibility factor ETPs for all ANG applicants. (T-1).
1.3.7. Director, Military Force Management Policy (AF/A1P) updates this manual and staffs
ADSC disputes to SAF/MR for consideration. (T-1).
1.3.8. Directorate of Manpower, Organization and Resources (AF/A1M) will provide Human
Resources Data Analytic and Decision Support Division (AF/A1XD) with the count of funded
authorizations by Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC) which are used to model the desired
number of RegAF technical training graduates each FY. (T-1).
1.3.9. AFPC Commander (AFPC/CC) will:
1.3.9.1. Serve as final authority for action in coordination with AF/A1P and AF, Deputy
Chief of Staff Strategic Deterrence and Nuclear Integration (AF/A10) for Missileer
Crossflow Program. (T-1).
1.3.9.2. Serve as the authority to overrule the Nonrated Line Crossflow Panel or Missileer
Crossflow Program results and disapprove a recommendation when appropriate. (T-1).
1.3.9.3. Serve as the final reclassification and separation authority for line officer initial
skills training eliminees. (T-1).
8 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 2
CLASSIFYING MILITARY PERSONNEL (OFFICER AND ENLISTED)
2.1. Classification Overview, Concept, Responsibilities, and Structure.
2.1.1. Overview. The military personnel classification system identifies duties and tasks for
every position needed to accomplish the Air Force mission. The system is designed to identify
qualifications and abilities necessary to accomplish these duties and tasks, as well as provide
clear and visible career progression patterns. It links duties and tasks into cohesive job clusters
used to match personnel requirements with personal aptitudes, attributes, and qualifications.
The classification system also provides concise award, upgrade, and retention criteria for
career progression.
2.1.2. Classification Concepts and Parameters.
2.1.2.1. Functional Grouping Concept. The classification system groups related work
requirements (positions) into Air Force Specialties (AFS) (Tables 2.1 and 2.2 break down
enlisted and officer AFSC structures). Positions are grouped on similarity of functions and
requirements for knowledge, education, training, experience, ability, and other common
criteria. Air Force Specialties are further combined into broader and more general
functional categories called career fields. This functional grouping provides a
classification and utilization system that:
2.1.2.1.1. Remains stable regardless of organizational structure changes.
2.1.2.1.2. Provides a framework to procure, train, and develop specialized and broadly
experienced personnel.
2.1.2.1.3. Easily adapts and responds to changes in Air Force skill requirements.
2.1.2.1.4. Supports utilization and other personnel program needs.
2.1.2.2. Practical Specialization Concept. AFS qualifications are listed in each specialty
description within the Air Force Officer Classification Directory (AFOCD) and the Air
Force Enlisted Classification Directory (AFECD), which may be accessed through the Air
Force Portal. Qualifications include knowledge, education, training, experience, and other
factors. These are defined as mandatory or desirable for each skill (enlisted) or
qualification (officer) level. While no one person is likely to perform all functions of an
AFS at any one time, Airmen can be developed to perform all duties and responsibilities
of the various duty positions within an AFS at different times throughout a career. When
Airmen meet all of the mandatory qualifications of the specialty and have shown skill
and/or qualification in all tasks of the positions to which assigned, they are considered
qualified for award of the AFSC.
2.1.2.3. The following are the basic parameters of the classification structure:
2.1.2.3.1. Identify requirements (typically associated with unit manpower document
authorizations) and Airmen qualified to fill those requirements.
2.1.2.3.2. Design AFSCs which make sense in the objective Air Force structure.
2.1.2.3.3. Use simple, clear, logical groupings.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 9
2.1.2.3.4. Provide visible AFSC qualification and/or skill levels for officer and enlisted
personnel.
2.1.2.3.5. Maintain the ability to identify career fields, specialties, subspecialties, and
skill and/or qualification levels.
2.1.2.3.6. Maintain the ability to identify special job requirements and positions,
Special Duty Identifiers (SDIs), Reporting Identifiers (RIs), and Special Experience
Identifiers (SEIs), as defined in paragraphs 2.3.4, 2.3.5, and 2.3.13.
2.1.2.3.7. Eliminate redundant identifiers. Do not duplicate other Military Personnel
Data System (MilPDS) identifiers.
2.1.2.3.8. Group AFSCs functionally.
2.1.2.3.9. Maintain a balance of specialist versus generalist specialties to allow
maximum efficiency and equity in assignment and promotion opportunities.
2.1.2.3.10. Do not overpopulate small population specialties that adversely limit the
ability to effectively manage the resource.
2.1.2.3.11. Specialty description (contained in the respective AFOCD and AFECD)
for each occupational grouping will contain general occupational information (what
most of the people do most of the time) and quantify the minimum requirements
necessary to reasonably predict success in and retain the specialty.
2.1.2.3.12. Specialty description is broad in scope to adequately portray all enlisted
skill/officer qualification levels represented by the description and will not normally
contain a grade requirement.
2.1.2.3.13. Grade requirements on unit manpower document authorizations are
determined by manpower, in conjunction with the Career Field Manager (CFM) of the
respective component. However, in certain instances minimum grade and/or grade
range requirements are authorized for AFSCs, SDIs, and RIs as identified in the
respective AFOCD and AFECD.
2.1.2.3.14. Specialty description format is standardized to maintain simplicity, clarity,
and ease of publishing.
2.1.2.3.15. Specialty descriptions are generally no more than two pages in length (may
exceed this length to include descriptions, when needed).
2.1.2.3.16. Changes to the classification sytem are staffed using the classification
system with all impacted agencies using the execution guidance within the CFM Guide
available on the My Personnel Services (myPers) website.

10 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.1. Enlisted AFSC Explained.
L
I
N
E
A
B
Character
Identifies (see Note 1)
1
first position
(numeric)
Career group.
1 - Operations 4 - Medical or Dental 7 - Special Investigation
2 - Logistics 5 - Legal or Chaplain 8 - Special Duty Identifier
3 - Support 6 - Acquisition or Finance 9 - Reporting Identifier
2
second combined
with first character
(alpha)
Career field.
Example: 2T - Logistics, Transportation and Vehicle Management
3
third combined with
first and second
character (numeric)
Career field subdivision.
Example: 2T3 - Logistics, Transportation and Vehicle Management, Vehicle
Management
4
fourth (numeric)
Skill level of AFSC.
1 - Helper 7 - Craftsman
3 - Apprentice 9 - Superintendent
5 - Journeyman 0 - Chief Enlisted Manager
5
fifth combined with
other four characters
(numeric) (see Note
2)
Specific AFSC.
Example: 2T351 - Logistics, Transportation and Vehicle Management,
Vehicle Management Journeyman, Mission Generation Vehicular Equipment
Maintenance
6
alpha prefix
An ability, skill, special qualification, or system designator not restricted to a
single AFSC.
Example: T - Formal Training Instructor
7
alpha suffix (shred-
out) (see Note 3)
Positions associated with particular equipment or functions within a single
specialty. Example: 2T351A - Logistics, Transportation and Vehicle
Management, Vehicle Management Journeyman, Mission Generation
Vehicular Equipment, Firefighting and Refueling Vehicle & Equipment
Maintenance
Notes:
1. Use an "X" in any character position of an AFSC when addressing all authorized characters in that
position of the AFSC. For example, X2TXXXX denotes all 2T AFSCs, to include all career field
subdivisions, prefixes, skill levels, and suffixes.
2. When two or more career ladders are combined at the 7- or 9-skill level, they are called capper AFSCs.
And, when combined, the number in the fifth position will almost always be “0.” Example: 2T371and
2T377 merge into a common 9-level 2T390. Depending on prior AFSC structure changes, it may have to
be a different number (other than 0 at the 9-skill level), as necessary.
3. Not applicable at the 9-level skill or Chief Enlisted Manager level.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 11
Table 2.2. Officer AFSC Explained.
L
I
N
E
A
B
Character
Identifies (see Note 1)
1
first (numeric)
Career group.
1 - Operations 4 - Medical or Dental 7 - Special Investigations
2 - Logistics 5 - Legal or Chaplain 8 - Special Duty Identifier
3 - Support 6 - Acquisition or Finance 9 - Reporting Identifier
2
second combined
with first character
(numeric)
Utilization field.
Example: 11 - Operations, Pilot
3
third combined
with first and
second character
(alpha)
Functional area.
Example: 11B - Operations, Pilot, Bomber Pilot
4
fourth (numeric)
Qualification level.
1 - Entry (any AFSC)
2 - Intermediate (only for AFSCs so designated in the AFOCD)
3 - Qualified (any AFSC)
4 - Staff (See Note 2): Designation of “staff level” relates only to the level of
functional responsibility and is restricted to positions above wing level. It does
not denote additional specialty qualifications.
Examples: 11B3 - Operations, Pilot, Bomber Pilot, qualified.
11B4 - Operations, Pilot, Bomber Pilot, qualified and serving in a staff
position above wing level
0- Qualified commander (when used in conjunction with “C” in 3rd position),
or
- Senior Leader or Leader (when other than a “C” in the 3rd position for 62S0,
63G0 or 63S0)
5
alpha prefix
An ability, skill, special qualification, or system designator not restricted to a
single AFSC.
Example: A – Operational Warfare Instructor
6
alpha suffix (shred-
out)
Positions associated with particular equipment or functions within a single
specialty.
Example: 11B3A - Operations, Pilot, Bomber Pilot, qualified, B-1

12 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Notes:
1. Use an "X" in any character position of an AFSC when addressing all authorized characters in that
position of the AFSC. For example, X12XXX denotes all “12” AFSCs, to include all utilization fields,
prefixes, qualification levels, and suffixes.
2. In addition, not all positions above wing level qualify for the staff AFSC. For positions above wing
level, Manpower uses the staff AFSC requirements for determining applicability (vice the 3-qualification
level): Staff AFSC identifies an officer position above wing level specifically on the duty requirements of
the role performed, not the fact that the authorization is on a staff above wing level. Use staff AFSCs
(XXX4) to identify planning and policy-making positions above wing level. It requires the same skills as
those for the qualified AFSC (XXX3), but applied to developing broad policies, plans, and procedures.
Management responsibility increases without a corresponding increase in knowledge of the technical
aspects of the function. Qualified (XXX3) officers filling or who have filled such positions are awarded
the staff AFSC.
2.1.3. Program Processes.
2.1.3.1. Director, Military Force Management Policy (AF/A1P) will:
2.1.3.1.1. Establish procedures for development and publication of program
requirements for technical training programs.
2.1.3.1.2. Conduct an annual technical training data call that provides guidance and
suspense dates for submitting out-year Air Force-directed and MAJCOM mission
technical training requirements for Total Force, sister services, Department of Defense
(DoD), and other US government agencies for the following technical training
programs: Total Force enlisted initial skills, non-rated line officer initial skills, mission
readiness training (e.g., advanced, supplemental, and resident craftsman training),
trained dog requirements, field training detachment, mobile training teams, non-
resident (type-6 distance learning), language training, international military training,
and basic military training. Requires submission of program requirement requests
through proper channels.
2.1.3.1.3. Work with AF/A1XD and Air Force CFMs to validate each individual career
field’s health, challenges, and emerging missions. Balance individual career field
needs against overall force management goals and objectives.
2.1.3.1.4. Provide guidance to Air Education and Training Command (AETC) to
satisfy program and mission requirements and advocates for training resources via the
Air Force corporate structure.
2.1.3.1.5. For initial skills programs, build preliminary Total Force program guidance
letters and program requirement documents based on AF/A1XD career field
sustainment analysis, Air Force CFM input, and mission needs. Compiles the
requirements into draft program guidance letters and program requirement documents
and submits to AETC for assessment.
2.1.3.1.6. For mission readiness training, trained dog requirements, field training
detachment and non-resident programs, develop the program requirements documents
and program guidance letters and send to the AETC Force Development Resources
Branch (AETC/A3LR), AETC Technical Training Requirements Branch
(AETC/A3LZ), AETC Financial Management Analysis Division (AETC/FMA),
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 13
Second Air Force (2 AF), AF directed users, MAJCOMs, Air Force Personnel Center’s
Workforce Development Section (AFPC/DP2LWD), training requester quota identifier
managers, forward operating agencies, direct reporting units, and non-Air Force users.
2.1.3.1.7. Co-chair, with AETC/A3LZ, the annual Officer Initial Skills Working
Group, Training Flow Management Working Group and Mission Readiness Training
Program Working Group. See paragraph 5.5 for more details.
2.1.3.1.8. Finalizes the program guidance letters and program requirements documents
for initial skills programs following the working groups identified in paragraph 5.5.
This involves balancing resources, training prioritization, training capacity, and
accession limits.
2.1.3.1.9. Forward all signed program guidance letters and program requirements
documents to AETC.
2.1.3.1.10. Approve changes to the program guidance letters and program
requirements documents through requirements adjustments.
2.1.3.1.11. Approve officer and enlisted initial skills unused quotas for redistribution
and updates program guidance letters based on approvals. Develops the accessions
program guidance letter that identifies Total Force accession levels for the current fiscal
year (FY) and across the Future Years Defense Program.
2.1.3.1.12. Develop and identify the number of enlisted non-prior service (NPS) and
prior service (PS) recruits the Air Force will access for a given FY on the accessions
program guidance letters.
2.1.3.1.13. Develop and identify the number of line and non-line officer accessions for
a given FY on the accessions program guidance letters.
2.1.3.1.14. Appoint members to the annual Training Flow Management Working
Group.
2.1.3.1.15. Work with AETC, AFPC and RegAF CFMs to assess impacts of proposed
and approved additions, deletions, mergers, or changes to AFSCs in the
AFECD/AFOCD. Reflects approved changes to AFSCs in the appropriate program
guidance letters and program requirements documents.
2.1.3.1.16. Establish officer crossflow and initial skills training elimination
reclassification guidance and policy, monitor for necessary adjustments, and update as
required.
2.1.3.1.17. Determine officer crossflow requirements by AFSC and year group based
on AFSCs with inventory imbalances and provide that information to AFPC for use in
crossflow and initial skills training reclassification programs.
2.1.3.1.18. Consider impact of other force management initiatives (e.g., force shaping
and reduction-in-force boards) and prior enlisted populations within each career field
when determining crossflow targets. AFSCs with specific or unique qualification
requirements (e.g., technical education) should be filled first before crossflowing
officers with specific or unique qualifications to other career fields.
14 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.1.3.1.19. Approve or disapprove waiver of crossflow eligibility criteria and
adjudicate crossflow in and out targets with CFMs and other stakeholders.
2.1.3.1.20. Produce monthly officer sustainment matrices showing manning overages
and gaps by career field and year group for AFPC to use in determining out-of-cycle
crossflow requests.
2.1.3.2. AFPC Military Classification (AFPC/DP3DW – Business Process Owner and
AFPC/DP2SSM – Military Classification Development), will:
2.1.3.2.1. (AFPC/DP3DW) Establish and oversee processes for classifying personnel
including developing, reviewing, interpreting, and changing classification procedures
for classifying military personnel based on specialty data, special studies, analyses, and
CFM input. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2. (AFPC/DP3DW) Manage the Air Force Military Classification System, to
include actions establishing, deleting, changing, or revising necessary identifiers and
specialty descriptions by means of the AFOCD, AFECD, and Job Code and SEI tables
in MilPDS, in order to manage Air Force manpower requirements and human
resources. (T-1). Serve as approval authority for all military classification changes.
(T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.1. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Partner with Air Force CFMs (and other
stakeholders) proposing changes to the Air Force Military Classification System.
(T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.2. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Develop Air Force specialties, titles, and codes to
identify required military skills associated with specialty restructuring, new
systems development, acquisition, operation, etc., upon request of the Air Force
CFM and staff agencies. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.3. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Coordinate extensively with functional,
manpower, and personnel agencies on all classification changes due to the impact
these actions have on a variety of programs. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.4. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Staff and coordinate AFS restructuring actions
with affected agencies, Air Force CFMs, Air Force Recruiting Service, AETC,
AF/A1PP, AF/A1PPR, Accessions and Training Division (AF/A1PT), AF/A1XD,
Air Force Manpower Analysis Agency, NGB/A1D and AF/REP. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.5. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Coordinate with computer systems managers on
classification matters impacting MilPDS Job Code and SEI/Experience Set tables
as well as the Manpower Programming and Execution System. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.5.1. Develop, coordinate, and process system change requests to
MilPDS with associated worksheets and tables to facilitate changes to the
officer and enlisted classification structures. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.5.2. Design, develop, implement, and publish the Air Force Officer
Classification System, Air Force Enlisted Classification System, and Change
Summary and Conversion Instruction Guides to be effective each 30 April and
3l October. (T-1).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 15
2.1.3.2.2.6. (AFPC/DP3DW) Review, approve, and submit for publication the
semi-annual AFOCD, AFECD, and Change Summary and Conversion Instruction
Guides to be effective each 30 April and 31 October. Prepare and submit Systems
Change Requests using the documentation provided above and enter into the
Requirements Management System. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.2.7. (AFPC/DP3DW and DP2SSM) Monitor Air Force classification
procedures and the AFSC conversions affecting classification of the total military
force. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.3. (AFPC/DP3DW) Develop and coordinate changes to Classifying Military
Personnel (Officer and Enlisted) program processes. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.4. (AFPC/DP3DW and DP2SSM) Conduct special studies and analyses to
validate and integrate occupational data. (T-1). Use this data to identify required
military skills and revise, develop, or delete Air Force occupational data impacting Air
Force specialties, titles, and codes accordingly. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.5. Provide extensive guidance and interpretation to MAJCOMs, Air Staff
agencies, units, and individuals regarding classification policy (AFPC/DP3DW) and
procedures (AFPC/DP2SSM). (T-1).
2.1.3.2.6. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Review, research, process, and approve or disapprove
requests for waiver (as applicable, see Tables 2.4 and 2.5) of specialty description
qualifications (as found in the AFOCD and AFECD), covering all aspects of
classification instructions, e.g., eyesight, aptitude, input AFSC. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.7. Waiver requests for Classifying Military Personnel (Officer and Enlisted)
guidance requirements. (T-1):
2.1.3.2.7.1. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Review, research, and prepare proposed
recommendations for waiver of Classifying Military Personnel (Officer and
Enlisted) guidance requirements. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.7.2. (AFPC/DP3DW) Review, revise, and process requests for waiver of
Classifying Military Personnel (Officer and Enlisted) guidance requirements to
AF/A1PT for approval or disapproval. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.8. High-level inquiries (e.g., IG, Chief of Staff, Secretary of the Air Force,
Secretary of Defense, Congressional, and Presidential inquiries) concerning
classification guidance, actions and procedures. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.8.1. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Review, research, and develop proposed responses
and supporting documentation. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.8.2. (AFPC/DP3DW) Review, revise, and coordinate proposed response
with AFPC releasing authority. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.9. Applications for Board for Correction of Military Records concerning
classification guidance, actions, and procedures. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.9.1. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Review, research, and develop proposed responses
and supporting documentation for Board Advisories and Administrative Fix
actions. (T-1).
16 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.1.3.2.9.2. (AFPC/DP3DW) Review, revise, and finalize Board Advisories and
Administrative Fix documentation. Coordinate and/or forward, as required, and
upload to the Board for Correction of Military Records application processing data
base. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.10. Classification procedures for downgrading or withdrawing identifiers from
individual Airmen. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.10.1. (AFPC/DP3DW) Establish, publish, and monitor classification
procedures for downgrading or withdrawing identifiers from individual Airmen.
(T-1).
2.1.3.2.10.2. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Employ classification procedures for
downgrading or withdrawing (not disqualification) identifiers from individual
Airmen. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.11. (AFPC/DP3DW) Provide policy interpretation for initial classification of
former officers as enlisted personnel. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.12. (AFPC/DP3DW) Develop standard operating procedures to manage
establishing, deleting, changing, or revising classification tools. (T-1).
(AFPC/DP2SSM) Employ standard operating procedures to manage establishing,
deleting, changing, or revising classification tools. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.13. (AFPC/DP3DW) Attend functionally oriented workshops, conferences,
meetings, etc. to provide expertise on classification matters and advise on known or
potential impacts resulting from specialty restructuring actions. (T-1).
2.1.3.2.14. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Review, coordinate, and approve or disapprove
requests for RegAF Officer and Enlisted Airman AFSC withdrawal (disqualification).
(T-2). Field Operation Agency AFPC only; AF/REP* or NGB/A1D* for Reserve
Component personnel, as appropriate. Update awarded AFSCs, Special Duty and RIs
on disqualified Airmen. Respond to requests to change disqualified Airmen RIs, as
needed.
2.1.3.2.15. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Approve or disapprove RegAF SEI withdrawals and/or
removals. (T-2). (AFPC, AF/REP* or NGB/A1D* for Reserve Component personnel,
as appropriate).
2.1.3.2.16. (AFPC/DP2SSM) Ensure adherence to minimum specialty requirements
according to the AFOCD and AFECD. (T-1).
2.1.3.3. The Surgeon General (AF/SG) will recommend to AF/A1 medical exceptions to
classification policies and procedures for Officer and Enlisted personnel.
2.1.3.4. AFPC, AF/REP, or NGB/A1D Commanders and Supervisors will assign
personnel to authorized positions consistent with requirements, Airman’s grade, and skill
and/or qualification level and will initiate or review and evaluate job proficiency and skill
qualifications of each Airman. (T-2). Limit the use of enlisted Airmen outside their
Control AFSC. Comply with criteria outlined in paragraph 2.3.34 when using enlisted
Airmen outside their control AFSC. Use the following source documents to award,
upgrade, downgrade, and withdraw AFSCs, SDIs, RIs, and SEIs:
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 17
2.1.3.4.1. AF Form 2096, Classification/On-the-Job Training Action, or
2.1.3.4.2. Case Management System (CMS)- or AFPC-generated action, or
2.1.3.4.3. MilPDS-generated Report on Individual Person (RIP).
2.1.3.5. The Force Support Squadron (FSS) and AFPC, AF/REP, or NGB/A1D
commanders will ensure accurate and timely reporting of qualifications of serviced
personnel. (T-2).
2.1.3.6. AFPC, AF/REP, or NGB/A1D manpower personnel will identify and code
manpower authorizations using the military personnel classification system outlined in this
manual, AFOCD/AFECD and manpower directives. (T-2).
2.1.3.7. The Airman shall gain and maintain specialty qualifications for awarded AFSC(s).
(T-1). Since individual effort is directly related to career progression, it is incumbent on
the Airman to develop professionally and keep abreast of specialty knowledge and
proficiency standards. Several programs blend specialty training with academic pursuits
to enable or enhance career progression. These include career development courses,
advanced specialty training, supplemental training, on-the-job training, and accredited
education.
2.1.3.8. The Air Force CFM, MAJCOM functional manager, and NGB/AFR CFM will
provide technical assistance in developing career field structures and classification
identifiers. (T-2). RegAF CFMs develop (in coordination with MAJCOM functional
managers and NGB/AFR CFMs) specialty descriptions, specialty prerequisites and
qualifications. RegAF CFMs (NGB/AFR CFMs, as appropriate) provide waiver
recommendations for mandatory AFSC requirements to waiver authority as stated in
Tables 2.4 and 2.5. NGB/AFR CFMs have waiver authority commensurate with the
RegAF CFMs as stated in Table 2.5. RegAF CFMs also:
2.1.3.8.1. Keep specialty descriptions current,
2.1.3.8.2. Initiate or coordinate on new and proposed classification changes,
2.1.3.8.3. Resolve all non-concurrences before submitting new classification changes
to AFPC/DP2SSM for formal coordination and implementation consideration.
2.2. Initial Classification.
2.2.1. Classifying Newly Accessed Commissioned Line Officers. The various sources of
commission, e.g., United States Air Force Academy (USAFA), Officer Training School (OTS),
Air Force Reserve Officer Training Corps, (AFROTC) and Total Force officer training will
select and designate candidates for flying using the following RIs: 92T0 (Pilot trainee); 92T1
(Navigator or CSO trainee); 92T2 (ABM trainee); and 92T3 (RPA Pilot trainee). (T-2). When
these RegAF individuals complete training, the FSS will award the appropriate entry-level
AFSC. (T-2). All other newly commissioned RegAF officers will be classified by
AFPC/DP2LT, Military Accession Branch. (T-2). AFR and ANG FSS classify newly
commissioned officers at their permanent duty stations (PDS). (T-2).
2.2.1.1. AFPC/DP2LT classifies USAFA and AFROTC cadets utilizing the OTS
classification process. The model optimizes USAF and AFROTC cadet classification
based on AF requirements, cadet qualifications, and cadet desires. OTS cadets are
18 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
classified using the same criteria, but not as a component of the model. Air Force
requirements have the highest priority.
2.2.1.2. Following initial classification, changes in AFSC may take place due to medical
disqualification from the AFSC, individual inability to qualify for associated Personnel
Reliability Program requirements, or other ineligibility reasons. AFROTC or USAFA will
notify the need to change AFSCs prior to entering active duty based on these categories
will be provided to AFPC/DP2LT for reclassification consideration. (T-3).
2.2.1.3. Requests for reclassification prior to attending initial skills training may be
addressed to AFPC/DP2LT for initial review. AF/A1P is the approval and disapproval
authority.
2.2.1.4. Respective accession authorities classify newly commissioned Non-Line Officers
and Line of the Air Force Judge Advocates as referenced in paragraphs 2.3.19, 2.3.20 and
2.3.21.
2.2.1.5. Air Reserve Component Line Officers returned to extended active duty (EAD) in
accordance with AFI 36-2008, Voluntary Extended Active Duty (EAD) for Air Reserve
Commissioned Officers. Reclassification is not required upon accession. MilPDS will
reflect the AFSC contained on the EAD orders issued by AFPC/DP2LT, Military
Accessions Branch.
2.2.1.6. Newly Commissioned Line Officers. The components (i.e., AFR, ANG, RegAF)
will select and designate candidates for flying using the following reporting identifiers:
92T0 (Pilot trainee); 92T1 (Navigator or CSO trainee); 92T2 (ABM trainee); and, 92T3
(RPA Pilot trainee). (T-2). When RegAF officers complete training, the Military Personnel
Section (MPS) will award the appropriate entry-level AFSC. (T-2). All other newly
commissioned RegAF officers will be classified by AFPC/DP2LT, Military Accessions
Branch. The Air Reserve Personnel Center (ARPC) Accessions Branch classifies newly
commissioned reserve officers with the exception of ANG officers and those projected to
be RegAF officers. The servicing force support unit classifies newly commissioned ANG
officers at their PDS.
2.2.1.7. Determining Officer Core ID (ANG and United States Air Force Reserve
(USAFR) only). ARPC is responsible for managing and periodically auditing Core IDs for
lieutenant colonels and below; except for The Judge Advocate General’s Corps officers,
who are managed by Headquarters (HQ) USAF/JAX.
2.2.1.8. The officer Core ID is initially based on the AFSC into which the member is
classified at the time of accession, approved for retraining, or approved for Competitive
Category Transfer in accordance with AFMAN 36-2032, Military Recruiting and
Accessions. For officers accessed to the Ready Reserve under an inter-service program,
the Core ID will be determined utilizing the Defense Manpower Data Center Occupational
Database (ODB) unless approved for retraining in conjunction with accession to the
USAFR.
2.2.1.9. Once a Core ID is established, it cannot be changed unless the officer formally
applies and is approved to retrain, is designated for involuntary cross flow or is approved
to transfer to another competitive category in accordance with AFMAN 36-2032. (T-2).
The new Core ID will be updated by ARPC for AFR officers and the servicing force
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 19
support unit for ANG officers. (T-2). The servicing force support unit (for both AFR and
ANG) will make corrections to the officer’s Primary AFSC or Secondary AFSC as
determined by this manual. (T-2).
2.2.2. Classifying NPS Enlistees. 2 AF/TTOC Detachment (Det) 1 classifies NPS RegAF
enlistees prior to their departure from Basic Military Training. 2 AF/TTOC Det 1 also
reclassifies those eliminated from initial skills training who will be retained in the Air Force.
RegAF Career Enlisted Aviators (1AXXX and 1UXXX) who have completed their AFSC-
awarding training but failing to complete their NPS training pipeline (to include weapon
system training) and are recommended for reclassification by their training commander may
be referred to 2 AF/TTOC Det 1 for consideration following AFSC disqualification in
accordance with paragraph 2.4. Disqualification is not required since the Airmen will have
completed their 3-skill level-awarding course prior to attending weapon system training but
not their NPS pipeline training. AFR and ANG FSSs will classify all Air Reserve Component
(ARC) NPS enlistees at their PDSs and, if needed, reclassify those eliminated from initial skills
training. (T-2). AFR and ANG FSSs should process waivers of mandatory entry requirements
according to paragraph 2.3.7 and use Table 2.5 to determine waiver authority and processing
instructions.
2.2.2.1. Guaranteed Training Enlistment Program. Prior to reserving a Guaranteed
Training Enlistment Program allocation, Recruiting Service will ensure applicant meets all
mandatory qualifications for entry into the AFSC. (T-2). Process waivers according to
paragraph 2.3.7 and use Table 2.5 to determine waiver authority and processing
instructions.
2.2.2.2. Aptitude Index. Applicants are guaranteed training in one of four aptitude areas:
Administrative, Electronic, General, or Mechanical. They will be assigned a specific job
during basic training. AFSC classification of enlistees with an Aptitude Index is
determined by 2 AF/TTOC Det 1, using MilPDS Technical Training Management System-
JM to validate that individuals meet mandatory qualifications for entry. (T-1).
Classification is based on individual’s initial enlistment contract, needs of the Air Force,
and personal preference. An Aptitude Index enlistee may request release from their
enlistment contract to volunteer for announced priority requirements. 2 AF/TTOC Det 1
is the approval authority for these requests. Normally, an individual may select as many
as 10 AFSC preferences from available openings, provided they are qualified for each.
Additional aptitude assessments may be directed by the AFSC functional community, as
necessary.
2.2.2.3. 2 AF/TTOC Det 1 screens applicants who enlist for training and initial assignment
into specific AFSCs which ensure enlistees meet qualifications. Guaranteed Training
Enlistment Program enlistees will be classified into their Guaranteed Training Enlistment
Program AFSC unless they are disqualified from their guaranteed job. (T-1). Guaranteed
Training Enlistment Program enlistees may also request a release to volunteer for
announced requirements. 2 AF/TTOC Det 1 is the approval authority for these requests
for RegAF Airmen.
2.2.2.4. Non-United States Citizens (excluding United States Nationals). Non-United
States citizens are restricted from classification in any specialty identified in the AFECD
20 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
(Attachment 4, Additional Mandatory Requirements for AFSC Entry) as not open to Non-
United States citizens.
2.2.2.5. Dis-enrolled Cadets. The USAFA or HQ AFROTC, in conjunction with HQ Air
Education and Training Command (AETC), Student Resources Divisions, and
AFPC/DP2LT, classify dis-enrolled PS and NPS cadets (see DD Form 785, Record of
Disenrollment from Officer Candidate-Type Training). Consider the following in the order
presented:
2.2.2.5.1. College graduates. If Air Force requirements permit, college graduates are
classified consistently with their academic background.
2.2.2.5.2. Needs of the Air Force.
2.2.2.5.3. Personal qualifications such as education, job experience, vocations or
hobbies, physical condition, and eligibility for security clearance.
2.2.2.5.4. Individual Preference. Normally, an individual may select as many as eight
AFSC preferences, provided the individual is qualified for each in accordance with the
AFECD.
2.2.3. Classifying PS Enlistees. HQ United States Air Force Recruiting Service and
AFPC/DP2LT jointly classify PS RegAF enlisted Airmen. They determine if the individual
remains qualified for the AFSC possessed when separated using the specialty description in
the AFECD. Minimum aptitude requirements do not apply for previously held AFSCs. ANG
and AFR units will classify all PS enlistees and evaluate the member’s prior AFSCs, skills,
and experience for waiver to NGB/AFR CFM for re-award of AFSC. (T-2).
2.2.3.1. HQ United States Air Force Recruiting Service and AFPC/DP2LT award former
enlisted personnel the AFSC possessed at the time of separation, unless downgrade or
withdrawal procedures in paragraph 2.4.1 apply, provided the Airman remains qualified
for the AFSC. The Control AFSC is the AFSC in which the Airman enlisted. Award
AFSCs at the 3-skill level to enlistees from other Services that, upon separation, held
specialties convertible to Air Force skills (AFECD, Attachment 6, Convertible Skills List).
Air Force CFMs determine authorized conversions from other Service classification
identifiers to AFSCs for the convertible skills list. Award of the 3-skill level AFSC is
contingent on the other Service classification identifier’s initial skills training meeting or
exceeding the standards of the AFSC initial skills training, as determined by the Air Force
CFM.
2.2.3.2. Former Air Force personnel in technical training are awarded the 1-skill level
AFSC in the specialty in which they are enrolled at technical training as their Control
AFSC. Their former enlisted AFSC is assigned as the Primary AFSC. Award AFSC at
the 3-skill level or lower to personnel who hold a convertible skill earned in another Service
as a Primary AFSC.
2.2.3.3. Reclassifying PS Accession Retrainees Failing to Complete Retraining for Which
Accessed to Active Duty (RegAF). Former RegAF, AFR, ANG Airmen or other Service
members recruited by the Headquarters United States Air Force Recruiting Service to the
RegAF into an AFSC for which initial skills training (3-skill level AFSC-awarding) is not
required will be disqualified by AFPC/DP2SSM when failing to successfully complete
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 21
required training. (T-1). These Airmen will be assessed by Air Force Retraining for
retraining consideration eligibility.
2.2.4. Classifying Former Air Force Officers. For RegAF, AFPC/DP2LT; for ARC Airmen,
the ANG/AFR FSS:
2.2.4.1. Assists in determining the enlisted AFSCs for which the officer qualifies (AFPC
will base AFSC selection on prior experience and training). (T-1).
2.2.4.2. Classifies the former officer before enlistment, when possible.
2.2.4.3. Awards AFSCs and accurately records qualifications at the proper skill level.
After initial classification, normal AFSC skill upgrade requirements apply. Award enlisted
SDI or RI, if applicable.
2.2.4.4. Use the following steps to classify former officers in the following sequence:
2.2.4.4.1. Schedule applicants without Mechanical, Administrative, General, or
Electronics scores to take the Armed Forces Classification Test. Other AFSC-specific
assessment tools identified in the AFECD may be required as well.
2.2.4.4.2. Verify the enlisted AFSCs previously held by the applicant by ensuring they
meet the mandatory specialty qualifications in the AFECD. Apply downgrading and
withdrawing provisions specified in paragraph 2.4. Award previously held AFSCs,
at the proper skill levels, to qualified applicants. Use applicants in their previous
enlisted AFSC when it meets the needs of the Air Force (see paragraphs 2.2.4.4.3 and
2.2.4.5.).
2.2.4.4.3. When they do not qualify for or cannot be used in a previously held AFS,
award an enlisted AFSC closely related to their officer AFS if they meet specialty
qualifications in the AFECD.
2.2.4.4.3.1. Use a technical advisor proficient in the requested AFS to review the
officer’s records (including technical knowledge requirements) and interview the
officer (as needed) to determine the appropriate AFSC and skill level.
2.2.4.4.3.2. Award AFSCs at the 3-skill level unless the technical advisor
recommends, and the RegAF CFM or AFR/ANG CFM approves (for ARC) and
concurs in writing, awarding the 5-skill level. Determine whether or not to award
an AFSC above the 5-skill level after having been assigned in the AFSC at the
permanent duty location. The supervisor, after evaluating the experience and
training, may recommend awarding the 7-skill level with RegAF CFM or
AFR/ANG CFM written concurrence.
2.2.4.4.3.3. If award of 7-level skill level is supported, the supervisor will submit
a written evaluation with documentation showing the qualifications to
AFPC/DP2SSM (RegAF Airmen) or ANG/AFR CFM (ARC Airmen) as
designated in Table 2.5 for review. (T-2). After AFPC/DP2SSM review, the
supervisor will forward to the RegAF CFM or AFR/ANG CFM for
recommendation. (T-2). AFPC/DP2SSM, ANG or AFR approve or disapprove the
request in accordance with authorities in Table 2.5. (T-2).
22 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.2.4.5. If an AFSC is not awarded under paragraphs 2.2.4.4.2 or 2.2.4.4.3, the FSS awards
an AFSC at the 1-skill level after completing the following process:
2.2.4.5.1. RegAF applicants go to the On-line Retraining Advisory, located on the
myPers website, to select up to five AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs, from those listed as shortages.
While Chapter 6, also applies to AFR/ANG Airmen, ARC Airmen must contact an
ARC recruiter specific to the vacancies. (T-3). Note: Chapter 6 procedures apply for
ARC Airmen despite the different application process identified here.
2.2.4.5.1.1. Former officers must meet the mandatory qualifications listed for the
specialties chosen (refer to the AFECD). (T-2). If additional tests are required,
administer them. If waivers are necessary, use Table 2.5 for approval authorities
and Table 2.6 for processing.
2.2.4.5.1.2. For RegAF, former officers may select an AFSC, SDI, or RI; however,
in addition to meeting mandatory specialty qualifications, the former officer must
meet assignment criteria outlined in AFI 36-2110. (T-2).
2.2.4.5.2. Advise AFPC/DP2LT of the RegAF applicant’s choices. AFPC/DP2LT,
using Chapter 6 of this manual and the AFECD, classifies the applicant and notifies
the FSS. While Chapter 6 applies to AFR/ANG Airmen, applicants must contact an
ARC recruiter specific to the vacancies. (T-3).
2.2.4.6. AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs for which they are found qualified will be designated as
awarded AFSCs, SDIs, and RIs. It is important to accurately record AFSC qualification at
the proper skill level because of promotion impacts and the possibility that future Air Force
needs may dictate assignment into an awarded specialty.
2.2.5. Initial Skills Training Eliminees. RegAF Line Officer initial skills training eliminees
on EAD, regardless of whether elimination was self-initiated or not, or whether it occurred
before or after training commences (to include initial training declination), are considered for
reclassification contingent on current AF requirements and in accordance with AFPCI 36-112,
Line Officer Initial Skill Training Reclassification Procedures. AF/A1PT provides
AFPC/DP2LT all AFSCs open to receive eliminees, based on projected requirements and
career field sustainment data. (T-1). The Division Chief, Logistics and Support Airman Career
Management Division at AFPC/DP2L will determine when the contents of an elimination
package requires review by the IST Reclassification Panel. (T-2). When the Division Chief
determines the contents of the elimination package do not require further review, the Division
Chief will select a reclassification AFSC from the list of available AFSCs AF/A1PT provided
to AFPC/DP2LT. (T-2). In cases where an IST Reclassification Panel is appropriate, the
Division Chief, Logistics and Support Airman Career Management Division, will convene a
panel at AFPC and serve as president. The panel will consist of the president (Colonel) and
four additional panel members, in the grade of Lt Col or above, for each panel from the various
functional areas within AFPC. (T-2). ANG officer eliminations are reported to the Initial Skills
Training ANG liaison, and AFR officer eliminations are reported to the officer’s home unit for
disposition.
2.2.5.1. Reclassification and Separation Authority. Commander, AFPC is the
reclassification and separation authority for RegAF Line Officer initial skills training
eliminees. Using a panel process, the commander approves reclassification or separation

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 23
of an officer. When not approved for reclassification, the commander refers the case to the
officer’s command for processing under AFI 36-3206 or AFI 36-3208 or forwards the case
to the Secretary of the Air Force’s Personnel Council for action.
2.2.5.2. Panel Members. The panel reviews the elimination package using the whole
person concept to determine if the officer will be reclassified. Panel members consider an
officer’s potential to develop and contribute in subject career field, as well as degree,
special coursework, commander’s assessment, and the officer’s preferences. (T-2). The
final determination must meet the needs of the Air Force and the officer’s ability to meet
or exceed those needs. (T-2). Panel members must comply with panel procedures. (T-2).
AF/A1PT provides reclassification requirements to AFPC quarterly using career field
sustainment data provided by AF/A1XD. (T-1). Exceptions must be coordinated with
AF/A1PT. (T-1). If qualified, the officer is to be placed in the most critical AFSC first, to
include reclassification into another rated AFSC. Panel members are to use careful
consideration when reviewing and/or scoring each package. Officers not selected for
reclassification via this panel will be separated and recoupment of educational costs is a
real possibility. (T-1).
2.2.6. Strength Aptitude Test. The mandatory strength standards required for entry into all
enlisted career fields are shown in the AFECD, Attachment 4, Additional Mandatory
Requirements for AFSC Entry.
2.2.7. Determining the Initial Control AFSC. The FSS (or detachments for Individual
Reservists (IRs)) use Table 2.3 to determine initial classification, Table 2.13 to determine the
Control AFSC for Airmen in training status, and Table 2.14 to determine the Control AFSC
as a result of assigning or withdrawing awarded AFSCs.
Table 2.3. Initial Determination of Control AFSC.
L
I
N
E
A
B
If the enlistee is
then the Control AFSC will be
1
assigned by 2 AF/TTOC Det 1, Joint Base
San Antonio (JBSA) Lackland, to a formal
technical training school
the 1-skill level AFSC in which being trained
2
a PS enlisted Airman who enlists for duty
assignment (see Note)
the AFSC for which enlisted (see Note)
3
a PS enlisted Airman who enlists for
technical training
the 1-skill level AFSC in which enlisted
Note: Skill level restrictions in paragraph 2.3.33 apply.
2.2.8. Determining Officer Core Identifier (RegAF only). AFPC Officer assignment teams
are responsible for managing and periodically auditing Core Identifiers for lieutenant colonels
and below, except for Line of the Air Force Judge Advocate officers, who are managed by
AF/JAX.
2.2.8.1. The officer Core Identifier is initially based on the AFSC into which the member
is classified at the time of accession into EAD, approved retraining, or approved
Competitive Category Transfer in accordance with AFMAN 36-2032. For officers
24 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
accessed to EAD under a Voluntary Return to Active Duty Program, the Core Identifier
will match the critical AFSC for which they were approved to return to active duty.
2.2.8.2. The Core Identifier for all line officers will be the first three digits of the AFSC
into which an officer was originally accessed into EAD, retrained, or approved for a
category transfer.
2.2.8.3. Once a Core Identifier is established, it cannot be changed unless the officer
formally applies and is approved to retrain, is designated for involuntary cross flow (in
accordance with Chapter 6), or is approved to transfer to another competitive category.
The assignment team accepting the retrainee or Competitive Category Transfer Airman is
responsible for updating the new Core Identifier. The FSS will make corrections to the
officer’s Primary AFSC/Secondary AFSC as determined by this manual. (T-3).
2.3. Classification Actions at Base of Assignment.
2.3.1. Designating a Primary AFSC. The FSS is responsible for designating the Primary
AFSC (AFSC, SDI, or RI) for each officer and enlisted Airman. It will be the AFSC, SDI, or
RI in which the individual is most qualified to perform duty, but not always the identifier in
which the Airman is currently performing duty. Use the following factors, in the order
presented, to determine the Primary AFSC:
2.3.1.1. Skill and Qualification Level. Usually, the AFSC denoting an individual’s highest
level of skill/qualification is designated as the Primary AFSC. Award of higher skill levels
(enlisted) or qualification levels (officer) is contingent on meeting the qualifications
outlined in the appropriate specialty description contained in the AFOCD/AFECD. SDIs
and RIs do not have skill levels and as such are not listed as the Primary AFSC unless the
Airman possesses no awarded AFSCs (1XXX/1XXXX – 7XXX/7XXXX).
2.3.1.2. Experience. Length and currency of experience are to be considered. Length of
experience can include comparable military or civilian experience.
2.3.1.3. Complexity of the specialty. Specialties requiring a comparatively high degree of
knowledge and responsibility are given preference over the less complex, consistent with
experience.
2.3.1.4. Formal education and training. The extent of an individual’s formal education
and training that led to specialty qualification is to be considered.
2.3.1.5. Currency of Equipment. Qualification on state-of-the-art equipment is to be
considered.
2.3.1.6. Desires and interests of the individual (lowest priority).
2.3.2. Designating Other Classification Identifiers.
2.3.2.1. The FSS awards AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs representing additional qualifications, in
the order of best qualification as second, third, and fourth AFSCs (enlisted only). Feeder
AFSCs are retained according to paragraph 2.2.4.3.
2.3.2.2. AFSCs, RIs, or SDIs showing additional qualifications beyond those identified in
paragraph 2.2.4.2 will not be designated. (T-2). There are no provisions to retain more
AFSCs, RIs, or SDIs than are available in the MilPDS (enlisted may have four awarded
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 25
AFSCs [Primary, Second, Third, and Fourth AFSC] and officers three [Primary, Second,
and Third AFSC]).
2.3.2.3. Rated officers will possess a Primary, Second, and Third AFSC denoting best
aircrew qualification. (T-3). "Best aircrew qualification" means aircrew AFSC 11XX,
12XX, 13BX and 18XX with suffix for aircraft type, including "other."
2.3.2.4. Designating SEIs. Designate (award) all SEIs for which qualified.
2.3.3. Designating a Duty AFSC. A Duty AFSC, including prefixes and suffixes, must match
the authorized funded unit manpower document position except for the enlisted skill or officer
qualification level. (T-2). For example, an entry level (31P1) Security Forces officer assigned
to a position with the qualified (31P3) AFSC will have the 31P1 Duty AFSC. Upon meeting
the requirements for and award of the 31P3 AFSC, change the Duty AFSC to 31P3.
2.3.3.1. Officers are not to be assigned duty to an AFSC in which they are not expected to
progress to the qualified level, except for emergency short-term manning requirements.
2.3.3.2. Officer Duty AFSC changes are approved by both the losing and gaining AFPC
assignment managers for RegAF officers. ANG/AFR CFM will approve or disapprove
Authorization Change Requests and ETPs and will submit Manpower Change Requests to
update the Unit Manpower Document (UMD) for ANG/AFR officers. (T-2).
2.3.3.3. Table 2.10 provides Duty AFSC criteria for officer students.
2.3.3.4. If the authorized position does not accurately identify the duties being performed,
the unit commander requests the FSS conduct a position analysis. The FSS corrects the
Duty AFSC retroactively if the analysis results in a change to the UMD.
2.3.3.5. An officer appointed as a section commander may be awarded 38F3Q AFSC only
when the officer so appointed is assigned to a valid 38F3Q UMD authorization and meets
the eligibility requirements for award in the AFOCD. For units that do not qualify for a
full-time section commander UMD authorization, officers may be appointed as the section
commander and remain in their current AFSC without the 38F3Q AFSC. In this case,
officers use the duty title “section commander” only when performing duties requiring
command authority. In all cases, an officer’s performance as section commander requires
evaluation and recording under the provisions of AFI 36-2406, Officer and Enlisted
Evaluation Systems.
2.3.4. Awarding Special Duty Identifiers. SDIs are awarded to denote qualifications the same
way AFSCs are awarded. SDIs are not awarded as the Primary AFSC unless the Airman
possesses no awarded AFSCs (1XXX/1XXXX – 7XXX/7XXXX). The AFOCD and AFECD
specify SDI qualifications for entry and retention. AFPC/DP2L, DP2O, and DP2N (Officer
Assignments) approve award of RegAF officer SDIs according to Table 2.9. Enlisted SDIs
are awarded according to Table 2.11. SDIs are withdrawn according to the appropriate
subparagraph in paragraph 2.4 of this manual. Airmen performing additional duty SDI roles
are not authorized award of the SDIs.
2.3.5. Awarding or Designating Reporting Identifiers (RIs). RIs are established primarily to
identify conditions or jobs where a specific specialty description is not practical, such as
General Officer (90G0), Wing Commander (91W0), Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force
(9C000), student, patient, prisoner, disqualified Airman etc. RIs are awarded (if authorized for
26 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
award) or designated to denote qualification or to report a condition the same way AFSCs are
awarded. FSSs award or designate RIs as defined in the AFOCD/AFECD and according to
Tables 2.9, 2.10, and 2.11, except Wounded Warrior (9WXXX or 92WX) and disqualified
Airmen (9AXXX/96A0/96B0) RIs. AFPC/DPFW (Warrior and Survivor Care Division) is the
only update and/or removal authority for Wounded Warrior RIs and AFPC/DP2SSM for
disqualified Airmen RIs (RegAF). AFR and ANG FSSs are the authority for disqualified ARC
Airmen. RegAF enlisted personnel released (not disqualified) from a SDI without an awarded
AFSC to which the Airman is eligible to return, are to be declared surplus in accordance with
AFI 36-2110. The Assignment Support Section (AFPC/DP2LW) may use these Airmen for
continued utilization consideration.
2.3.6. Reinstating AFSCs, SDIs, RIs, SEIs. AFSCs, SDIs, RIs, and SEIs withdrawn using
appropriate authority in this manual may be reinstated by the Air Force CFM if the original
reason for withdrawal or disqualification no longer exists. Reinstatement requests originate
with the Airman and may be in email or memorandum format, endorsed by the Airman’s
supervisor and commander, and forwarded by email (digitally signed and encrypted) to the
FSS. The FSS ensures each request is fully documented and forwarded to AFPC/DP2SSM by
CMS AFSC disqualification case for RegAF Airmen. The reinstatement request outlines the
circumstances leading to withdrawal and/or disqualification, what has changed since removal,
and justification for reinstatement. Requests without justification and supporting document(s)
are unable to be processed. For RegAF Airmen, AFPC/DP2SSM coordinates with the
appropriate Air Force CFM, approves or disapproves the request, and notifies the FSS. The
FSS notifies the Airman requesting reinstatement and the Airman’s parent unit. If approved
for reinstatement, AFPC/DP2SSM will award the AFSC at the skill level designated by the Air
Force CFM. (T-2).
2.3.6.1. Reinstatement request for AFR members will be documented as above and the
FSS will forward the reinstatement request electronically to HQ ARPC/DPAT for
processing to AFR CFM for approval or disapproval. (T-2). HQ ARPC/DPAT notifies the
FSS of the AFR CFM’s decision and the FSS will notify the individual requesting the
reinstatement and the individual’s unit. (T-2). If approved for reinstatement, the FSS will
award the AFSC at the skill level designated by the AFR CFM. (T-3).
2.3.6.2. The FSS will forward the reinstatement request electronically to NGB/A1D via
CMS for processing to the ANG CFM for approval or disapproval. (T-2). The FSS will
notify the individual requesting the reinstatement and the individual’s unit. If approved for
reinstatement, the FSS will award the AFSC at the skill level designated by the ANG CFM.
(T-2).
2.3.7. Waiving Mandatory Requirements. Mandatory requirements for awarding AFSCs may
be waived in extremely rare instances for individuals possessing exceptional qualifications
determined to be equivalent to the mandatory requirements. Approval authority and
procedures to request classification waivers are outlined in Tables 2.4 and 2.5. A waiver
request originates with the individual or the individual’s immediate supervisor. Waiver
requests are to be fully justified and documented. Only requests for reinstatement
recommended for approval are to be forwarded to the next review level (see paragraph 2.3.7.5
and Table 2.6 for processing instructions). Note: Procedures to request waivers pertaining to
on-the-job training, time-in-training for AFSC upgrade are contained Table 2.7.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 27
2.3.7.1. Experience: Consider waivers for individuals with experience in a closely-related
AFS, or who have had civilian experience considered a counterpart of the military specialty
being considered. The length of like civilian or related experience equaling the time
required for upgrade is the basis for awarding the appropriate skill level (for enlisted) or
qualified level (XXX3 for officers) in the AFSC.
2.3.7.2. Training: Consider waivers of training (formal, initial skills training, career
development course, etc.) for individuals who have performed exceptionally well in the
specialty over an extended period or have gained the required knowledge through other
avenues.
2.3.7.3. Minimum Aptitude Scores for Retraining (Enlisted). Waiver requests need to
explain why waiver of the mandatory aptitude score is in the best interest of the Air Force
and not simply to allow retraining consideration for the individual. Consider requests for
individuals who have a sustained record of outstanding performance and identify the
specific rationale for supporting the waiver. Commanders should screen each waiver and
only forward those justified and recommended for approval.
2.3.7.4. Other Mandatory Requirements. Waiver requests are to be justified and
documented. Use Tables 2.4 and 2.5 to determine approval authorities for waivers of
mandatory requirements. Forward officer medical, legal, and chaplain waivers as follows:
2.3.7.4.1. Medical Officers (AFSCs 4XXX): MAJCOM to HQ AFPC/DP2N.
2.3.7.4.2. Judge Advocates (AFSCs 51JX): HQ USAF/JAX.
2.3.7.4.3. Chaplains (AFSCs 52RX): HQ USAF/HC.
28 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.4. Waiver Authority for Mandatory Classification Requirements—Officers (See
paragraph 1.3.7).
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
If the requirement is (see Note
1)
and the officer has
then approval authority is
1
education
provided justification
Air Force CFM (see Note
2)
2
experience
experience or other training
which equates to that in the AFS
3
a prerequisite AFSC (see Note
3)
experience in assigned AFSC that
equals or exceeds the experience
requirement shown for the
immediate prerequisite AFSC,
and completed training
requirements shown as mandatory
in the prerequisite AFSC
specialty description (see
paragraph 2.3.7)
4
training
completed other training or has
extensive experience which can
be equated to the training
requirement
Air Force CFM (see
paragraph 2.3.7 and Note
2)
Exception: AFSC 71SX
(see Note 4).
5
other mandatory requirements
(not specified above) in the
AFOCD specialty description
provided justification
HQ AFPC/DP2SSM
(see Notes 5, 6, and 3).
Notes:
1. The FSS ensures the Airman requesting the waiver justifies why the waiver is warranted and includes
appropriate supporting documentation (e.g., transcripts, training records, performance reports, test
results, letters of recommendation, medical evaluations, or other documents justifying the request).
(T-2).
2. Waiver authority equivalent to that of the RegAF CFM is delegated to HQ-level ANG/AFR CFMs
for ARC Airmen.
3. Prerequisite AFSC requirements are listed in the “experience” or “other” paragraph of the specialty
description. In either case, the RegAF CFM is contacted for a recommendation by the approval
authority. ANG and AFR officers requesting waiver under this rule complete waiver requests in
accordance with the respective Classification Waiver Guide and send to ANG/AFR CFM for review and
coordination. Waiver packages are forwarded to AFPC/DP2SSM for coordination with the RegAF
CFM.
4. Approval authority for AFSC 71SX is HQ Air Force Office of Special Investigations (AFOSI)
AFOSI/CC.
5. If a waiver is requested for medical and/or physical reasons, forward only those recommended for
approval by appropriate medical authority (AF Form 422, Notification of Air Force Member’s
Qualification Status, AFMAN 36-2032, DD Form 2992, Medical Recommendation for Flying or Special
Operational Duty).
6. A copy of the waiver decision is forwarded to the Air Force CFM.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 29
Table 2.5. Waiver Authority For Mandatory Classification Requirements—Enlisted
Personnel (See paragraph 2.3.7).
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the enlisted Airman's waiver is for (see Notes 1 and
4)
then approval authority is (see Note 2)
1
mandatory training as listed in the specialty description
Air Force CFM (see Notes 3 and 6).
2
experience (including input AFSC for an AFSC or
prefix in AFECD) (see Note 8)
3
mandatory education as listed in the specialty
description
4
Career Development Course
5
Defense Language Aptitude Battery Score
6
other mandatory requirements (not specified above) in
the specialty description or Other Mandatory Entry
Requirements listed in the AFECD; or any of the above
HQ AFPC/DP2SSM (see Notes 5 and
7).
Notes:
1. The FSS ensures the Airman requesting the waiver justifies (using official memorandum format) why
the waiver is warranted and includes supporting documentation, (e.g., transcripts, training records,
performance reports, test results, letters of recommendation, medical evaluations, or other documents
justifying request).
2. Follow the processing guidelines established in paragraph 2.3.7.5.
3. Before approving training and/or qualification waivers for RegAF enlisted Airmen with approved
retraining class quotas, coordinate with AFPC/DP1SSR. For ARC Airmen, the FSS contacts NGB/A1D
or HQ AFRC/DPAT, respectively.
4. Prior to processing a waiver request, commanders ensure trainees have completed all subject and task
knowledge requirements as identified by the supervisor. Refer to the applicable AFSC specialty
description in the AFECD to identify specific mandatory requirements for award.
5. A copy of the waiver decision is forwarded to the RegAF CFM or ANG/AFR CFM for ARC Airmen.
6. Waiver authority equivalent to that of the Air Force CFM is delegated to the HQ-level ANG and AFR
Command CFMs for their ARC Airmen. Exception: AFSC 3E7XX and 4N0XXX waiver authority
remains with RegAF CFM.
7. Waiver authority for two-time Career Development Course failures will not be further delegated.
(T-1). The Fire Protection Career Field (3E7XX) and Aerospace Medical Service (4N0XXX) Career
Development Courses are part of a National Certification and Accreditation system. Unit and Base
Education and Training Managers (for locations not having a Base Training Manager, the senior training
manager will fill this role) ensure waiver packages are properly documented and recommendations well
justified. (T-1).
8. Prerequisite AFSC requirements may be listed in the “experience” or “other” paragraph of the
specialty description. AFPC/DP2SSM coordinates waivers with the RegAF CFM. ARC enlisted Airmen
requesting waiver under this rule complete waiver requests in accordance with the ARC Classification
Waiver Guide and send to ANG/AFR CFM for review and coordination. Waiver packages are then
forwarded to the waiver approval authority (AFPC/DP2SSM) for coordination with the RegAF CFM.
Examples could be Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery, lift factor, physical stamina, upper
body, lower body, hearing, eyes, stability, and any other requirements in the AFSC specialty description
not identified in Table 2.5 Rules 1-6.
2.3.7.5. Processing Waiver Requests. Use Table 2.6. (Table 2.7 is for enlisted On-the-
Job-Training, Time-in-Training) to determine appropriate routing for waiver requests. The
individual’s immediate supervisor recommends, and their commander decides when a
30 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
waiver submission is appropriate. All waiver requests must be justified and include
sufficient rationale or documentation for the next level of review to adequately and fairly
determine disposition (T-2). Each level of review has the responsibility to use their best
judgment of what is fair and equitable to the individual, and what is in the best interest of
the Air Force. Return or disapprove cases lacking sufficient justification to warrant
consideration. Note: There are no provisions to award additional AFSCs solely to match
UMD authorization AFSCs, or to show future, potential, or possible utilization. Return
such requests without action and advise the Airman to apply for formal retraining if they
wish to pursue utilization in another specialty.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 31
Table 2.6. Processing of All Classification Waiver Requests (Except Enlisted On-the-Job-
Training, Time-in-Training for AFSC Upgrade) (Note 1).
If the individual
requests a waiver, then
the (see Note 2)
of organization
must:
Supervisor
Unit
decide whether a waiver is appropriate. Weigh
documentation and circumstances. If supportable,
provide the individual's commander the request in
Air Force memorandum format, include rationale
and attach documentation to support request. If
applicable, coordinate with the Base Training
Manager to evaluate the request and identify any
deficiencies in the training or to request a
recommendation and provide detailed rationale for
the recommendation. If request is not appropriate,
document why and return to individual. All
completed requests must be forwarded to the
commander. (T-3).
Commander
Unit
review the request and determine whether further
evaluation is necessary. If recommended for
approval, include appropriate endorsement and
forward complete request to the FSS. (T-3).
FSS
Unit
review the request for thoroughness and forward to
AFPC/DP2SSM (ANG/AFR CFM for ARC
Airmen). (See Notes 3 and 4.) (T-2).
ANG/AFR CFM
ANG/AFR
evaluate the request to determine whether further
evaluation is necessary. If request is not
appropriate, document why and return to the action
office for disposition. If recommended for
approval and within the scope of ANG/AFR CFM
approval authority, approve waiver. (T-2). If not
within the scope of ANG/AFR CFM approval
authority, include appropriate endorsement and
forward completed request to AFPC/DP2SSM for
waivers requiring approval by Air Force CFM or
DP2SSM. (See Note 4). (T-1).
Classification
Representative
(AFPC/DP2SSM for
RegAF Airmen; HQ
ARPC/DPAT or
NGB/A1D for ARC
Airmen)
HQ AFPC (HQ
ARPC/DPAT or
NGB/A1D for ARC
Airmen)
evaluate request. Forward coordinated requests
recommending approval, along with supporting
documentation, to the applicable RegAF approval
authority (see Tables 2.4 and 2.5.). Do not
forward incomplete cases or cases lacking rationale
or justification. Return disapproved requests to the
action office for disposition. (T-1).
Training Manager
(DP2LT)
AFPC
If needed, evaluate request and identify any
deficiencies in the training or the request. Provide
a recommendation and coordinate it with the

32 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
If the individual
requests a waiver, then
the (see Note 2)
of organization
must:
MAJCOM functional manager, if applicable (see
Tables 2.4 and 2.5). Do not forward incomplete
cases or cases lacking rationale or justification.
Return disapproved requests to the Unit for
disposition. (T-2).
Air Force CFM
Air Force
evaluate request and either approve or disapprove
those within approval authority (see Tables 2.4
and 2.5). Forward all other cases with
recommendation to AFPC/DP2SSM. (T-1).
Classification
Representative
(DP2SSM)
AFPC
evaluate request and either approve or disapprove.
Approved requests are routed to the applicable
office. Disapproved requests will be returned to
the applicable action office with rationale for
disapproval. A courtesy copy of all actions will be
provided to the applicable RegAF CFM or
ANG/AFR CFM. (T-1).
Notes:
1. AFR and ANG members and/or units will use their respective classification waiver guide for
processing. (T-2).
2. All waiver requests are written in either email or official memorandum format.
3. Requests to waive mandatory training or Career Development Courses are to be forwarded by email
to AFPC/DP2SSM for further staffing to the AFPC Education and Training Branch, as necessary.
4. ANG/AFR CFMs, consistent with waiver authority in Table 2.5.(Waiver Authority For Mandatory
Classification Requirements--Enlisted Personnel), approve or disapprove waivers within their authority.
All others are sent with recommendation to AFPC/DP2SSM.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 33
Table 2.7. Processing of On-the-Job-Training, Time-in-Training Waiver Requests for
AFSC Upgrade for Enlisted RegAF, ANG, and AFR Airmen (See Note).
R
U
L
E
If an individual
requests a waiver
under Table 2.5, rule
1, then the
of organization
must:
1
Supervisor
Unit
RegAF/ANG/AFR: Review the member's request
and, if concur, complete a memorandum for record
detailing the request and justification for waiver
approval. (T-3).
2
Training Manager
Unit
RegAF: Review the request package for
compliance with instructional guidance. If
recommended for approval, place the memorandum
for record on top of the waiver package and process
through the unit commander, group commander, and
finally to the wing commander or designee for final
approval or disapproval authority. (T-3).
AFR: N/A; supervisor forwards to Unit
Commander, Rule 3. (T-3).
ANG: Review the request package for compliance
with instructional guidance. If recommended for
approval, place the memorandum for record on top
of the waiver package and forward to the unit
commander for endorsement. (T-3).
3
Commander
Unit or Wing
RegAF: Review the memorandum for record and
corresponding package and determine whether
further evaluation is necessary. If recommended for
approval, commander will include appropriate
endorsement and forward completed request to the
Unit Training Manager for update. (T-3).
AFR: Review the memorandum for record and
corresponding package and determine whether
further evaluation is necessary. If recommended for
approval, include appropriate endorsement and
forward completed request to the Base Training
Manager for processing. (T-3).
ANG: Unit commander reviews the memorandum
for record and corresponding package to determine
whether further evaluation is necessary. If
recommended for approval, include appropriate
endorsement and forward completed package to the
Force Development Office (FDO) for final review
and processing with the Wing Commander or
Mission Support Group Commander (determined at
Wing level). (T-3).

34 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If an individual
requests a waiver
under Table 2.5, rule
1, then the
of organization
must:
4
Wing or Base
Training Manager
FSS/Wing
RegAF: Initiate upgrade action in MilPDS
following Commander approval. (T-2).
AFR: Review and forward to HQ ARPC/DPAT.
(T-2).
ANG: FDO initiate the upgrade action in MilPDS
following the final approved package endorsement
listed for the AFS in the ANG Classification Waiver
Guide. (T-2).
5
Miltary Personnel
Management Office
MAJCOM
AFR ONLY: Review and add a concurrence or
non-concurrence MFR to the electronic waiver
package. Forward to MAJCOM functional manager
for final disposition. (T-2).
6
HQ ARPC/DPAT
MAJCOM
AFR ONLY: Review and add a concurrence or
non-concurrence MFR to the electronic waiver
package. Forward to MAJCOM functional manager
for final disposition. (T-2).
7
CFM
HQ Air
Force/MAJCOM
AFR ONLY: Once received from HQ
ARPC/DPAT, CFM must evaluate request, approve
or disapprove, complete a memorandum of record of
action, and add it to the request as the first page.
Approved request packages are sent back to HQ
ARPC/DPAT via email and routed to the Wing
Training and Education Office of origin. (T-2).
8
Wing or Base
Training Manager
Wing
AFR ONLY: Forward final disposition to unit of
origin for appropriate action.
9
Unit Training
Manager
FSS/Unit
RegAF ONLY: Initiate upgrade action in the
Personnel Data System. (T-2).
Note: ANG and AFR units use their respective Classification Waiver Standard Operating Procedures.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 35
2.3.8. Converting to New or Revised AFS.
2.3.8.1. Conversion instructions for establishing and revising an AFS are published in the
Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide with each update to either the AFOCD
or AFECD. The Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide specifies the action(s)
required by the FSS, AFPC and Manpower.
2.3.8.2. If a review and evaluation of the Airman’s qualification is required (e.g., an
indirect conversion action), this is accomplished as a pre-conversion action to ensure award
of the correct authorized AFSC occurs immediately following the AFSC conversion
effective date (see the applicable Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide and
AFSC Conversion execution guidance in the myPers website for detailed conversion
instructions). Conversion actions are to be completed immediately following the
conversion effective date. However, in cases where the actions are not completed, FSS are
authorized to award AFSCs based on conversion instructions for up to 30 days after the
effective date. Indirect conversion actions are tied to specific time periods identified in the
Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide and are not open-ended.
2.3.8.3. Conversion to new or revised AFS is at a comparable skill and/or qualification
level unless otherwise noted in the conversion guide instructions.
2.3.8.4. During the initial conversion period and for up to 30 days after the effective date,
testing and mandatory training, experience, and education may be waived for awarding
new AFSCs unless otherwise specified in conversion guide instructions. Waiver
authorities are identified in Tables 2.6 and 2.7.
2.3.8.5. When existing AFSCs are revised and new mandatory prerequisites are
established, personnel will retain their awarded AFSC even if they no longer meet the
newly established prerequisites, unless otherwise specified in the Change Summary &
Conversion Instruction Guide.
2.3.8.6. FSS will ensure individuals are classified in accordance with Change Summary &
Conversion Instruction Guide. (T-2). Technically qualified FSS personnel assist in the
conversion process. For indirect conversions, the senior functional for the AFSC(s)
concerned or a MAJCOM functional manager (ANG/AFR CFM) are to assist in identifying
the correct AFSC(s) from those listed in the Change Summary & Conversion Instruction
Guide.
2.3.9. Changes in Mission, Weapon System, or Equipment. A change in basic mission,
weapon system, or equipment may require changes to authorized AFSCs and reevaluation of
training and individual qualifications. Local functional manager for the specialty develop
functional (from the RegAF CFMs for the AFSC[s] involved) conversion instructions for
Airmen affected by the change in coordination with the MAJCOM Functional Area Manager,
RegAF CFM, AFR CFM and ANG CFM.
2.3.9.1. Air Force CFM functional conversion instructions identify transitional training
requirements and skill level determination procedures for accomplishing the conversion, if
required.
36 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.3.9.2. FSS, with the help of the local functional representatives impacted by the
conversion, determine appropriate Duty AFSC, Control AFSC (enlisted only), and
awarded AFSCs according to the Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide and
update accordingly.
2.3.9.3. Source documents for Control and awarded AFSC updates resulting from an
indirect AFSC conversion are the conversion RIP (generated by the FSS from MilPDS
within five days of the conversion cycle) or the manually prepared AF Form 2096. For
either source document, forward to AFPC/DP1ORM (Automated Records Management
System office) for scanning into each Airman’s digital Automated Records Management
System record.
2.3.10. Using Suffixes. Suffixes identify positions and Airmen qualified to perform duty in
those positions related to particular equipment or functions within an AFSC.
2.3.10.1. Classification actions for suffixes are the same as those prescribed for AFSCs.
When AFSC suffixes are awarded, they become an integral part of the AFSC.
2.3.10.2. When an enlisted Airman is retraining into a different AFSC, including a
different suffix of an AFSC, the Control AFSC is designated at the 1-skill level for the
AFSC into which the Airman is retraining (see Table 2.13., Rule 2). In those rare instances
where a RegAF CFM (or ANG/AFR CFM) determines an Airman possesses the knowledge
and skills associated with the 3-skill level AFSC-awarding initial skills training, a CFM-
approved waiver is required to designate the 3-skill level Control AFSC and awarded
AFSC. Attach the approved waiver to the AF Form 2096 awarding the AFSC and send to
AFPC/DP1ORM for scanning into each Airman’s digital Automated Records Management
System record.
2.3.10.3. AFSCs authorized for use without shreds and/or suffixes are identified in the
AFOCD by a (+) preceding the AFSC number on the Officer Classification Structure Chart
and in the AFECD by an (*) preceding the AFSC on the Enlisted Classification Structure
Chart.
2.3.10.4. Enlisted Airmen awarded AFSCs authorized for use without shreds and/or suffix
are considered proficient in the basic AFSC (non-shredded and/or suffixed) and may be
used in either the shred and/or suffix or the basic AFSC. Example: An enlisted Airman’s
Primary AFSC is 1C551D. Because 1C551 is authorized to be used without the shred
and/or suffix, the enlisted Airman is considered qualified to work in either AFSC 1C551
or 1C551D. Note: An Airman with a Primary AFSC of 1C551 requires eligibility per the
1C5X1 AFSC specialty description for award and utilization of the 1C551D AFSC. This
is a retraining action unless the Airman has previously completed the 1C5X1D initial skills
training.
2.3.11. Using Prefixes. Prefixes are authorized for use with specific AFSCs when there is a
need to identify an ability or skill not restricted to a single utilization field or career field. A
prefix used with the authorized AFSC in the prefix section of the AFOCD and AFECD
identifies manning document position requirements (where required) and Airmen qualified to
perform duty in the position.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 37
2.3.11.1. More than one prefix to the same specialty is authorized (for example, Primary
AFSC T3F071 and Second AFSC W3F071). However, do not award multiple prefixes to
the same AFSC if it results in deleting another awarded AFSC qualification.
2.3.11.2. Prefix award is managed using the guidance contained in Section I of the
AFOCD or AFECD. Award the prefixed AFSC when the Airman meets the specified
award criteria in the prefix description.
2.3.11.3. Prefix withdrawal is managed using the same guidance as AFSC withdrawal (see
paragraph 2.4.). However, periods of nonperformance will not be used as a sole basis for
withdrawing a prefix. Once awarded, prefixes will be retained as long as the authorized
AFSC is retained. If an AFSC is withdrawn, the prefix associated with the AFSC is also
withdrawn. This includes the officer C prefix. Note: The C prefix denotes commander
duties within a functional AFSC, (i.e., C31P3, Commander, Security Forces). Award it
according to the authorized prefix listing contained in the AFOCD stipulating the
mandatory criteria for award.
2.3.11.4. When awarding officers prefix N or prefix P, an appropriate shred and/or suffix,
specified in the AFOCD Section I explanation for the applicable prefix, must be affixed to
the AFSC.
2.3.12. Classifying Patients. Use RI 93P0 as the Duty AFSC for officer patients and RI 9P000
for the Duty AFSC of enlisted patients hospitalized or expected to be hospitalized for 90 days
or more. Airmen will retain their Control AFSC (enlisted only), Primary AFSC, and other
awarded AFSCs unless withdrawn according to paragraph 2.4. See the AFECD and AFOCD
for other RIs and their applicability.
2.3.13. Managing Special Experience Identifiers.
2.3.13.1. SEIs are established to identify special experience and training not otherwise
identified within MilPDS. SEIs complement the assignment process, but are not substitutes
for AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Manager codes, prefixes, suffixes, SDIs, RIs, or professional
specialty course codes. They are established when identifying training, skills or experience
as critical to the assignment match, force management or deployment needs, etc., when no
other MilPDS-based identification is appropriate or available. SEIs can be used to rapidly
identify an already experienced resource to meet unique circumstances, contingency
requirements or management needs. They provide a means to track individuals and
identify positions requiring or providing unique experience or training that would
otherwise be lost. Enlisted SEIs are three-character numeric or alpha-numeric codes.
Officer SEIs are comprised of two separate codes: the activity code and experience set.
See the AFECD/AFOCD for approved codes and requirements. Note: Once awarded,
officer and enlisted SEIs simply exist in the Airman’s record within the MilPDS. They do
not expire nor are they automatically removed based on time or other eligibility
requirements.
2.3.13.2. Responsibilities. RegAF CFMs, MAJCOM functional managers, ANG/AFR
CFMs, commanders, supervisors, AFPC assignment managers, and AFPC military
classification personnel share responsibility for overall management of the SEI program.
They can determine how SEIs are tied to the assignment process, as required, when specific
38 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
experience requirements are justified for specific situations for assignment selection to
AFPC assignment teams.
2.3.13.2.1. AFPC/DP2SSM establishes, revises, and deletes SEIs from the
AFECD/AFOCD and MilPDS SEI tables when requested by the RegAF CFM (or
ANG/AFR CFM if ARC-specific). The RegAF CFM, in conjunction with MAJCOM
functional managers and ANG/AFR CFMs, are responsible for annually reviewing
established SEIs to determine validity and usefulness (see AFOCD and AFECD for
additional SEI information). Notify AFPC/DP2SSM when SEIs are no longer needed
in the MilPDS tables. AFPC/DP2SSM does not update SEIs for individual Airmen,
but is the approval authority for all RegAF SEI withdrawal actions processed through
CMS SEI Removal cases, in accordance with the SEIs Removal execution guidance in
the myPers website. For ANG/AFR Airmen, the unit commander approves withdrawal
of awarded SEIs and CMS is not used.
2.3.13.2.2. Commanders and supervisors review an individual's qualification for
award and request SEI update by the servicing FSS using AF Form 2096 according to
SEI execution guidance in the myPers website.
2.3.13.2.3. Functional managers at the appropriate level (RegAF CFM, ANG/AFR
CFM, MAJCOM, field operating agency, direct reporting unit, detachment, etc.), in
conjunction with Manpower, review authorizations to determine if positions require
SEI coding. They review individual UMD authorizations to determine if the job will
provide the incumbent with the special experience that the SEI denotes (enlisted only).
A key element to the success of the SEI program is to identify the appropriate positions
requiring the training and/or experience reflected by the SEI for assignment to the
authorization.
2.3.13.2.4. AFPC assignment officers and/or managers may use SEIs, when
appropriate, in the assignment selection process for RegAF Airmen.
2.3.13.2.5. RegAF Officers (lieutenant colonel and below) may request award or
withdrawal of SEIs in accordance with the SEI execution guidance in the myPers
website. If the AFOCD Experience Set criteria allows for removal based on the
officer’s request, AFPC/DP2SSM may approve the action.
2.3.13.3. FSS may award SEIs for colonels and colonel-selects according to SEI criteria
specified in the AFOCD in accordance with the SEI execution guidance in the myPers
website.
2.3.13.4. Enlisted SEIs. The FSS’s role is to:
2.3.13.4.1. Update award of or request enlisted SEI removal actions. The commander,
other designated representative (documented by a memorandum of delegation attached
to the Air Force Form 2096) or as specified in the SEI award criteria is the approving
authority (AF Form 2096, section VI).
2.3.13.4.2. Monitor incoming and locally initiated assignment actions and consider
special experience and training in determining an individual's duty position.
2.3.13.4.3. Award SEIs during in-processing, classification interviews, or when
determined appropriate by an individual's supervisor or commander.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 39
2.3.13.5. The AFECD contains the complete list of authorized enlisted SEIs and includes
designation criteria, authorized AFSC combinations where required, and special
instructions. FSS awards the SEI to the appropriate AFSC (i.e., by AFSC type [Primary
AFSC, 2/3/4 AFSCs]) in accordance with the SEI execution guidance in the myPers
website, after the Airman meets experience, training, and any other requirements outlined
in the AFECD. Note: Enlisted Airmen assigned to SEI-coded UMD authorizations either
possess the necessary experience or be able to gain the necessary experience with training
and time spent in the position. Enlisted SEIs encompass both general and restricted types,
contain three characters and are in both alphabetical and alpha-numeric format. In the
AFECD, general SEIs are identified as associated with “any AFSC.” Restricted SEIs are
identified as associated with the specific SEIs /skill levels stated or a range of AFSCs (e.g.,
1XXXX or 1AXXX/1UXXX). In addition, certain SEIs have been designated as “auto
award” or “auto notify” and provide limited MilPDS functionality to track and award the
SEI or notify the commander that the Airman may be eligible for award. See the SEI
execution guidance in the myPers website. Approved SEI tables are contained in the
AFECD, available on the myPers website.
2.3.13.6. If the SEI area in MilPDS is full and a new SEI is to be awarded, consider the
following factors in evaluating which SEIs to retain in MilPDS:
2.3.13.6.1. Retain experience on modern equipment or systems (functional managers
determine equipment currency).
2.3.13.6.2. Retain SEIs based on the extent of experience and training versus SEIs with
minimum experience or those of lesser importance at the time of review.
2.3.13.6.3. Officer SEIs are all general as MilPDS has no capability to associate officer
SEIs with AFSCs. In addition, the officer SEI is composed of two distinct data fields:
the one-character alpha “Activity Code” and the two-character alpha or alpha-numeric
“Experience Set.” Approved activity code and experience set tables are contained in
the AFOCD, available on the myPers website. Officer SEIs are not awarded for simply
occupying an SEIs coded position. SEIs are only awarded once the officer meets the
mandatory qualification criteria to include training and/or experience as identified in
the AFOCD, whether occupying a coded position or not.
2.3.13.7. RegAF CFMs at the appropriate level may code appropriate "no name
allocations" with desired SEI requirements when specific circumstances warrant SEIs
matches. These actions are pre-coordinated with the AFPC assignment manager.
2.3.13.7.1. Code SEI positions on the manpower documents.
2.3.13.7.2. Assign individuals with desired SEIs to matching positions.
2.3.13.8. Process requests for withdrawal of awarded SEIs in accordance with the SEI
execution guidance on the myPers website.
2.3.14. Classifying General Officers. RI 90G0 is the Primary and Duty AFSC of all general
officers. Award it after confirmation of promotion to brigadier general and effective on the
date selected for promotion by the Secretary of Defense. Withdraw all other awarded AFSCs
when adding the 90G0 AFSC. Classification procedures contained elsewhere in this manual
do not apply to general officers.
40 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.3.15. Awarding AFSCs to Officers. Use specialty description qualifications in the AFOCD
and this manual to award or change AFSCs. An officer must meet the mandatory entry
requirements for award of AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs. (T-2). The specialty description contains
mandatory and desirable entry, award, and upgrade criteria. In addition, for those AFSCs with
a Career Field Education and Training Plan, officers must meet the requirements therein for
upgrade. Designate other AFSCs according to paragraph 2.3. (T-2).
2.3.16. Awarding Intermediate or Qualified AFSCs. Approval authority is the unit
commander, unless otherwise specified in Tables 2.8 and 2.9. The FSS monitors the eligibility
of officers for upgrade to an intermediate (if applicable) or qualified AFSC. Establish a 6-
month upgrade suspense date when no minimum experience is shown in the specialty
description in the AFOCD. Use this date strictly to monitor the award action. It is not a
minimum experience requirement; it is simply a monitoring tool. See paragraphs 2.3.17 and
2.3.18 for commanders’ upgrade and award actions.
2.3.16.1. Use the officer upgrade RIP (or other communication, as applicable) to notify
commanders or supervisors when officers have met identified experience requirements.
2.3.16.2. Commanders or supervisors review an officer's qualification for upgrade and
return annotated RIP (or provide completed AF Form 2096) to the FSS. If an officer is not
qualified for upgrade, the commander or supervisor advises the FSS in writing to establish
a new suspense date. The new suspense date represents the commander’s or supervisor’s
estimate as to when the individual should be ready for upgrade.
2.3.17. Classifying Commanders. A variety of AFSCs, SDIs, and Report Identifiers are
available to identify commander UMD authorizations. Use the AFOCD to determine which
identifier is appropriate for the role and position under consideration. Personnel selected for
commander positions (AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs such as XXC0, SDI 80C0, SDI 81T0, RI 91C0,
and RI 91W0) are considered qualified upon assignment to the position. Such commander
specialties encompass command, direction, planning, and staff supervision; cut across career
fields of diverse functions and activities; and are only awarded to officers assigned to valid
commander or deputy commander authorizations. They carry a high level of responsibility
and extreme care must be exercised in their award. They are not awarded to show potential
qualification.
2.3.18. Using the Commander Prefix. Use the prefix "C" to identify functional AFSC
commander positions below Group level. It is only authorized to be used with the 3
qualification level and is not available for use with the 1, 2 or 4 qualification levels. C-prefixed
AFSCs at other than the 3 qualification level do not exist in MilPDS. Note: The C prefix
denotes commander duties within a functional AFSC, (i.e., C31P3, Commander, Security
Forces). Award it according to the authorized prefix listing contained in the AFOCD
stipulating the mandatory criteria for award.
2.3.18.1. The minimum experience for award of the C prefix is 12 months assigned to a
valid, funded C-prefixed authorization as a unit commander performing that role, provided
the officer has already been upgraded to the qualified AFSC (XXX3) level in the non-
prefixed AFSC at the time of award. Officers are not authorized award of the C-prefixed
functional AFSC until they meet the prefix award criteria in the AFOCD and are awarded
the qualified AFSC.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 41
2.3.18.2. The C prefix is not authorized (nor are they in MilPDS as a valid prefix-AFSC
combination) for specialties specifically established to identify commander functions as
denoted by the term "commander" in the specialty title. Example: SDI 80C0,
Commander, Cadet Squadron, USAFA; SDI 81C0, Training Commander, OTS; RI 91C0,
Commander; RI 91W0, Wing Commander; AFSC 38P3Q, Section Commander; AFSC
10C0, Operations Commander; AFSC 20C0, Logistics Commander; AFSC 30C0, Support
Commander; AFSC 40C0, Medical Commander; or AFSC 60C0, Program Director. Note:
See C Prefix definition in the prefix listing contained in the AFOCD for a complete listing
of AFSCs not authorized for use with the prefix.
2.3.18.3. Eligibility Criteria for Wear of Air Force Command Insignia.
2.3.18.3.1. The command insignia must be worn by all eligible commissioned officers
in the rank of Colonel (O-6) and below as authorized in Air Force Instruction 36-2903,
Dress and Personal Appearance of Air Force Personnel. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2. Eligibility criteria. To wear the command insignia, an officer:
2.3.18.3.2.1. Must possess and exercise Uniformed Code of Military Justice
authority via appointment on G-Series orders (Permanent Assumption or
Permanent Appointment) and be serving in a position coded as a Command Billet
with a C-prefix or a specified command AFSC such as 10C0, 30C0, etc. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.2. RegAF units:
2.3.18.3.2.2.1. For Lieutenant Colonels and below: Must be competitively
selected by an Air Force-level command board. (T-1). This includes selectees
from Air Force-level squadron commander boards, Military Entrance
Processing Station Commander board, and USAFA Cadet Squadron and Group
Air Officer Commander positions. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.2.2. ANG units: Must be competitively selected for command at the
Wing or State-level at either the wing, group, squadron, numbered flight, or
detachment level. (T-1). This includes Numbered Flights Commanders within
the ANG that fall outside of normal reporting channels (i.e., the flight reports
directly to a Group Level). (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.2.3. AFR units: Must fill one of the following positions: squadron
commander, group commander or wing commander, and Readiness and
Integration Organization (RIO) detachment commander. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.3. Must serve a minimum of one year in command for permanent wear.
(T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.4. Command insignia will not be worn by:
2.3.18.3.2.4.1. Temporary, acting, detachment, element and section
commanders as designated on G-series orders. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.4.2. Vice and Deputy Commanders. However, they may wear the
insignia as a graduated commander from previously held command positions.
(T-1).
42 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.3.18.3.2.4.3. General Officers. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.4.4. Officers removed from command for cause are not authorized
permanent wear of the command insignia. (T-1). Exception: Officers
authorized permanent wear of the command insignia due to prior successful
commands. (T-1).
2.3.18.3.2.5. ETPs: Previously granted exceptions to policy are no longer valid.
Officers must meet the criteria above to be authorized wear of the command
insignia. (T-1). New ETP requests must be submitted to AF/A1S through the
MAJCOM/A1. (T-1).
2.3.19. Awarding Medical Utilization Field AFSCs (4XXX). Award medical AFSCs only to
officers designated as members of the Medical Service, United States Air Force, according to
Title 10, USC § 9063(a) through (f), Designation, Officers to perform certain professional
functions. A medical officer may be awarded an AFSC other than those in the 4XXX series if
approved by AFPC/DP2N, AFRC/SG, or NGB/SG, as applicable.
2.3.20. Awarding Chaplain Utilization Field AFSCs (52RX). Award and assign AFSCs 52RX
only to officers who are accepted for Air Force service as chaplains, possess ecclesiastical
endorsements listed in Department of Defense Directive 1304.19, Appointment of Chaplains
for the Military Departments, and are accepted by HQ USAF/HC, Chief of Air Force Chaplains
(RegAF and AFR only). Chaplains wear their occupational badge after graduating from
technical school (which for Chaplains is the Basic Chaplain Course). For specific award
criteria refer to AFI 52-101, Planning and Organizing.
2.3.21. Awarding Legal Utilization Field AFSCs (51JX). A Juris Doctor degree issued by an
accredited law school, active (or equivalent) status with a current license in good standing to
practice law before the highest court of a U.S. state, commonwealth or territory, or the District
of Columbia, and designation by The Judge Advocate General according to 10 USC § 9063(g),
are mandatory for entry and award of 51JX AFSCs. In addition, award the qualified AFSC to
those officers who have met all training and experience requirements prescribed in the AFOCD
AFSC specialty description. Award 51JX AFSCs only to those ARC officers designated as
judge advocates (JAs) by The Judge Advocate General, in accordance with AFI 51-101, The
Air Force Judge Advocate General’s Corps (AFJAGC) Operations, Accessions, and
Professional Development. Officers awarded a 51JX AFSC, but who do not have an
appointment in The Judge Advocate General’s Corps Reserve in accordance with AFI 51-101,
shall have the AFSC withdrawn and will be reclassified. (T-2). Award the qualified AFSC to
those officers who have met all training and experience requirements prescribed in AFI 51-
101 and the AFSC specialty description in the AFOCD. For ANG officers reference AFMAN
36-2032.
2.3.22. Rated Officers. Loss of Aircraft Qualification. Rated officers placed in an inactive
aviation service code (flying status codes J, K, L, P, S, or T) retain their awarded AFSC at the
qualified or staff level. Paragraph 2.4.3.3.9.2 contains guidance and instructions for rated
officers disqualified from aviation service. There is no requirement to downgrade the AFSC
as a result of these circumstances. An awarded AFSC will reflect the highest held qualification
level, regardless if it is the Primary, Second, or Third AFSC. (T-2).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 43
2.3.23. Classifying Officers of Other Services Working in the Air Force. Assign officers of
allied countries or other DoD agencies attached to the Air Force for duty in AFSCs authorized
for Air Force use. Because these officers fill specific manning requirements within the Air
Force, give them duty assignments that maximize their technical training and experience. Do
not delete military specialties recorded by other departments from their records.
2.3.24. Competitive Category Transfers. For RegAF officers, requests to transfer between
competitive categories are accomplished in accordance with AFMAN 36-2032, initiated by the
officer, and coordinated through the appropriate functional assignment officer. Application
requirements for a competitive category vary based on the gaining AFSC requirements.
Transfer application requirements are available on the myPers website. Note: Officers
eliminated from initial skills training may be reclassified under paragraph 2.2.5. AFR and
ANG competitive category transfers will be accomplished in accordance with AFMAN 36-
2032. (T-2).
2.3.25. Awarding AFSCs in Enlisted Career Fields. Award or change AFSCs based on
specialty standards in the AFECD, this manual, and the execution guidance in the myPers
website.
2.3.25.1. Award of an AFSC must be based on one of the following:
2.3.25.1.1. Initial classification. (T-3).
2.3.25.1.2. Enlisted skill level upgrade (see Table 2.11). (T-3).
2.3.25.1.3. AFSC downgrade or withdrawal. (T-3).
2.3.25.1.4. AFSC conversions (see Change Summary & Conversion Instruction Guide
and periodic revisions to the AFECD). (T-3).
2.3.25.1.5. Enlisted retraining (see Chapter 6 for requirements). (T-3).
2.3.25.1.6. Waiver of mandatory requirements (see paragraph 2.3.7 and Tables 2.4 or
2.5). (T-3).
2.3.25.1.7. Awarding helper-level AFSCs to ANG and AFR enlisted personnel based
on civilian experience. (T-3).
2.3.25.2. Additional AFSCs will not be awarded solely to show future, potential, or
possible utilization. (T-3).
2.3.25.3. The 7-skill level will only be awarded to Staff Sergeant select through Master
Sergeant. (T-1). The 9-skill level will only be awarded to Senior Master Sergeant. (T-1).
The Chief Enlisted Manager code will only be awarded to Chief Master Sergeant and Chief
Master Sergeant-select. (T-1). Use Table 2.12 for authorizing manpower positions. Note:
AFSCs will only be awarded through the methods cited in paragraph 2.3.25. (T-3). The
FSS will return requests that do not comply with this paragraph to the originator. (T-3).
2.3.26. Strength Aptitude. Mandatory strength standards for entry into all enlisted career
fields are shown in the AFECD, Attachment 4.
44 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.3.27. Classifying Airmen in Retraining Status. Retrainees in the grade of Senior Master
Sergeant and below must complete all mandatory requirements (see Chapter 6) to qualify for
award of a new skill level unless waived by appropriate waiver authority in Table 2.5. Review
Tables 2.4, 2.5, and 2.6 for waiver approval levels and processing requirements. (T-2).
2.3.27.1. AF/A1LE, Chiefs’ Group, Assignments Division, manages cross-flow into other
than an awarded Chief Enlisted Manager code for all RegAF Chief Master Sergeants and
Chief Master Sergeant-selects. Note: ANG and AFR Command Chief Master Sergeants
cross-flowing into another AFSC outside the career field ladder must submit a waiver to
bypass normal skill level qualifications to NGB/A1D for ANG personnel and HQ
ARPC/DPAT for AFR personnel. (T-2). NGB/A1D or HQ ARPC/DPAT will review for
thoroughness and coordinate with ANG or AFR CFM and training managers before
approving or disapproving. (T-2).
2.3.27.2. Chief Enlisted Manager codes are awarded using Rule 6 of Table 2.11.
2.3.28. Classifying Students. Retain a student's awarded AFSC except as indicated in
paragraph 2.4.2. For classifying student officers refer to Table 2.10. The Duty AFSC of
enlisted personnel attending a formal school is the AFSC to which the course trains according
to the Education and Training Course Announcement (ETCA) (an online version of the Air
Force Course Catalog). If the course does not train to a specific AFSC, the Duty AFSC remains
the same as it was at the base of assignment. Award a 3-skill level AFSC upon graduation
from the AFSC-awarding course. To determine the Control AFSC of enlisted personnel in
training status, see Table 2.13.
2.3.29. Classifying Religious Affairs Personnel. The 37th Training Wing, JBSA-Lackland
TX, using policies established by HQ USAF/HC, determines initial entry of RegAF NPS
enlisted Airmen into the Religious Affairs AFSC (5R0X1). The wing chaplain and chapel
non-commissioned officer in charge interview retrainees into this AFSC, then forward
recommendations to the AETC command chaplain for review or approval.
2.3.29.1. HQ AFRC/HC, using policies established by HQ USAF/HC, will approve or
disapprove retraining applications for AFR enlisted Airmen into the Religious Affairs
career field (AFR does not accept NPS Airmen into AFSC 5R0X1). (T-3). The wing
chaplain and chapel non-commissioned officer in charge interview retraining applicants,
then forward recommendations to HQ AFRC/HC for command chaplain review and/or
approval. (T-3).
2.3.29.2. NGB Religious Affairs CFM approval is required for ANG enlisted personnel
entry into the AFS and follow-on initial skills training (ANG does not accept NPS Airmen
into AFSC 5R0X1).
2.3.30. Classifying Instrumentalists. The Air Force Military Training Center classifies initial
enlistees into AFSCs 3N1X1 and 3N2X1 using AFMAN 36-2032, and AFI 35-101, Public
Affairs Operations. Band commanders may award appropriate instrumental suffixes to
qualified persons assigned and classified in AFSC 3N151 if there is a vacancy in the unit of
assignment. Requirements and testing procedures are specified in AFI 35-101.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 45
2.3.31. Classification Interviews and Audits.
2.3.31.1. Classification specialists (5-skill levels or higher with classification experience
[for ANG, the Force Development Office]), conduct classification audits during in-
processing and when an Airman receives an assignment in an AFSC other than their
Control AFSC.
2.3.31.2. Auditors or Personnel specialists (AFPC for RegAF; HQ ARPC/DPAT or
NGB/A1D for ARC Airmen) will:
2.3.31.2.1. Evaluate accuracy and currency of the AFSC data. (T-2). Ensure a source
document (see paragraph 2.3) exists for each awarded AFSC, SDI, or RI and verify
accuracy of awarded AFSC skill and/or qualification level. (T-2).
2.3.31.2.2. Downgrade or withdraw AFSCs according to paragraph 2.4.1. (T-2).
2.3.31.2.3. Provide classification counseling. (T-2).
2.3.31.2.4. Determine whether designated SEIs are accurate. Work with units to award
SEIs via AF Form 2096 or submit SEIs removal actions via CMS, as necessary. AFR
and ANG SEI removals are not processed in CMS. (T-2).
2.3.32. Using Feeder AFSCs. When enlisted Airmen progress to the 5-, 7-, or 9-skill level
AFSC or Chief Enlisted Manager code in which two or more AFSCs merge, retain the feeder
AFSC (the AFSC from which they progressed) as an awarded AFSC. Retain only the feeder
AFSC immediately preceding the enlisted Airman’s highest awarded AFSC. Example:
Primary AFSC 2A590, Second AFSC 2A573 would be retained as a feeder AFSC. When the
enlisted Airman is selected for promotion to Chief Master Sergeant and is designated with
Chief Enlisted Manager 2A300, Second AFSC 2A590 will be retained to denote the enlisted
Airman’s technical qualifications. AFSC 2A573 would be withdrawn. AFSCs with shreds
and/or /suffixes at the 3-skill level and combined at the 5-skill level are used to facilitate the
first duty assignment. Therefore, delete the feeder 3-skill level AFSC when upgrading the
enlisted Airman to the 5-skill level.
2.3.33. Designating Control AFSC. AFPC/DP3AM (Military Assignments Program Branch)
manages Control AFSCs for RegAF enlisted Airmen; ANG/AFR FSSs manage Control
AFSCs for assigned ARC Airmen.
2.3.33.1. The Control AFSC is initially based on the AFSC into which the member is
classified at the time of enlistment or during basic training (See Table 2.3.). It will be
identical to the highest awarded AFSC or Chief Enlisted Manager code in the ladder in
which the member is being used or trained with the following restrictions:
2.3.33.1.1. The Control AFSC for members performing duty in a 3-, 5-, 7-, or 9-skill
level structure will not exceed the:
2.3.33.1.1.1. 3-skill level for Airman Basic through Airman First Class. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.1.2. 5-skill level for Senior Airmen and Staff Sergeants. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.1.3. 7-skill level for Technical Sergeants and Master Sergeants. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.1.4. 9-skill level for Senior Master Sergeants. (T-2).
46 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.3.33.1.2. The Control AFSC for members performing in an AFS without a 5-skill
level will not exceed the:
2.3.33.1.2.1. 3-skill level for Airman Basic through Staff Sergeant. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.2.2. 7-skill level for Technical Sergeants and Master Sergeants. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.2.3. 9-skill level for Senior Master Sergeants. (T-2).
2.3.33.1.3. The Control AFSC for Chiefs and Chief-selects is the Chief Enlisted
Manager code of the career ladder to which assigned. (T-2).
2.3.33.2. Although the FSS can change the Control AFSC, changes other than initial,
retraining, normal skill-level upgrade, and SDI actions are reviewed for propriety by both
the gaining and losing AFPC assignment managers for RegAF Airmen and ANG/AFR
CFMs for ARC Airmen. Base-level changes of Control AFSC can be disapproved based
on the overall Air Force resource need. Note: Airmen with more than one awarded AFSC
can be assigned based on the needs of the Air Force in any of their awarded AFSCs for
which they remain qualified. The date the Control AFSC is changed is based on how that
change is affected. If an Airman is locally reassigned via Permanent Change of
Assignment (PCA), the effective date of the Control AFSC is the date assigned to the
position. If an Airmen is reassigned via Permanent Change of Station (PCS) to another
base, the effective date of the Control AFSC is the date departed last duty station. Do not
change the Control AFSC locally for an Airman being disqualified from their current
Control AFSC and/or awarded AFSC (see paragraph 2.4.).
2.3.33.2.1. Control AFSC changes are not authorized at base-level for Airmen who
have received an initial enlistment bonus or receiving a selective reenlistment bonus in
their current enlistment. For RegAF Airmen, contact AFPC/DP0SW, Procedures and
Student Management Assignments Branch for assistance if Control AFSC change is
needed other than for AFSC disqualification. Note: Bonus termination and/or
recoupment may occur if the Control AFSC changes from the Control AFSC in which
the bonus was contracted. Contact AFPC/DP3SA (Airman Support Branch) for
selective reenlistment bonus or DP2LT for initial enlistment bonus issues.
2.3.33.2.2. For ARC Airmen, the servicing FSS performs these actions. For IR and
Reserve HQ Active Guard and Reserve (AGR)s, ARPC performs these actions.
2.3.34. Use of Outside of Control AFSC. Local emergencies or overages may be the basis for
an Airman’s prolonged assignment outside of the normal career progression pattern. However,
to negate any career regression, such temporary assignments should be rotated among all
Airmen in the same Control AFSC, if the source Control AFSC represents the most appropriate
resource pool. If pulling from any AFSC, all available Airmen should rotate for periods not to
exceed 130 days.
2.3.34.1. FSS (RegAF and ARC):
2.3.34.1.1. May authorize using Airmen through Senior Master Sergeant outside their
Control AFSC up to 130 days in any 12-month period.
2.3.34.1.2. Are responsible for ensuring Chief Master Sergeants and Chief Master
Sergeant-selects are not performing duty out of their Control AFSC for more than 270
days in a 12-month period.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 47
2.3.34.2. Must request and receive an approved waiver from AFPC/DP0SW to use Airmen
out of their Control AFSC if they have an assignment limitation code "O" which indicates
receipt of an initial enlistment bonus in the current enlistment, a selective retention bonus
(SRB), or a break in service. (T-1). Airmen receiving an SRB may not perform duty
outside their SRB specialty for more than 90 consecutive days within a 360-day period or
a combined total of 90 days within a 360-day period. For Airmen receiving an SRB, see
AFI 36-2606, Reenlistment and Extension of Enlistment in the United States Air Force,
Chapter 4. Duties in the Control AFSC skill are defined in accordance with with the
AFECD. Send waiver requests for RegAF Airmen to the Systems, Procedures and Student
Management Assignments Branch at HQ AFPC/DP0SW. ARC waiver requests are to be
coordinated with NGB/A1D or HQ ARPC/DPAT. (T-2).
2.3.34.3. AFPC Assignment Managers or ANG/AFR CFMs may, upon receipt of the unit
commander’s memo or email (no specific format) with detailed justification:
2.3.34.3.1. Approve using Airmen through Senior Master Sergeant outside their
Control AFSC in excess of 130 days.
2.3.34.3.2. Forward waiver request (memo or email; no specific format) with detailed
justification for using RegAF Chief Master Sergeants and Chief Master Sergeant-
selects outside their Control AFSC to HQ USAF/A1LE, Chiefs’ Group Assignments.
For NGB/AFR Chief Master Sergeants and Chief Master Sergeant-selects, forward
waiver requests to the applicable ARC CFM.
2.3.34.4. Using outside of Control AFSC does not waive requirements to terminate special
duty assignment pay when the period of temporary duty (TDY) exceeds 90 days (see
AFMAN 36-3012, Military Entitlements). Note: The Airman continues to count in the
unit’s authorized versus assigned manning in the Control AFSC while performing duties
outside of the Control AFSC.

48 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.8. Criteria for Awarding Officer Rated AFSCs (see Note 1).
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the officer serving in the position.
then officer is qualified for award of
1
is newly commissioned, and selected for Pilot training
or is undergoing Basic Pilot training.
RI 92T0.
2
is newly commissioned, and selected for CSO or
undergoing Basic CSO training.
RI 92T1.
3
is newly commissioned, and selected for ABM training
or undergoing Basic ABM training.
RI 92T2.
4
is newly commissioned, and selected for RPA Pilot
training or undergoing basic RPA Pilot training.
RI 92T3.
5
is a pilot (completed Pilot training), but does not meet
mandatory specialty qualification for the qualified level
AFSC (11X3X), including suffix.
entry AFSC (1 level).
6
is a qualified pilot or copilot in the aircraft identified by
the suffix, but has not qualified as an aircraft
commander (11X3X).
intermediate AFSC (2 level, when
available).
7
meets all mandatory specialty qualifications, and is
certified by the unit commander or designated
representative as being aircraft commander qualified in
the aircraft identified by the suffix.
aircraft commander AFSC (3 level).
8
is a CSO (completed CSO training), but does not meet
mandatory specialty qualifications for the qualified
level AFSC (12X3X), including suffix.
entry AFSC (1 level).
9
is a CSO who meets all mandatory specialty
qualifications, and is certified by the unit commander
or designated representative as being qualified in the
specific weapon system as identified by the suffix.
qualified AFSC (3 level).
10
is a B-52 navigator but not a B-52 radar navigator.
intermediate AFSC (2 level) (see Note 2).
11
possesses a rated qualified AFSC (3 qualification level)
and is serving in a staff position (above wing level) in
the same AFSC. The UMD must reflect a XXX4X
authorization.
staff AFSC (XXX4) (see Note 3).
Notes:
1. Gaining commands conduct training for ANG and AFRs personnel (including IRs) for AFSCs listed in
the AFOCD and AFECD according to the same standards as RegAF personnel.
2. A Bomber CSO qualified as B-52 radar navigator will possess a 12B3E AFSC. (T-3). A Bomber CSO
not qualified as B-52 navigator will possess a 12B2E AFSC. (T-3).
3. Manpower will not change XXX3X authorizations at wing level and below to XXX4X. (T-2). In
addition, not all positions above wing level qualify for the staff AFSC. For those positions above wing
level, Manpower will use the staff AFSC requirements for determining applicability: “Staff AFSC—
Identifies an officer position above wing level specifically on the duty requirements of the role performed,
not the fact that the authorization is on a staff above wing level. (T-2). Use staff AFSCs (XXX4) to
identify planning and policy-making positions above wing level. It requires the same skills as those for the
qualified AFSC (XXX3), but applied to developing broad policies, plans, and procedures. Management
responsibility increases without a corresponding increase in knowledge of the technical aspects of the
function. Officers filling or have filled such positions are awarded the staff AFSC.”

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 49
Table 2.9. Criteria for Awarding Officer AFSCs, SDIs and RIs Other Than Rated AFSCs
(See Note 1).
L
I
N
E
A
B
If the officer meets AFSC entry qualifications contained
in the specialty description in the AFOCD and
then the officer qualifies for award of
an (see Note 2).
1
is assigned principal duty in an AFSC and continued
assignment is intended, but the officer does not meet
mandatory upgrade requirements in specialty
description.
entry AFSC (XXX1 qualification
level).
2
possesses significant experience in an AFSC not
previously awarded, but is not serving in the AFSC (for
example, by performing in an AFSC as additional duty
or through civilian experience or education).
entry AFSC. This does not apply to
award of commander specialties. (see
Note 3).
3
is a qualified deputy missile combat crew commander
but has not qualified as a missile combat crew
commander.
intermediate AFSC. (XXX2
qualification level).
4
is currently serving in the AFSC and is demonstrating
qualifying proficiency and meets mandatory upgrade
requirements.
qualified (XXX3 qualification level)
AFSC. (See Note 4).
5
is serving in the SDI (assigned to a SDI/RI coded
manpower authorization) or RI and meets mandatory
qualifications identified in the AFOCD. Do not award
to individuals performing a SDI role as an additional
duty. Most RIs identify a status, not a role such as
general officer or wing commander and as such may or
may not have an associated manpower authorization.
SDI or RI.
6
possesses a qualified AFSC (3 level) and is serving in a
qualifying staff position (above wing level) in the same
AFSC.
Staff AFSC. (XXX4—4 qualification
level) (see Note 5).
7
is approved for Wounded Warrior designation by HQ
AFPC/DPFW
appropriate 92WX RI (see Note 6)
Notes:
1. Gaining commands conduct training for ANG and AFR personnel (including IRs) for AFSCs listed
in the AFOCD and AFECD according to the same standards as RegAF personnel.
2. Only the AFOSI awards 71SX AFSCs. The parent MAJCOM commander or the Secretary of the
Air Force approves the award of the 60C0 AFSC.
3. Requests for award of additional AFSCs must include a recommendation by an individual
possessing the specialty at the qualified level. If technical evaluation is not available at base level, then
forward the request to the RegAF CFM or ANG/AFR CFM. If the officer lacks sufficient training
and/or experience to perform the role of the AFSC, do not award.
4. Time spent in staff duty positions (XXX4) can be applied to the award of the qualified level (3 or 4
level).
5. Manpower will not change XXX3X authorizations at wing level or below to XXX4X. (T-2). In
addition, not all positions above wing level qualify for the staff AFSC. For positions above wing level,
Manpower will use the staff AFSC requirements for determining applicability (vice the 3-qualification
level): Staff AFSC identifies an officer position above wing level specifically on the duty requirements
of the role performed, not the fact that the authorization is on a staff above wing level. Use staff
AFSCs (XXX4) to identify planning and policy-making positions above wing level. It requires the
same skills as those for the qualified AFSC (XXX3), but applied to developing broad policies, plans,

50 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
L
I
N
E
A
B
If the officer meets AFSC entry qualifications contained
in the specialty description in the AFOCD and
then the officer qualifies for award of
an (see Note 2).
and procedures. Management responsibility increases without a corresponding increase in knowledge
of the technical aspects of the function. Qualified (XXX3) officers filling or who have filled such
positions are awarded the staff AFSC.
6. AFPC/DPFW determines Wounded Warrior eligibility and updates the appropriate 92WX RI to the
secondary or third AFSC for tracking purposes only. No further updates or removals are allowed other
than by AFPC/DPFW. RI 92WX will not be updated as the Primary AFSC or Duty AFSC. (T-2).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 51
Table 2.10. Classifying Students—Officers.
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the officer is
then the officer’s awarded and duty AFSC will be
1
attending a course of training that leads to
the award of a nonrated AFSC.
an entry-level AFSC (XXX1) toward which the
course trains. (see Note 1).
a student who was previously awarded
the qualified level of the AFSC into
which training.
at the qualified level (XXX3).
2
attending Undergraduate Flying Training.
RI 92T0 for Undergraduate Pilot Training and 92T1
for specialized Undergraduate Navigator Training or
Undergraduate CSO Training. (see Note 2).
3
attending Undergraduate ABM Training.
RI 92T2. (see Note 2).
4
attending Undergraduate RPA Pilot
Training.
RI 92T3 (see Note 2).
4
in TDY status while attending a course
not leading to the award of a specific
Control AFSC.
the duty AFSC indicated by the parent organization.
5
in PCS status while attending formal
training not leading to the award of a
specific AFSC.
the same as previous duty AFSC, except rated
officers in flying categories other than 2 and 3R.
Give these officers a Duty AFSC in their best
qualified rated AFSC if their previous duty was in a
nonrated AFSC.
6
in PCS status while attending
Professional Military Education (PME).
RI 92S0, except AFR non-EAD officers. These
officers will have the Duty AFSC assigned to them
at their Reserve unit of assignment.
Notes:
1. Award a primary AFSC, at the entry-level, to officers selected for school when they do not already
have an awarded AFSC. Otherwise, award the entry-level AFSC as the second or third AFSC.
2. Following graduation from rated officer initial skills training (92T0, 92T1, 92T2 or 92T3), the FSS
awards the officer the entry-level primary (or Second AFSC or Third AFSC if already awarded an
AFSC 1XXX – 7XXX) and duty AFSC for the specific weapons system in which they are being
trained.

52 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.11. Criteria for Awarding Enlisted AFSCs, SDIs, RIs or CEM Codes.
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the enlisted Airman
then the enlisted Airman is
qualified for award of AFSCs,
SDI, or Chief Enlisted Manager
code as indicated (See Note 7)
1
is assigned permanent duty or training in a helper AFSC and
meets specialty entry qualifications for the AFS as listed in
the AFECD.
1-skill level. (see Note 1).
2
completes an AFSC-awarding course listed in the Education
and Training Course Announcements, possesses an approved
waiver (in accordance with Table 2.5), or via on-the-job-
training alone only when specified in the retraining
instructions and as approved by the respective component
CFM (see Notes 2 and 8).
3-skill level.
3
Successfully completes mandatory Career Development
Course (when required for AFSC) and applicable mandatory
core tasks identified in the Career Field Education and
Training Plan. Award of the 5-skill level (see parts 1 and 2
of the Career Field Education and Training Plan) also
requires completion of time in upgrade training (if
applicable) as determined by the Career Field Manager;
mandatory requirements listed in the AFECD; a
recommendation from their supervisor, and approval by their
commander. Individuals in retraining status (Training Status
Code F) are subject to the same training requirements and
must complete time in upgrade training (if applicable) as
determined by the Career Field Manager. Unit commanders
may approve time-in-training waivers. Time-in-training
waivers for ARC are processed according to Table 2.7.
Coordinate requests for respective component CFM approval
through the MAJCOM functional manager. Note:
Supervisors may identify and standardize local tasks for
upgrade with the RegAF CFM approval.
5-skill level. (see Notes 3 and
10).
4
is at least a Staff Sergeant select, completes mandatory
Career Development Courses (when required for AFSC) and
applicable mandatory core tasks identified in the Career
Field Education and Training Plan (see parts 1 and 2).
Supervisors may identify and standardize local tasks for
upgrade with the RegAF CFM approval. Coordinate
requests for RegAF CFM approval through the MAJCOM
functional manager. Award of the 7-skill level also requires
completion of a 7-skill level craftsman course (if required),
mandatory requirements listed in AFECD, completion of
time in upgrade training (if applicable) as determined by the
Career Field Manager, recommendation by the supervisor,
and approval of the commander. Individuals in retraining
status (Training Status Code G) are subject to the same
training requirements and completion of upgrade training
timelines (if applicable) as determined by the Career Field
7-skill level. (see Notes 3 and 7).

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 53
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the enlisted Airman
then the enlisted Airman is
qualified for award of AFSCs,
SDI, or Chief Enlisted Manager
code as indicated (See Note 7)
Manager. Group Commanders may approve time-in-training
waivers. Note: For additional information on time-in-
training waivers see Table 2.7.
5
is a Senior Master Sergeant, possesses a 7-skill level AFSC
which is the normal input source into 9-skill level AFSC
(use the most current AFECD Structure Chart), meets
mandatory 9-skill level requirements in the specialty
description in the AFECD, is recommended by supervisor,
and approved by their commander.
9-skill level. (see Notes 3 and 7).
6
is a Chief Master Sergeant or Chief Master Sergeant-select
and has 9-skill level feeder AFSC that is normal input source
into Chief Enlisted Manager code (use the most current
AFECD Structure Chart).
Chief Enlisted Manager code.
(see Notes 3, 4, and 5).
7
is approved for duty in a SDI or RI.
SDI or RI. (see Note 6).
8
is approved for Wounded Warrior designation by
AFPC/DPFW.
appropriate 9WXXX RI (See
Note 9).
Notes:
1. Designate 1-skill level AFSC to identify initial classification or retraining into an AFSC. Remove it
when the member is upgraded to the 3-skill level following completion of the 3-skill level-awarding
course, disqualified from the AFSC, or retrained into another specialty.
2. Effective date of award is the course completion date or on-the-job-training completion date.
Remove the 1-skill level AFSC.
3. AFSCs withdrawn as a result of a reduction in grade may be restored immediately upon promotion,
provided the enlisted Airman meets all current mandatory requirements for the award of the withdrawn
AFSC.
4. Effective date of award for Chief Master Sergeant-selects is the date of release of the selection list.
5. The 9-skill level feeder skill is not required for the award of Chief Enlisted Manager code to Chief
Master Sergeant assigned or authorized permanent duty by HQ USAF/A1LE outside the career field
ladder.
6. The effective date of the award of SDI or RI will coincide with the effective date of the Control
AFSC according to Table 2.13.
7. Must possess the prerequisite AFSC skill level for award of the next higher skill level. (T-2).
8. Complete knowledge training on all tasks taught in the initial skills training; complete duty position
requirements identified by the supervisor and all mandatory requirements.
9. AFPC/DPFW determines Wounded Warrior eligibility and updates the appropriate 9WXXX RI to
the secondary or third (or fourth for enlisted) AFSC for tracking purposes only. No further updates or
removals are allowed other than by AFPC/DPFW. RIs 9WXXX will not be updated to the Primary
AFSC, Control AFSC, or Duty AFSC.
10. To be awarded AFSC 1AX5X/1UX5X, the trainee must complete requirements as listed in the
applicable MAJCOM aircrew training directives, initial qualification training, and a successful AF
Form 8, Certificate of Aircrew Qualification. (T-2).
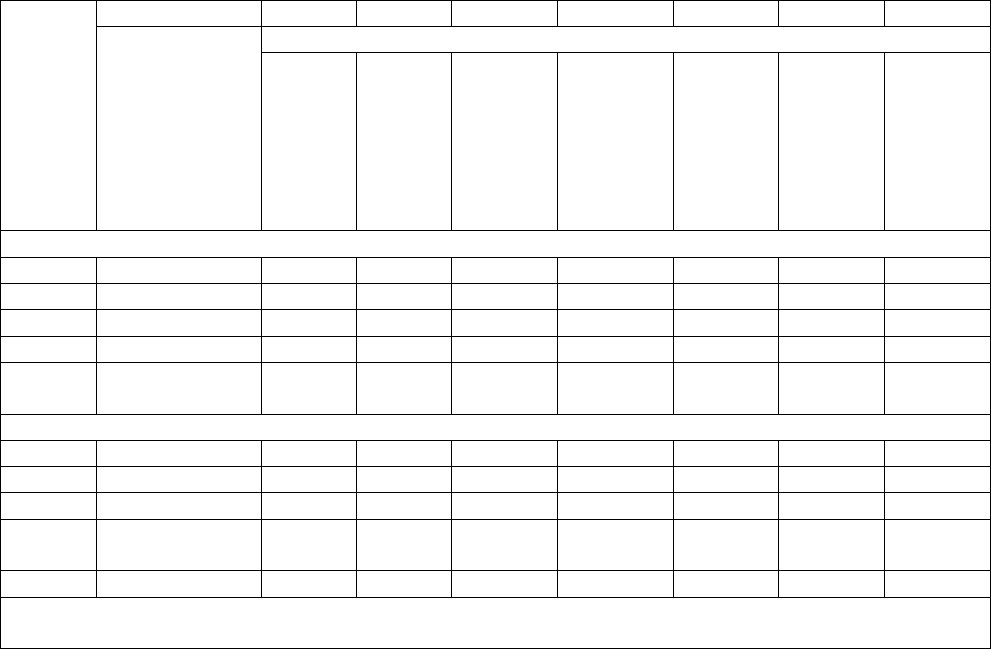
54 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.12. Grade and Skill-Level Authorizations for Use in Establishing Manpower
Positions.
I
T
E
M
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
Required
Skill-Level
Authorized Grade (see Note)
Airman
1st
Class
Senior
Airman
Staff
Sergeant
Technical
Sergeant
Master
Sergeant
Senior
Master
Sergeant
Chief
Master
Sergeant
or Chief
Master
Sergeant
-select
AFS With 5 Skill
1
3-skill level
X
2
5-skill level
X
X
3
7-skill level
X
X
4
9-skill level
X
5
Chief Enlisted
Manager code
X
AFS Without 5 Skill
6
3-skill level
X
X
7
7-skill level
X
X
8
9-skill level
X
9
Chief Enlisted
Manager code
X
10
SDI or RI
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Note: The authorized grade for SDI 8F000 must be Master Sergeant or higher

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 55
Table 2.13. Determining the Control AFSC (CAFSC) for Enlisted Personnel in Training
Status.
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the enlisted Airman is
then the Control AFSC is
1
a basic trainee or performing at a helper level and is
entered into training for SDI, RI, or 3-skill level AFSC.
an SDI, RI, or a 1-skill level AFSC.
2
entered into retraining for SDI, RI, or 3-skill level AFSC.
an SDI, RI, or 1-skill level AFSC.
(see Notes 1, 2, and 3)
3
in normal upgrade training from awarded 3-skill level
AFSC
the highest awarded AFSC in career
ladder. (see Note 4)
4
Chief Master Sergeant or Chief Master Sergeant-select in
retraining status
the Chief Enlisted Manager code of
assignment.
Notes:
1. Effective date of change for the Control AFSC for unclassified enlisted personnel (9U000) is the date of
receipt of training or transaction identifier code AA47Q, whichever comes first.
2. Control AFSC effective date (for retraining through a formal school [including special duty]) is the date
the Airman departed current duty station for TDY to accomplish required training (either en-route to new
duty station or when returning to present duty station). If there is not a PCS or PCA and no formal training,
the Control AFSC will be changed when assigned duty. Do not change Control AFSC prior to date of
departure. Exception: For RegAF disqualified Airmen (9A000 or 9A100), upon retraining approval in
MilPDS, the Control AFSC and Primary AFSC is automatically updated to the 1-skill level AFSC. For
ANG Airmen, update the entry level Control AFSC (and award the entry level AFSC to the applicable
Primary, Second, Third, or Fourth AFSC) at the time the Airman is assigned to the duty position with the
AFSC in which they will be attending the 3-skill level-awarding course.
3. Individuals returned to previous duty station following completion of training and who work in their
previous AFSC will be reported as working duty out of Control AFSC. The Duty AFSC will match the
position the individual is assigned to, but the Control AFSC will remain the new AFSC. (T-3).
4. Skill restrictions of paragraph 2.3.33 apply.

56 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 2.14. Determining CAFSC as a Result of Assigning or Withdrawing Awarded
CEMs, AFSCs, SDIs, or RIs.
R
U
L
E
A
B
If the enlisted Airman
then the Control AFSC is
1
is assigned permanent duty (assigned
to a funded manpower authorization,
RegAF only) in an already awarded
AFSC other than Control AFSC
highest awarded AFSC in ladder of assignment as identified in
the AFECD Enlisted Classification Structure Chart. (see Notes
1 and 3)
2
is assigned permanent duty (assigned
to a funded manpower authorization,
RegAF only) in Chief Enlisted
Manager code, RI, or SDI
Chief Enlisted Manager code, RI, or SDI. (see Notes 1, 2, and
3)
3
is a prisoner, not dropped from rolls,
and is in confinement (not to be used
for pretrial status)
RI 9J000. (see Note 4)
4
is selected as an officer trainee
RI 9T100 effective on class start date.
5
has awarded AFSC, RI, or SDI
withdrawn, and has no other awarded
AFSC (1XXXX – 7XXXX)
RI 9A000, 9A100, 9A200 or 9A300 effective the date approved
by AFPC/DP2SSM. Only AFPC/DP2SSM is authorized to
update or change these RIs for RegAF. ANG/AFR FSSs
update ARC Airmen. (see Notes 2 and 5)
6
an Air Force Return to Duty program
(see AFMAN 31-115, Vol 1, Air Force
Corrections System) candidate being
returned to an regular unit and is no
longer qualified to serve in previously
awarded AFSC (s)
RI 9A400, (approved and updated by AFPC/DP2SSM only)
7
is awaiting appellate review (duty
status code 52)
RI 9A200 only (approved and updated by AFPC/DP2SSM
only) if member is disqualified
8
has had the awarded AFSC associated
with the Control AFSC downgraded in
accordance with paragraph 2.4.
At the skill level authorized in paragraph 2.3.31.
Notes:
1. See Note 2, Table 2.11.
2. RIs 9W000 – 9W900 are not authorized for Control AFSC.
3. Skill level restrictions reflected in paragraph 2.3.33 apply.
4. Only use RI 9J000 upon confinement as a result of court-martial or when confined as the result of conviction
by a United States state or federal court or foreign civilian court. Do not use for Airmen in pretrial confinement
status. AFPC/DP3AM updates the Control AFSC to RI 9J000 following receipt of orders directing convicted or
court-martialed individual(s) to enter civilian or military confinement under the administrative control of the Air
Force Correction System at HQ AFSFC/SFC, JBSA-Lackland TX.
5. Effective date of disqualification (and Control AFSC) for enlisted Airmen. Medical disqualification actions
use the date of medical disqualification on the AF FM 422 or DD Form 2992 as the effective date of AFSC
disqualification. For failure to maintain mandatory AFSC, SDI, RI, or Chief Enlisted Manager qualification
standards, the disqualification (Control AFSC effective date) is the date of the triggering event and/or document
rendering the Airman no longer eligible to retain the AFSC, SDI, RI, or Chief Enlisted Manager code in
accordance with the requirements for retention of the identifier (AFSC, SDI specialty description, RI, Chief
Enlisted Manager code, etc.).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 57
2.4. Downgrading and Withdrawing AFSC.
2.4.1. Downgrading AFSCs or Withdrawing Awarded AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Manager
Codes, SDIs, or RIs. The FSS and unit monitors the downgrade of AFSCs as well as the
withdrawal of AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Manager codes, SDI, and RI codes and processes
appropriate forms and actions according to this manual, the Officer and Enlisted AFSC
Disqualification execution guidance in the myPers website and the AFOCD andAFECD (see
Table 2.17.). Commanders review conditions in paragraphs 2.4.1.3 through 2.4.3.3.11 to
determine when to downgrade or withdraw an awarded AFSC, SDI, RI, or Chief Enlisted
Manager code. FSSs ensure downgraded enlisted AFSCs match grade and skill-level
authorizations in Table 2.12. Commanders and supervisors considering downgrade or
withdrawal recommendations need to carefully evaluate all of the facts before proceeding.
2.4.1.1. Actions under this chapter resulting in the downgrade of an awarded AFSC skill
and/or qualification level or withdrawal of the AFSC, SDI, RI or Chief Enlisted Manager
code (other than due to lack of recent performance) are categorized as either “not within
the Airman’s control” (“not for cause”) or “within the Airman’s control (“for cause”).
2.4.1.1.1. Typical downgrade or disqualification actions characterized as “not within
the Airman’s control” are medical disqualification (except alcohol and drug abuse
prevention and treatment failure), some training failures (purely beyond the Airman’s
capabilities despite meeting entrance requirements), some failures to maintain
mandatory AFSC qualification requirements, etc.
2.4.1.1.2. Downgrade or withdrawal actions characterized as within the Airman’s
control (“for cause”) include other training failures, medical disqualification due to
alcohol and drug abuse prevention and treatment failure, substandard duty
performance, denial and/or revocation of security clearance, failure to maintain AFSC
qualification requirements, etc.
2.4.1.2. AFSC withdrawal cases (other than for lack of recent performance) are processed
through the CMS as AFSC disqualification actions.
2.4.1.2.1. AFPC/DP2SSM is the approval authority for all RegAF AFSC
disqualification actions and the resulting AFSC withdrawal, award, redesignation
actions. See Table 2.17 for approval authority.
2.4.1.2.2. For AFSC downgrade or withdrawal CMS case of ARC Airmen,
AFPC/DP2SSM will forward the CMS case to NGB/A1D or HQ ARPC/DPAT, for
internal processing. ANG and AFR squadron or flight commanders are the approval
authority for their assigned Airmen (For IRs and/or Participating Individual Ready
Reserve Airmen, the RegAF commander in coordination with the Airman’s detachment
commander is the approval authority.) Detachment will update MilPDS. If approved,
the servicing ARC FSS updates MilPDS. AFPC/DP2SSM, NGB/A1D, or HQ
ARPC/DPAT may initiate a disqualification action when available evidence in MilPDS
indicates the Airman is ineligible to remain in the AFSC and direct the Military
Personnel System or unit to complete the unit or base-level requirements for
disqualification. Similarly, the same OPR may initiate or reopen a closed CMS AFSC
disqualification case to change the RI to the most appropriate under the new
circumstances when an enlisted Airman’s eligibility for retraining changes following

58 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
initial disqualification. AFPC/DP2SSM determines eligibility for award of and updates
RI 9A400 (return to duty program) for RegAF Airmen.
2.4.1.3. Downgrading or withdrawing an AFSC, SDI, RI, or Chief Enlisted Manager code
is not to be used as an alternative to more appropriate disciplinary or quality force action.
Conversely, while punitive action may not be taken against an individual solely because of
their failure to remain qualified in an AFSC at a specific skill level, the reason for
downgrade may require appropriate administrative action.
2.4.1.4. Lack of Recent Performance (Enlisted Only). FSS will downgrade AFSCs using
Table 2.15.
2.4.1.5. Enlisted Airman Reduced in Grade (AFSC Skill Level Downgrade). The FSS
(detachments for IRs) downgrades to the skill level as shown in Table 2.16. Restore
AFSCs downgraded due to reduction in grade effective upon promotion, provided the
enlisted Airman meets all mandatory requirements. Reinstate original effective dates when
demotion appeals result in restoration of former grade and original date of rank.
2.4.1.6. Downgrading a skill level for substandard duty performance (Enlisted Only). Use
the same procedures outlined in paragraph 2.4.4 for AFSC disqualification (except for
CMS case initiation if the downgrade is concurred with at the local level). However, if the
commander, supervisor, Airman, and FSS concur with the AFSC downgrade action, the
FSS approves the downgrade. No CMS case is required under these circumstances. If one
of the above non-concurs, create the CMS case for AFPC/DP2SSM processing and
approval or disapproval. Note: See AFI 36-2502, Enlisted Airman Promotion/Demotion
Programs, for demotion instructions, as applicable.
2.4.1.7. Downgrading an improperly awarded AFSC. When discovered, the unit requests
withdrawal of an improperly awarded enlisted AFSC. The request (official memorandum
or email format) contains a synopsis of the requested action, supporting documentation,
and a recommendation from the Airman's supervisor. An assessment by an individual
technically proficient in the specialty accompanies the AFSC downgrade request. This
assessment addresses the Airman’s training and capability to perform in the AFSC at the
current skill level. With FSS commander concurrence, the unit commander is the approval
authority.
Table 2.15. Downgrading Enlisted AFSCs for Lack of Recent Performance (see Note).
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
If the Airman possesses an
awarded AFSC at the
and the date last performed
duty in the AFSC has been
then downgrade the
awarded AFSC to
1
5-skill level
4 years
3-skill level
2
7-skill level
6 years
3-skill level
3
9-skill level
6 years
3-skill level
Note: AFSCs not downgraded using the above table are to be downgraded and/or withdrawn
effective the date the action should have taken place.
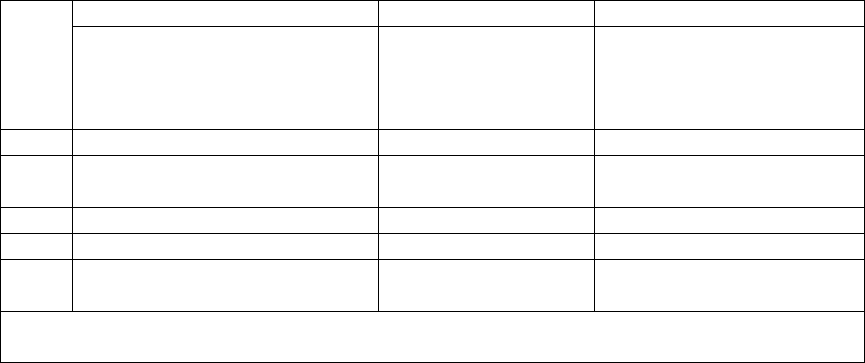
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 59
Table 2.16. Downgrading AFSCs as a Result of Demotion.
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
If the enlisted Airman is
demoted to
downgrade the
Control AFSC to
downgrade the Primary
AFSC and other awarded
AFSCs (when applicable)
to
1
Senior Master Sergeant
9-skill level
9-skill level
2
Technical Sergeant or Master
Sergeant
7-skill level
7-skill level
3
Staff Sergeant (See Note)
5-skill level
7-skill level
4
Senior Airman (see Note)
5-skill level
5-skill level
5
Airman Basic through Airman
1st Class
3-skill level
5-skill level
Note: Downgrade the Control AFSC and awarded AFSC to 3-skill level for AFSCs without a
5-skill level.
2.4.2. Withdrawing Awarded AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Managers, SDIs, or Reporting
Instructions (Non-Disqualification). The FSS monitors the withdrawal of AFSCs and
processes appropriate forms and actions according to this manual. Unit commander is the
approval authority.
2.4.2.1. 3-skill level AFSCs are withdrawn after two years of nonperformance whether
downgraded using Table 2.15 or never having been upgraded to the 5 or 7-skill level (See
Table 2.14 to determine Control AFSC).
2.4.2.2. SDIs and RIs are withdrawn after eight consecutive years of nonperformance.
2.4.2.3. Although downgrade action based on consecutive nonperformance in the specialty
may or may not have been accomplished, AFSCs awarded at the 7- or 9-skill level are
withdrawn after eight years, and 5-skill level (3-skill level, if no 5-skill level exists in the
ladder) are withdrawn after six years. Failure to downgrade or withdraw AFSCs within
the specified time frames does not indicate the Airman remains qualified. The AFSC(s)
are downgraded and/or withdrawn (as appropriate) upon discovery effective the date the
action should have taken place.
2.4.2.4. Re-awarding AFSCs that are withdrawn under this provision at the 3-skill level
for RegAF Airmen requires approval by the Air Force Personnel Center assignment
manager and RegAF CFM. The Airman is required to meet mandatory AFSC entry, award,
and retention specialty requirements as listed in the AFECD for re-award. (T-2). The
commander’s request for re-award includes written certification by a technical advisor
proficient in the AFSC of the Airman’s eligibility and proficiency level for consideration.
The technical advisor assesses the Airman’s training, experience, and current capability to
perform in the AFSC at the current 3-skill level. For those times when a technical advisor
proficient in the AFSC is not available, nearby bases and the MAJCOM staff may be able
to assist with the certification. Upgrade to the highest previously held skill level only
requires qualification training and duty position certification by the supervisor.
2.4.2.4.1. ANG and AFR Command CFMs are the approval authorities for ARC
enlisted actions review and approval in accordance with their waiver approval authority
in Table 2.5. The respective ARC FSSs finalize the action.
60 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.4.2.4.2. Documentation requirements for ARC Airmen include a copy of the
certified Career Field Education and Training Plan, position description, or coordinated
memorandum for record with supervisor and command of host location to document
tasks performed. All documentation will be provided to the servicing FSS for
ANG/AFR FSS verification. (T-2).
2.4.2.5. Lack of recent performance does not apply to feeder AFSCs (see paragraph
2.3.32.). Note: Time spent in a TDY status (contingency or other) or performing duties in
an AFSC, SDI, or RI other than the Control AFSC counts as time performing in the
specialty. Example: An Airman’s Primary AFSC, Control AFSC, and Duty AFSC is
3P0X1 and is on TDY performing duty in a previously awarded AFSC (that has not been
withdrawn for lack of recent performance). This performance establishes a new date from
which to count years outside of the AFSC.
2.4.2.6. Withdrawing due to lack of recent performance (Officer):
2.4.2.6.1. Rated AFSCs are not subject to withdrawal due to lack of recent
performance.
2.4.2.6.2. Do not withdraw an awarded AFSC for at least three years after the date that
duty was last performed.
2.4.2.6.3. Do not withdraw an awarded AFSC based on extensive formal training (20
weeks or longer) for at least five years after the date that duty was last performed.
2.4.2.6.4. Officers may request withdrawal of awarded AFSCs after meeting the
requirements of paragraphs 2.4.2.6.2 or 2.4.2.6.3. The FSS reviews the request and
forwards to AFPC assignment manager (RegAF) for final action.
2.4.2.6.5. Withdraw officer SDIs after eight years of non-performance.
2.4.2.6.6. Reporting Identifiers: Withdraw awarded training RIs following completion
of training and award of the associated AFSC.
2.4.2.7. Withdrawing due to prerequisite AFSC (FSS Action).
2.4.2.7.1. Enlisted. When an enlisted Airman progresses to the next higher skill level
in the same career ladder, delete the lower skill level AFSC. Exception: When enlisted
Airmen progress to a 5-, 7-, or 9-skill level AFSC or Chief Enlisted Manager code in
which two or more AFSCs combine, retain the feeder AFSC as an awarded AFSC.
2.4.2.7.2. Officer. After award of the qualified or intermediate-level AFSC, remove
the entry-level officer AFSC. After awarding the qualified (3-level) AFSC, remove the
intermediate-level AFSC (2- level), as applicable.
2.4.2.8. Withdrawing an improperly awarded AFSC (Officer and Enlisted). When
discovered, the FSS and/or unit requests withdrawal of an improperly awarded AFSC. The
request is in official memorandum or email format and contains a synopsis of the requested
action, supporting documentation, and a recommendation from the individual's supervisor.
An assessment by an individual proficient in the specialty addresses the individual’s
training and capability to perform in the improperly awarded AFSC at the current skill
and/or qualification level. The FSS submits an AFSC disqualification action with the
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 61
request and assessment via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM for approval or disapproval. Final
approval authority for RegAF Airmen is AFPC/DP2SSM.
2.4.3. Withdrawing Awarded AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Manager Codes, SDIs, or RIs
(Disqualification). The FSS and unit monitors report disqualifying circumstances for
continued retention of Officer and Enlisted AFSCs, Chief Enlisted Manager Codes, SDIs, and
RIs via a CMS AFSC disqualification case. Submit a CMS AFSC disqualification case with
the draft (unsigned) Air Force Form 2096 and supporting documentation to AFPC/DP2SSM
for review. Unit Commander is the approval authority where noted; otherwise approval
authority for RegAF Airmen is AFPC/DP2SSM. Submit documentation in the CMS AFSC
disqualification case according to this manual, the AFOCD/AFECD and the Officer and/or
Enlisted AFSC disqualification execution guidance on the myPers website.
2.4.3.1. AFPC/DP2SSM determines qualifications for, approves or disapproves
disqualification actions, and updates RIs (9A000, 9A100, 9A200, 9A300, 9A400 and
9A500) for RegAF enlisted Airmen upon initial disqualification from all awarded AFSCs
and 96A0 or 96B0 for RegAF officers.
2.4.3.2. Follow-on utilization of disqualified Airmen will be in accordance with AFI 36-
2110, AFI 36-3208, AFI 36-3209 Separation and Retirement Procedures for Air National
Guard and Air Force Reserve Members for AFR, and Chapter 6 of this manual.
2.4.3.3. Airmen disqualified from their current AFSC and retaining a valid AFSC to which
eligible to return are normally returned to that AFSC instead of being considered for
retraining. Note: AFSC disqualification actions involving AFSCs in which the Airmen
have received or are receiving Initial Enlistment or Selective Reenlistment Bonus payments
in their current enlistment require review by the appropriate AFPC/NGB/ARPC offices for
bonus termination and/or recoupment action according to AFMAN 36-2032 and AFI 36-
2606.
2.4.3.3.1. Substandard Performance (Withdrawal (Disqualification)). Commander
initiates withdrawal (disqualification) action when duty performance indicates an
officer or enlisted Airman is not performing tasks associated with their skill and/or
qualification level over an extended period of time. Review the individual's record for
adequate training. Substandard duty performance relates directly to the Airman having
been trained to properly perform the assigned duties (and documented accordingly) and
subsequently does not perform them correctly despite repeated task decertification,
retraining, recertification, and continued substandard performance of the same task(s).
Note: Most officer AFSCs do not require task certification. For RegAF Airmen,
contact AFPC/DP2SSM to review circumstances or issues or documentation believed
to support AFSC disqualification under this paragraph prior to creating the CMS case.
If determined sufficient, the FSS submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS (in
accordance with the execution guidance in the myPers website) to AFPC/DP2SSM for
processing.
2.4.3.3.2. Commander Actions. Notify the Airman by memorandum that AFSC
withdrawal has been initiated on an Air Force Form 2096. The Airman concurs or non-
concurs at the time of notification, and then signs and dates the Air Force Form 2096.
The commander's notification will include: The reasons for the action (specifically
each documented failure to perform the duties to standard) and advisement to the
62 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Airman that if the Airman non-concurs with the action, the Airman may submit a
written rebuttal when interviewed by an evaluation official. (T-2). The commander
submits the following documentation to the FSS:
2.4.3.3.2.1. Notification letter signed by unit commander with the completed,
signed, and dated Air Force Form 2096 prepared according to the Officer or
Enlisted AFSC disqualification execution guidance in the myPers website.
2.4.3.3.2.2. Last three performance reports; or, if the Airman has not received a
performance report, a memorandum from the member's immediate supervisor
assessing past duty performance. Note: It is very difficult to support
disqualification for substandard duty performance when the officer or enlisted
performance report reflects the Airman is meeting or exceeding standards.
However, if the substandard duty performance occurred after the closeout of the
last performance report, provide a memorandum from the Airman’s immediate
supervisor assessing duty performance from the closeout date of that report to
present.
2.4.3.3.2.3. Supporting training documentation. Note: This disqualification
reason is the most difficult to use in that the enlisted Airman’s training
documentation needs to show the unit has decertified the enlisted Airman from
specific tasks in which the enlisted Airman has performed in a substandard manner,
been retrained, recertified, and continues to perform in a substandard manner
despite the additional and/or remedial training, etc.
2.4.3.3.2.3.1. Two complete cycles of decertification, retraining,
recertification, and monitoring performance are sufficient for this purpose.
2.4.3.3.2.3.2. For officers, if defined training requirements exist and the officer
fails to perform to standards, use the same steps and documentation as identified
for enlisted.
2.4.3.3.2.3.3. Depending on the AFSC, there may be no documentation to
support the officer has been trained (initial skills training, Career Field
Education and Training Plan, etc.) and substantiating the substandard duty
performance may be much more difficult to support. Where such defined
training requirements do not exist, use CFM guidance to validate substandard
duty performance. Misconduct is not the same as substandard duty
performance. While such documentation can be added as attachments to the
notification memo, they may not be of value in determining approval or
disapproval of the case.
2.4.3.3.2.4. Letters of counseling (or other administrative documentation) relative
to the duty performance cited as the reason for the disqualification action.
2.4.3.3.2.5. Any additional documentation germane to the case.
2.4.3.3.3. If the commander, supervisor, Airman, and FSS/CC concur with the AFSC
withdrawal (disqualification) action, the FSS or unit documents and forwards the action
via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM. AFPC/DP2SSM reviews and approves or disapproves
and update MilPDS for RegAF approvals.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 63
2.4.3.3.4. When the Airman or the FSS Chief does not concur with the withdrawal
(disqualification) action, the FSS/CC either disapproves the request if it is considered
without merit, or appoints a disinterested evaluation official.
2.4.3.3.4.1. The evaluation official is to be a field grade officer or Senior Non-
Commissioned Officer, senior in grade to the individual being reviewed. The
evaluation official cannot be in the member’s chain of command. (T-2).
2.4.3.3.4.1.1. The evaluation official must have a thorough understanding of
AFSC withdrawal and downgrade procedures.
2.4.3.3.4.1.2. The evaluation official reviews the case file and the supporting
documentation.
2.4.3.3.4.1.3. The evaluation official obtains a written evaluation of the
substandard duty performance relative to the requirements of the AFSC by a
technical advisor qualified with the technical aspects of the specialty involved
(the technical advisor cannot be in the individual’s chain of command).
2.4.3.3.4.1.4. The evaluation official explains the recommended action and
counsels the Airman, advises him or her of the right to submit a written rebuttal
that may include statements from people knowledgeable of the duty
substandard performance identified, and helps the Airman prepare any written
rebuttal. Airmen not submitting a rebuttal acknowledge such in writing as well
as understanding of "disqualified Airman processing" according to the Officer
or Enlisted AFSC disqualification execution guidance in the myPers website.
2.4.3.3.4.1.5. The evaluation official prepares a written summary within 30
days with recommendation as a part of the official disqualification case file for
the FSS/CC. If base-level actions take more than 30 days to complete, include
an explanation in the case file for the delay.
2.4.3.3.4.2. The FSS/CC reviews and disapproves the action (returns to unit) or
recommends approval and forwards the case file via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM for
review and approval or disapproval for RegAF Airmen.
2.4.3.3.4.3. For technical evaluation of training provided for enlisted RegAF
Airmen, DP2SSM may forward the CMS case to AFPC/DP2LWD and then to the
RegAF CFM if additional evaluation is needed.
2.4.3.3.5. Certifying and Withdrawing Certification for AFOSI (AFSC withdrawal
and/or disqualification).
2.4.3.3.5.1. The AFOSI/CC has sole authority for certifying and withdrawing
AFOSI certification for RegAF and ARC Airmen in the 71XX and 7SXXX AFSCs.
2.4.3.3.5.2. Withdrawing certification requires the withdrawal of the AFSC
(disqualification) unless the AFOSI/CC grants an exception. The FSS submits
AFSC disqualification actions via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM.
64 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.4.3.3.6. Failure to Maintain Mandatory AFSC, SDI, or Chief Enlisted Manager
Qualification Standards (withdrawal (disqualification)).
2.4.3.3.6.1. The FSS and/or unit submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS
to AFPC/DP2SSM. For RegAF Airmen, if approved, DP2SSM will withdraw the
AFSC, SDI, or Chief Enlisted Manager code if either of the following occurs:
2.4.3.3.6.1.1. An officer fails to maintain the mandatory award and/or retention
(not entry) specialty requirements listed as "other" in the AFOCD specialty
descriptions. (T-2). or
2.4.3.3.6.1.2. An enlisted Airman fails to meet award and retention (not entry)
specialty requirements in specialty descriptions contained in the AFECD. (T-2).
2.4.3.3.6.2. For enlisted Airmen, do not use failure to meet a mandatory AFSC
entry requirement as the basis for AFSC withdrawal after award of an AFSC above
the 1-skill level.
2.4.3.3.6.3. For enlisted Airmen, request withdrawal of the AFSC or Chief Enlisted
Manager Code if an Airman fails to maintain the mandatory qualifications listed as
award and/or retention requirements for the 3-, 5-, 7-, 9-, or Chief Enlisted Manager
skill level in the AFSC specialty description. Exception: An enlistee with PS, who
has an AFSC awarded according to paragraph 2.2.3, retains the AFSC pending
determination of eligibility for reinstatement of mandatory security clearance if
previously administratively withdrawn (DoDI 5200.02, DoD Personnel Security
Program (PSP), DoDM 5200.02_AFMAN 16-1405, Air Force Personnel Security
Program).
2.4.3.3.7. Medical Disqualification (Withdrawal (Disqualification)). When the
medical evaluation reviewing or approving authority determines a medical defect
prevents the individual from being used in the awarded AFSC, an AF Form 422 or DD
Form 2992 is generated. The FSS submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS
to AFPC/DP2SSM for approval or disapproval. DP2SSM refers RegAF line of the Air
Force officer disqualification cases to AFPC/DP2OSS, Special Duty Career
Management Section for review and follow-on utilization consideration, if
disqualification is approved. See also DAFMAN 48-123, Medical Examinations and
Standards, the Medical Standards Directory, and AFI 48-133, Duty Limiting
Conditions, for further guidance.
2.4.3.3.7.1. A change of the physical profile from the AFSC entrance requirement alone
(to include enlisted physical capacity and/or stamina, upper body, lower body, hearing,
eyes, and stability minimums) does not disqualify an enlisted Airman for continued duty
in the AFSC. Consider other factors (such as recorded evaluation of duty performance,
extent to which physical restriction does or would affect duty performance, etc.) in
determining whether the current non-temporary physical limitations preclude the Airman
from performing effectively in the awarded AFSC. Submit documentation describing the
impact for medical evaluation reviewing or approving authority consideration. Do not send
in the AFSC disqualification case. Ensure the completed AF Form 422 or DD Form 2992
is submitted with the disqualification action. Temporary limitations do not qualify for
disqualification under paragraph 2.4.3.3.8.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 65
2.4.3.3.7.2. If the Airman has been processed through the Disability Evaluation
System (AFI 36-3212, Physical Evaluation for Retention, Retirement, and
Separation) and retained on active duty, the local Medical Evaluation Board
reviewing and approval authority provides the FSS an AF Form 422. The AF Form
422 comments should clearly define the scope of the medical problem and whether
the physical limitations preclude the Airman from performing effectively in the
awarded AFSC. Complete the AF Form 422 using provisions in DAFMAN 48-
123, the Medical Standards Directory, and AFI 48-133.
2.4.3.3.8. Prerequisite AFSC (FSS action):
2.4.3.3.8.1. Officers Withdrawal. After award of the qualified or intermediate-
level AFSC, delete the entry-level officer AFSCs. After awarding the qualified 3-
level AFSC, delete the intermediate-level AFSC (2- level).
2.4.3.3.8.2. Enlisted Withdrawal. When an enlisted Airman progresses to the next
higher skill level in the same career ladder, delete the lower skill level AFSC.
Exception: When enlisted Airmen progress to a 5-, 7-, or 9-skill level AFSC or
Chief Enlisted Manager code in which two or more AFSCs combine, retain the
feeder AFSC as an awarded AFSC.
2.4.3.3.9. Medically Disqualified for Aviation Services. Aviation service
disqualification actions are processed in accordance with AFMAN 11-402, Aviation
and Parachutist Service. Following disqualification from aviation service, AFSC
disqualification actions are processed using the CMS, as indicated below. The FSS
and/or unit submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM for
approval or disapproval on RegAF Airmen.
2.4.3.3.9.1. The effective date would be the date on the AF Form 422, DD Form
2992, or aeronautical orders provided by the flight records office.
2.4.3.3.9.2. Rated Officers. Rated AFSCs (11XX, 12XX, 13BX, 18XX) are
retained for four years from the medical disqualification date from aviation service
only if the officer continues to perform duty in the rated AFSC not involving flying.
However, further duty not involving flying in a rated AFSC requires AFPC/DP2OR
(NGB/A1PO or HQ ARPC/DPAT for ARC Airmen) approval. Four years after the
medical disqualification from aviation service while performing duty in a rated
AFSC not involving flying, the rated AFSC is withdrawn unless AFPC/DP2OR
(NGB/A1PO or ARPC/DPAT for ARC Airmen) approves further duty beyond the
initial four years. When rated officers medically disqualified from aviation service
are not selected to perform non-flying rated duties and/or are determined no longer
needed to perform in this capacity, the FSS and/or unit submits an AFSC
disqualification action via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM. Applicable medical
disqualification supporting documents include AF Form 422, DD Form 2992, or an
aviation order assigning Aviation Service Code 03. An AFSC withdrawn under
this provision may be re-awarded at the appropriate qualification level in
accordance with paragraph 2.3.6 if the medical defect no longer exists (or is
waived by appropriate authority) and the individual is returned to active flying
status. The unit commander coordinates with AFPC/DP2OR (NGB/A1PO or
ARPC/DPAT for ARC Airmen) prior to submission of the reinstatement request
66 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
for proposed assignment instructions. Approval authority for reinstatement is the
RegAF CFM for the rated AFSC per paragraph 2.3.6.
2.4.3.3.9.3. Career Enlisted Aviators Withdrawal (Disqualification). Withdraw
Career Enlisted Aviators AFSCs 365 days after medical authority signs AF Form
422, DD Form 2992, or aeronautical order placing Career Enlisted Aviator on duty
not to include flying (Duty Not to Include Flying, Aviation Service Code 04), or
when assigned Aviation Service Code 03 (medically disqualified), whichever
occurs first.
2.4.3.3.9.4. Nonrated Officers. Withdraw officer nonrated AFSCs requiring
qualification for aviation service or parachute duties when permanently medically
disqualified via AF Forms 422, DD Form 2992, or aviation order assigning
Aviation Service Code 03. Officers temporarily disqualified for failure to maintain
medical fitness according to AFMAN 11-402, may retain their AFSCs for 9 months
from the date assigned Aviation Service Code 03 (medical disqualification), unless
further extended by AFPC/DP2SSM. An officer’s non-prefixed AFSC in and of
itself may not require qualification under AFMAN 11-402 to retain the AFSC. In
these instances, the disqualification case is to address the X or J prefixes only and
the officer retains the non-prefixed AFSC if still eligible.
2.4.3.3.10. Disqualified for Aviation Service for Other Than Medical Reasons
(Withdrawal (Disqualification)). When an Airman is removed from aviation service
for other than physical reasons (Aviation Service Codes 00, 01, 02, 05, 06, 07, 08, or
09), the FSS submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS to AFPC/DP2SSM for
review and approval or disapproval. The CMS case includes the documentation
supporting the disqualification (loss of security clearance, training failure, failure to
maintain AFSC specialty description qualification requirements, etc.).
AFPC/DP2SSM is the approval authority for RegAF Airmen. The effective date, if
approved, will be the effective date on the aeronautical order. (T-2). DP2SSM refers
the disqualification case to AFPC/DP2OSS for review and follow-on utilization
consideration for RegAF officers, if approved.
2.4.3.3.11. Failing to Progress While in Upgrade Training (Withdrawal
(Disqualification)):
2.4.3.3.11.1. Officers.
2.4.3.3.11.2. For officers failing to meet proficiency requirements for upgrade to
the intermediate (if applicable) or qualified AFSC, identify the training provided
and other associated documentation supporting the denial of upgrade via CMS to
AFPC/DP2SSM for approval or disapproval.
2.4.3.3.11.3. Reclassification or retention of the officer will be considered based
on Air Force needs.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 67
2.4.3.3.11.4. Enlisted.
2.4.3.3.11.4.1. If the training manager removes an individual in upgrade
training in accordance with AFI 36-2670, Total Force Development, the FSS
submits an AFSC disqualification action via CMS to HQ AFPC/DP2SSM.
2.4.3.3.11.4.2. Withdraw the AFSC when an enlisted Airman is eliminated
from an AFSC-awarding course or formal training course required for skill
progression and listed as mandatory in the AFECD. Note: See Chapter 6 of
this manual for disposition of retraining formal school eliminees.
2.4.3.3.11.5. AFSC withdrawal (disqualification) for Airmen returned to active
duty under the Return To Duty Program (AFMAN 31-115, Volume 1, Department
of the Air Force Corrections System) and who no longer qualify to retain awarded
AFSCs. HQ AFSFC initiates withdrawal of awarded AFSCs for which the Airman
no longer qualifies via CMS to Reenlistments and Special Programs
(AFPC/DPSIC) for review, processing, and updating of RI 9A400. This RI remains
until such time as the Airman is retrained or separated and/or discharged.
2.4.3.3.11.6. Enlisted Airmen leaving a SDI, regardless of reason (Voluntary or
Involuntary) without an awarded military skill (valid awarded AFSC at the 3-level
or higher) to which they are eligible to return, must be reviewed for future
utilization.
2.4.3.3.11.6.1. Assess feasibility of returning to AFSCs previously withdrawn
(or to have been withdrawn) for lack of recent performance.
2.4.3.3.11.6.2. If the RegAF Airman cannot be utilized in a prior AFSC, the
unit commander or FSS notifies AFPC/(DP2L, DP2O, or DP2N, as applicable)
that the Airman is surplus to requirements and does not possess a valid AFSC
(not 8XXXX or 9XXXX) for continued utilization. Airmen eligible for
retraining consideration in accordance with Chapter 6 may be referred to Air
Force Personnel Center Retraining.
2.4.3.3.11.6.3. AFR and ANG Airmen will be considered for continued
utilization by HQ ARPC/DPAT or ANG/A1D, respectively. (T-2).
2.4.3.3.11.7. Airmen disqualified in accordance with this manual from an awarded
AFSC, yet qualified for reclassification into a designated alternate AFSC (see
AFSC specialty description), provided all entrance, award, and retention
requirements in the AFSC specialty description are met, require review for future
utilization. While the AFSC disqualification action is processed to conclusion, the
Airman may be awarded the designated alternate AFSC. AFECD AFSC specialty
descriptions designate the alternate AFSC if Airmen are not qualified to retain their
awarded AFSC but are qualified for reclassification into the designated alternate
AFSC. Examples include 1A8X1X no longer qualified for aviation service to
1N3X1X, 1Z4X1 no longer qualified for the additional requirements in that AFSC
but remaining qualified for 1W0X1.
68 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
2.4.3.3.11.7.1. For RegAF Airmen, the AFPC/DP2LT functional assignment
manager for the designated alternate AFSC reviews the AFSC disqualification
case to determine Airman’s qualifications and utilization potential. For Airmen
not selected for the designated alternate AFSC, Airmen are disqualified and
classified as disqualified Airmen accordingly (RI 9AXXX), provided Airmen
do not have another awarded AFSC in which still qualified for return.
2.4.3.3.11.7.2. For Airmen not selected for the designated alternate AFSC,
Airmen are disqualified and classified as disqualified Airmen accordingly (RI
9AXXX), provided Airmen do not have another awarded AFSC in which still
qualified for return (For ANG Airmen, NGB/A1D provides RI guidance).
2.4.3.3.12. Certifying Intelligence Officers for Security Access (AFSCs 14NX):
2.4.3.3.12.1. Department of Defense Central Adjudication Facility (DoD CAF), is
solely responsible for determining and certifying eligibility for access to sensitive
compartmented information; see DoDM 5200.02_AFMAN 16-1405.
2.4.3.3.12.2. Personnel security certification standards are established by the
Director of National Security.
2.4.3.3.12.3. Sensitive Compartmented Information certification authority will not
be delegated.
2.4.3.3.12.4. Revocation of Sensitive Compartmented Information eligibility
requires withdrawal of 14NX AFSC, unless an exception is granted by the Deputy
Chief of Staff for Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance and Cyber Effects
Operations (HQ USAF/A2/6).
2.4.3.3.12.5. Revocation of an officer’s security clearance by DoD CAF requires
withdrawal of AFSC 14NX (disqualification), without exception under paragraph
2.4.3.3.12.4. (T-2).
2.4.4. Effective Date of Downgrade or Withdrawal and/or Disqualification Actions:
2.4.4.1. The effective date for the AF Form 2096, Section II, line 5 is directly related to
the disqualification reason and date of the action and/or documentation (or effective date
if identified therein) driving the disqualification action.
2.4.4.1.1. AFSC disqualification for medical or disqualification from aviation service
and/or jump and/or marine dive reasons will take effect on the date of the
disqualification as specified on the AF Form 422, DD Form 2992, or aeronautical order.
2.4.4.1.2. AFOSI agent decertification is the date of the AFOSI/CC decertification
memo.
2.4.4.2. Withdrawing an Airman's awarded AFSC and designating a new awarded AFSC
(if applicable) are concurrent actions.
2.4.4.3. If an Airman does not have an awarded AFSC (1XXX/1XXXX – 7XXX/7XXXX)
other than the one withdrawn via AFSC disqualification action under this chapter,
AFPC/DP2SSM designates RIs 9A000, 9A100, 9A200, 9A300, 9A400, or 9A500 (as
applicable) as the primary and control AFSC for RegAF enlisted Airmen or 96A0 or 96B0
as the primary AFSC for RegAF officers. RegAF FSSs will not award 9AXXX or 96XX

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 69
RIs and may delete only when departing for approved retraining; otherwise, retain until the
Airman is designated into a new AFSC (RegAF officers), separated, retired, or discharged.
Air Force Personnel Center will update all disqualified Airmen RIs following approval of
the disqualification action for RegAF Airmen (officer and enlisted).
Table 2.17. Processing Downgrade and Withdrawal and/or Disqualification Actions.
If the downgrade or
withdrawal is for:
then the:
must:
Lack of Recent
Performance,
paragraphs 2.4.1.4,
2.4.2.1, or 2.4.2.2 (see
Note 1).
FSS
review request and complete AF Form 2096
to document downgrade or withdrawal
action. FSS will only approve substantiated
cases where non-performance in the
specialty is verified (see Note 2). If request
is not substantiated, disapprove and return to
individual or unit with rationale.
Substandard
Performance, paragraph
2.4.1.6 or 2.4.3.3.1.
FSS
ensure appropriate documentation
outlined in paragraphs 2.4.3.3.2.1
through 2.4.3.3.2.5 is included.
Disapprove and return to the unit if all
requirements have not been met and/or if
the documentation is incomplete. If all
coordinating agencies and the member
agree on downgrading the AFSC,
approve the downgrade and update
MilPDS accordingly. If the member,
commander, and FSSs are not in
concurrence with the withdrawal,
forward the case to the FSS Commander
for continued processing. If complete
and (1) the commander has requested
withdrawing the AFSC and (2) the
member, commander, and FSS concur,
recommend approval and forward the
CMS case to AFPC/DP2SSM,
ANG/A1D, or HQ ARPC/DPAT for
processing. The servicing ARC FSS will
finalize the action and, if approved, and
update MilPDS.
Substandard
Performance, paragraph
2.4.1.6 or 2.4.3.3.1.
Force Support
Commander
either disapprove the request if
considered to be without merit, or
appoint a disinterested evaluation official
(Field Grade Officer or Senior Non-
Commissioned Officer, senior in grade to
member being reviewed). Evaluation
official cannot be in the member’s chain
of command and will make a
recommendation to FSS/CC.

70 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
If the downgrade or
withdrawal is for:
then the:
must:
Commander then forwards their final
recommendation to AFPC/DP2SSM as
the approval authority for RegAF
Airmen. The servicing ARC FSS will
finalize the action for RC members and,
if approved, update MilPDS.
Evaluation Official
follow procedures outlined in paragraphs
2.4.3.3.4.1 through 2.4.3.3.4.5.
Notes:
1. Table 2.15 applies for enlisted skill level downgrade.
2. Time spent in a TDY status (to include deployment) in the AFSC to be downgraded or withdrawn
counts as time performing in the specialty. Airman’s time starts over from the return date of the TDY.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 71
Chapter 3
DELETED
3.1. DELETED.
3.1.1. DELETED.
3.1.2. DELETED.
3.1.2.1. DELETED.
3.1.2.2. DELETED.
3.2. DELETED.
3.2.1. DELETED.
3.2.1.1. DELETED.
3.2.1.2. DELETED.
3.2.1.3. DELETED.
3.2.2. DELETED.
3.2.2.1. DELETED.
3.2.2.2. DELETED.
3.2.2.3. DELETED.
3.2.3. DELETED.
3.2.4. DELETED.
3.2.4.1. DELETED.
3.2.4.1.1. DELETED.
3.2.4.1.2. DELETED.
3.2.4.1.3. DELETED.
3.2.4.2. DELETED.
3.2.5. DELETED.
3.2.5.1. DELETED.
3.2.5.2. DELETED.
3.2.5.3. DELETED.
3.2.5.4. DELETED.
3.2.6. DELETED.
3.2.6.1. DELETED.
3.2.6.2. DELETED.
3.2.6.3. DELETED.

72 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
3.2.6.4. DELETED.
3.2.6.5. DELETED.
3.2.6.6. DELETED.
3.2.6.6.1. DELETED.
3.2.6.6.2. DELETED.
3.2.6.6.3. DELETED.
3.2.6.6.4. DELETED.
3.2.6.7. DELETED.
3.2.6.8. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.1. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.2. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3.1. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3.2. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3.3. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3.4. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.3.5. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.4. DELETED.
3.2.6.8.5. DELETED.
3.2.7. DELETED.
3.2.7.1. DELETED.
3.2.7.2. DELETED.
3.2.7.3. DELETED.
3.2.7.3.1. DELETED.
3.2.7.3.2. DELETED.
3.2.7.4. DELETED.
3.2.7.5. DELETED.
3.2.8. DELETED.
3.2.9. DELETED.
3.2.9.1. DELETED.
3.2.9.2. DELETED.
3.2.10. DELETED.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 73
3.2.10.1. DELETED.
3.2.10.1.1. DELETED.
3.2.10.1.2. DELETED.
3.2.10.1.3. DELETED.
3.2.10.1.4. DELETED.
3.2.10.1.5. DELETED.
3.2.10.2. DELETED.
3.2.10.2.1. DELETED.
3.2.10.2.2. DELETED.
3.2.10.2.3. DELETED.
3.2.10.2.4. DELETED.
3.2.11. DELETED.
3.2.11.1. DELETED.
3.2.11.2. DELETED.
3.2.11.3. DELETED.
3.2.11.4. DELETED.
3.2.12. DELETED.
3.2.12.1. DELETED.
3.2.12.2. DELETED.
3.3. DELETED.
3.3.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.3. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.4. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.4.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.4.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.4.3. DELETED.
3.3.1.1.4.4. DELETED.
3.3.1.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.1. DELETED.

74 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
3.3.1.2.1.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.1.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.2.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.2.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.3.
3.3.1.2.3.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.3.2. DELETED.
3.3.1.2.3.3. DELETED.
3.3.1.3. DELETED.
3.3.1.3.1. DELETED.
3.3.1.3.2. DELETED.
3.3.2. DELETED.
3.3.2.1. DELETED.
3.3.2.2. DELETED.
3.3.2.3. DELETED.
3.3.2.4. DELETED.
3.3.2.5. DELETED.
3.3.2.6. DELETED.
3.3.2.7. DELETED.
3.3.2.8. DELETED.
3.3.2.9. DELETED.
3.3.2.10. DELETED.
3.3.2.11. DELETED.
3.3.2.12. DELETED.
3.3.2.12.1. DELETED.
3.3.2.12.2. DELETED.
3.3.2.12.3. DELETED.
3.3.3. DELETED.
3.3.3.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.1.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.1.2. DELETED.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 75
3.3.3.2. DELETED.
3.3.3.3. DELETED.
3.3.3.4. DELETED.
3.3.3.4.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.4.2. DELETED.
3.3.3.4.3. DELETED.
3.3.3.5. DELETED.
3.3.3.6. DELETED.
3.3.3.7. DELETED.
3.3.3.7.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.7.2. DELETED.
3.3.3.7.3. DELETED.
3.3.3.7.4. DELETED.
3.3.3.8. DELETED.
3.3.3.8.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.8.2. DELETED.
3.3.3.8.3. DELETED.
3.3.3.9. DELETED.
3.3.3.10. DELETED.
3.3.3.10.1. DELETED.
3.3.3.10.2. DELETED.
3.4. DELETED.
3.4.1. DELETED.
3.4.1.1. DELETED.
3.4.1.1.1. DELETED.
3.4.1.1.2. DELETED.
3.4.1.1.3. DELETED.
3.4.1.2. DELETED.
3.4.1.2.1. DELETED.
3.4.1.3. DELETED.
3.4.1.3.1. DELETED.
3.4.1.3.2. DELETED.

76 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
3.4.2. DELETED.
3.4.2.1. DELETED.
3.4.2.2. DELETED.
3.4.2.3. DELETED.
3.4.2.4. DELETED.
3.4.2.5. DELETED.
3.4.2.6. DELETED.
3.4.2.6.1. DELETED.
3.4.2.6.2. DELETED.
3.4.3. DELETED.
3.4.3.1. DELETED.
3.4.3.2. DELETED.
3.4.3.3. DELETED.
3.4.3.4. DELETED.
3.4.3.5. DELETED.
3.4.3.6. DELETED.
3.4.3.7. DELETED.
3.4.3.8. DELETED.
3.4.3.9. DELETED.
3.4.3.10. DELETED.
3.5. DELETED.
3.5.1. DELETED.
3.5.1.1. DELETED.
3.5.1.2. DELETED.
3.5.1.3. DELETED.
3.5.2. DELETED.
3.5.2.1. DELETED.
3.5.2.2. DELETED.
3.5.2.3. DELETED.
3.5.3. DELETED.
3.5.3.1. DELETED.
3.5.3.1.1. DELETED.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 77
3.5.3.1.2. DELETED.
3.5.3.1.3. DELETED.
3.5.3.2. DELETED.
3.5.3.2.1. DELETED.
3.5.3.2.2. DELETED.
3.5.3.2.3. DELETED.
3.5.4. DELETED.
3.5.4.1. DELETED.
3.5.4.2. DELETED.
Table 3.1. DELETED.
Table 3.2. DELETED.
78 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 4
ACTIVE DUTY SERVICE COMMITMENTS AND RESERVE SERVICE
COMMITMENTS
4.1. Overview. This publication prescribes guidance, responsibilities, and procedures for ADSCs
and RSCs for members of the RegAF, the ANG, and the AFR.
4.1.1. ADSCs. ADSCs fulfill two very important functions. They assure the Air Force and
the taxpayers receive an appropriate return for their investment of money and/or time in
training, education, and bonuses. They also assure open communication to Air Force members
regarding the periods of obligated service they must complete before becoming eligible to
request to separate or retire from active duty.
4.1.1.1. Officers in the grade of colonel and below and all enlisted personnel incur an
ADSC when they complete all or a portion of ADSC-incurring events.
4.1.1.2. An ADSC does not establish, and is independent of, a DOS.
4.1.1.2.1. Enlisted personnel serve on active duty in accordance with their enlistment
contracts.
4.1.1.2.2. Officers serve indefinite active duty tours by appointment of the President
and must request release or discharge from their appointment from the Secretary of the
Air Force. (T-0). Needs of the Air Force may require continued service beyond an
ADSC.
4.1.1.2.3. Time spent in an excess leave status, as defined in AFI 36-3003, Military
Leave Program, does not count toward fulfilling any ADSCs.
4.1.1.2.4. An ADSC is not affected by a change in a member’s Duty AFSC unless the
member completed an ADSC incurring event that resulted in the change in the
member’s Duty AFSC.
4.1.2. ADSC-Incurring Events.
4.1.2.1. Events that incur ADSCs are established by statute or by Air Force policy. See
Attachment 2 for a summary of ADSC-incurring events.
4.1.2.2. Members usually serve new ADSCs concurrently with existing ADSCs; however,
some ADSCs are served consecutively and are outlined in Attachment 2 or in the ADSC
agreement form.
4.1.2.3. ADSCs incurred for training will become effective upon graduation date or
completion of required training. (T-2).
4.1.2.3.1. The estimated graduation or completion date is utilized when initially adding
the ADSC for training to a member’s record upon selection to attend the course.
4.1.2.3.2. AFPC will update the member’s ADSC to reflect the member’s actual
graduation or completion date after graduation or completion of training, except for JA
officers, whose ADSCs are updated by AF/JAX. (T-2).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 79
4.1.3. Advising Members of ADSCs. The FSS (FSS) (or delegated authority) advises
members of ADSC commitments and ensures each member accepts or declines the ADSC in
accordance with paragraphs 4.1.4, 4.3.5 or 4.3.6 of this manual (see paragraphs 4.2.6 and 4.2.7
for health professions officers and JAs). Note: PCS orders will not be authenticated until a
member has formally acknowledged understanding of the ADSC and the appropriate
documentation is loaded into the member’s record. (T-2).
4.1.3.1. In most cases, the AF Form 63, Active Duty Service Commitment (ADSC)
Acknowledgement Statement formally documents the member’s knowledge and acceptance
of the ADSC. In cases where the AF Form 63 is not required, another source document
serves as the member’s knowledge and acceptance (see paragraph 4.1.3.2.). Failure to be
notified or to complete an AF Form 63 (or other prescribed documentation) does not relieve
the member of the ADSC if the member attends the ADSC-incurring event. In these cases,
the member must follow the provisions outlined in paragraph 4.3.9 to request removal of
the ADSC. (T-1).
4.1.3.2. The following ADSC-incurring events require documentation other than the AF
Form 63:
4.1.3.2.1. Entry on EAD. AFROTC cadets. See AFMAN 36-2032.
4.1.3.2.2. PCS (see AFI 36-2110). Exception: The AF Form 63 is required only for
members (officer and enlisted) moving Continental United States (CONUS)-to-
CONUS and then only if they are or will become eligible for retirement before
completing the associated ADSC. In these cases, the AF Form 63 is not to be used as
the official assignment notification but should be signed by member within 7 calendar
days of official notification.
4.1.3.2.3. Accepting special and incentive pays (Health Professions, see DoDI
6000.13_DAFI 41-110, Medical Health Care Professions Scholarship Programs;
Aviation Bonus see AFMAN 36-3004, Aviation Bonus (AVB) Program.
4.1.3.2.4. Changing competitive categories.
4.1.3.2.5. Tuition Assistance (see paragraph 4.2.3.).
4.1.3.2.6. Participating in education or training programs listed in Attachment 2 (see
AFI 41-117, Medical Service Officer Education).
4.1.3.2.7. ADSC-incurring events affecting enlisted personnel. AF Form 63 is
required only if the member is or will become eligible for retirement before completing
the ADSC (see AFI 36-2606).
4.1.3.2.8. Enlisted promotion to Master Sergeant, Senior Master Sergeant and Chief
Master Sergeant will be documented on a Promotion Statement of Understanding
regardless of member’s Total Active Federal Military Service Date. (T-1).
4.1.3.2.9. Rated specialty begins at the completion of training and award of wings
and/or aeronautical rating. The ADSC is documented within the commissioning
contract or initial rated selection.
80 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
4.1.4. Retainability. Members who accept an ADSC-incurring event must have or obtain
retainability to serve the ADSC required for the event. (T-2).
4.1.4.1. Enlisted members who lack the necessary retainability must obtain it, if eligible,
through reenlistment or extension. (T-2). When an enlisted member cannot obtain the
retainability for an ADSC-incurring event, the MPF or Education Service and Human
Resource Flight must notify the selection authority and the member may apply for a waiver
of retainability. (T-2). Enlisted members who decline to obtain retainability must
document that decision on AF Form 964, PCS, TDY, or Training Declination Statement.
(T-2).
4.1.4.2. Airmen with an indefinite DOS will acknowledge the ADSC utilizing the AF
Form 63.
4.2. Program Processes.
4.2.1. Air Force Personnel Center, Accessions Branch (AFPC/DP3DA):
4.2.1.1. Provides policy interpretations to higher HQ and to the field.
4.2.1.2. Validates AFPC/DP2LT ADSC verifications and identifies necessary policy
changes to AF/A1P.
4.2.1.3. Adjudicates most ADSC disputes, but forwards some ADSC dispute requests to
AF/A1P for further staffing. Example: When a member disagrees with an ADSC, even
when it is clear one is applicable.
4.2.2. Air Force Personnel Center, Military Accessions Branch (AFPC/DP2LT):
4.2.2.1. As OPR for the ADSC Program, will execute all ADSCs, except for health
professions and JA officers.
4.2.2.2. Will determine and establish ADSC Dates (ADSCD) requiring an adjustment after
the initial ADSC-incurring event.
4.2.2.3. Is the office authorized to update ADSCs listed in AETC’s ETCA program and
the Oracle Training Announcement (OTA) database.
4.2.2.4. This office may establish an ADSC on an individual basis to cover a unique
situation as an ETP. Unique ADSCs are just as valid as any other ADSC. MAJCOM and
other Air Force activities may submit recommendations, with full justification, for the
establishment of a unique ADSC. The request can be for an event listed or not listed in
this manual.
4.2.3. Air Force Personnel Center, Military Training and Education Operations Section
(AFPC/DP2SST):
4.2.3.1. Is the OPR for ADSCs involving Tuition Assistance and the Post 911 GI Bill.
4.2.3.2. Will issue a Category One processing discrepancy to the responsible FSS who
allows a member to depart and/or enter into an ADSC-incurring event without proper
ADSC documentation.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 81
4.2.4. Air Force Personnel Center, Military Accessions and Assignment Section
(AFPC/DP1TAM) will initiate the AF Form 63 for all members selected for ADSC-incurring
events and sends to the member for signature and processing to the personnel record.
4.2.5. Air Force Personnel Center AFSC Assignment Team: When selecting someone for a
PCS that encompasses attending training in a PCS status for over 20 weeks or with Air Force
Training en-route will:
4.2.5.1. Notify AFPC/DP2LT of the selection through written or electronic means with all
available course information.
4.2.5.2. Provide course identification (Air Force Training only) to AFPC/DP2LT when the
Air Force Training Management System quotas or OTA updates are not available.
4.2.5.3. Notify AFPC/DP2LT when an ADSC for a PCS move is changed in accordance
with AFI 36-2110.
4.2.6. Nurse Utilization & Education Branch (AFPC/DP2NN) will:
4.2.6.1. Calculate and update ADSCs for health professions officers.
4.2.6.2. Ensure member completes the AF Form 63 or other required ADSC
acknowledgment and maintains original.
4.2.7. Office of The Judge Advocate General, Professional Development Directorate
(AF/JAX) will:
4.2.7.1. Calculate and update ADSCs for Funded Legal Education Program and/or Excess
Leave Program (FLEP/ELP) selectees.
4.2.7.2. Ensure member completes the AF Form 63 or other required ADSC
acknowledgment and forwards the signed original to AFPC/DP2LT.
4.2.8. AFIT/CI will:
4.2.8.1. Categorize AFIT students as scholarship or non-scholarship.
4.2.8.2. Ensure AFPC/DP2LT receives the AFIT Form 9, Initial or Change to Reporting
Instructions, which can be found at https://www.afit.edu/CIP/, or monthly production
roster, Initial or Change to Reporting Instructions. DP2LT will provide a copy to DP1TSA
to prepare extended active duty orders.
4.2.8.3. Inform AFPC/DP1TAM of any change to AFIT class dates or elimination and/or
removal of any Line, Chaplain or JA officer from the AFIT program.
4.2.9. FSS Commander (FSS/CC) will:
4.2.9.1. Ensure all TDY and PCS orders reflect the ADSC associated with the event in
accordance with AFMAN 36-2102, Base-Level Relocation Procedures. (T-1).
4.2.9.2. Ensure members (officers and enlisted) have either sufficient retainability to
complete the commitment associated with the ADSC-incurring event or a retainability
waiver prior to the members departure. (T-1).
4.2.9.3. Thoroughly review the Automated Records Management System to ensure it
contains the appropriate ADSC counseling statements for unexpired or projected ADSC
dates. (T-1).
82 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
4.2.9.4. Establish coordination procedures among and maintain an active liaison with all
MPF and Education Service and Human Resource Flight work centers and base units, to
ensure effective ADSC management. (T-1).
4.2.9.5. Ensure Education Services Officers and all serviced unit commanders understand
their responsibilities. (T-1).
4.2.9.6. At bases conducting any ADSC-incurring training, ensure all individuals
attending such training have a completed AF Form 63 on the first day of training (T-1).
Also ensures enlisted members have sufficient retainability to fulfill the ADSC associated
with the education or training. (T-1).
4.2.9.7. Not allow members to proceed to education or training contained in Attachment
2 without a completed AF Form 63 or other ADSC acknowledgment when required. (T-1).
Will not allow enlisted members without sufficient retainability to proceed to education or
training. (T-1).
4.2.9.8. Contact HQ AFPC/DP2LT for any ADSCD adjustments to include excess leave
adjustments (see paragraph 4.3.2). (T-1).
4.2.9.9. Verify the ADSCD on receipt of a notice of establishment or change of ADSCD
(see paragraph 4.2.11). (T-1).
4.2.9.10. Process requests for formal ADSC reviews (see paragraph 4.3.9.).
4.2.10. Education Services Officer:
4.2.10.1. When a member accepts Tuition Assistance, the Education Service Officer will
update the Air Force Automated Education Management System (AFAEMS). (T-1).
Normally, the update to AFAEMS will flow an update to the MilPDS to capture the
appropriate ADSC.
4.2.10.2. In the event the ADSC does not update automatically, the Education Service
Officer will utilize the AFAEMS to obtain the necessary documentation to send to
AFPC/DP2LT for a manual update. (T-1).
4.2.11. Unit Commander will ensure members who are directed to attend an education or
formal training course, whether via PCS, TDY, or PCA, process through the FSS’s MPF for
ADSC counseling and completion of the AF Form 63 or other required ADSC
acknowledgment before entering an ADSC-incurring event. (T-1).
4.2.12. Training Course Managers: Notify AFPC/DP2LT when new courses are added to
ETCA program or ADSC information on an existing course has changed in ETCA.
4.3. ADSC Procedures.
4.3.1. Completing an ADSC agreement (AF Form 63, AF Form 1056, Air Force Reserve
Officer Training Corps (AFROTC) Contract, or Statement of Understanding) (OPR:
AFPC/DP2LT).
4.3.1.1. The FSS’s MPF counsels the member on the ADSC-incurring event.
4.3.1.1.1. Accepting an ADSC-incurring event:
4.3.1.1.1.1. For officers: the member formally accepts the ADSC-incurring event
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 83
on the AF Form 63, Section II. Upon completion, the member returns the
completed form to AFPC/DP1TAM.
4.3.1.1.1.2. For enlisted the AF Form 63 is required only if the member is/or will
become eligible for retirement before completing the ADSC. The member formally
accepts the ADSC-incurring event on the AF Form 63, Section II. Upon
completion, the member returns the completed form to AFPC/DP2LT.
4.3.1.1.2. If a member declines an ADSC-incurring event:
4.3.1.1.2.1. For officers: The member formally declines the ADSC-incurring
event on the AF Form 63, Section II and returns it to AFPC/DP1TAM. The MPF
suspends all processing for the ADSC-incurring event.
4.3.1.1.2.2. For enlisted only. The member formally declines the ADSC-incurring
event on the AF Form 964 to the MPF of the FSS. The MPF updates the assignment
availability code to reflect mandatory separation (in accordance with AFI 36-2110).
Exceptions: For members applying for separation or retirement via the virtual
Military Personnel Flight self-service applications, the in-system application
automatically updates the assignment availability code. For members declining a
PCS only, the member signs an AF Form 964.
4.3.1.2. The MPF distributes a copy of the AF Form 964 to the member’s respective AFPC
AFSC Assignment Team.
4.3.2. Updating the ADSCD and ADSC Reason Code (see Attachment 2 for Reason Code
listing) (OPR: AFPC/DP1TAM and AFPC/DP2LT).
4.3.2.1. AFPC/DP1TAM updates the MilPDS with the ADSCD and ADSC Reason Code
for all members (except health professions and JA officers) upon receipt of completed AF
Form 63 or other ADSC documentation. Exception: AFPC/DP1TAM will update
ADSCD for the Air Force Intern Program or PME regardless of competitive category.
Also, after a decision is made by AF/JAX, AFPC/DP1TAM will update AFIT ADSCD for
JA officers. ADSCD begins upon graduation or completion date of training or education,
unless otherwise stated. ADSCD for Key Leadership Position (KLP) begin upon duty
effective date.
4.3.2.2. If course graduation date changes or the member does not complete the training,
the MPF will contact AFPC/DP1TAM to adjust the ADSCD.
4.3.2.3. When adjusting a person's service dates to account for lost time (e.g.,
confinement), AFPC/DP2LT will adjust the ADSCD upon receipt of the AF Form 2098,
Duty Status Change, from AFPC/DP2LT by adding one day for each lost day.
AFPC/DP2LT will also adjust ADSCDs by adding one day for each day of excess leave.
4.3.2.4. The OPR for ADSC MilPDS updates is:
4.3.2.4.1. Office of The Judge Advocate General, Professional Development
Directorate (AF/JAX) for JA officers who participated in ELP.
4.3.2.4.2. Nurse Utilization & Education Branch (AFPC/DP2NN) for Health
professions officers.
84 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
4.3.3. Verifying the ADSCD on receipt of a notice of establishment or change of ADSCD RIP.
The FSS will:
4.3.3.1. Ensure the ADSCD is correct on the RIP. If incorrect, contact AFPC/DP2LT.
(T-2).
4.3.3.2. Ensure supporting documents are archived in Automated Records Management
System. (T-2). If the documentation is not on file, the current servicing MPF should
immediately advise member of the ADSC and the requirement to document it. (T-3).
4.3.3.3. Give the RIP to the member if the ADSCD is correct and the documentation is in
the Automated Record Management System. (T-2).
4.3.4. Missing Documentation (OPR: AFPC/DP2LT). When a member’s personnel record
does not contain an AF Form 63 or other required ADSC acknowledgment for a specific
ADSC-incurring event in which the member participated, the current servicing MPF or
member takes the following actions:
4.3.4.1. Contact AFPC/DP2LT to determine if AFPC has a copy of the documentation.
4.3.4.2. If no copies of the documentation are found:
4.3.4.2.1. Advise the member of the discrepancy using documentation provided by
AFPC/DP2LT.
4.3.4.2.2. When the member in-processes for a PCS or on TDY without an AF Form
63, contact AFPC/DPTO to issue a Category One processing discrepancy (see AFMAN
36-2102) to the losing MPF. If the gaining MPF allows the member to enter the ADSC-
incurring event without requesting an AF Form 63, AFPC/DPTO will also charge the
gaining MPF with a Category One processing discrepancy. (T-2).
4.3.5. Declining an ADSC (7-day Option). A member who declines the ADSC for a PCS or
training must request separation or retirement within 7 calendar days of official notification
(Excludes Health Professions Officers sponsored for education in Table A2.2). (T-1).
4.3.5.1. Members who establish a separation or retirement date under the 7-day option
provisions as an alternative to accepting an ADSC, who subsequently complete the ADSC-
incurring event based on needs of the Air Force, are not obligated to serve beyond their
established DOS or retirement date unless they withdraw their DOS or retirement (see AFI
36-3206 or AFI 36-3208).
4.3.5.2. Those who decline an ADSC and establish a DOS or retirement date must serve
all existing ADSCs before separation or retirement unless an earlier DOS is approved.
(T-2).
4.3.6. Refusing to sign an ADSC Acknowledgment Form.
4.3.6.1. If a member is advised of an ADSC and is presented the AF Form 63, the member
cannot proceed on the ADSC-incurring event without completing the AF Form 63 and
returning it to the appropriate office at AFPC.
4.3.6.2. If a member refuses to sign the AF Form 63 to accept the ADSC, the member
cannot proceed on the ADSC-incurring event unless the member has met the provisions of
paragraph 4.3.5.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 85
4.3.6.3. If a member attends an ADSC-incurring event, but did not sign the AF Form 63
(at no fault of the member), the member will not later be administered the ADSC without
proper adjudication and advisement.
4.3.6.3.1. If evidence is presented that the member was or should have been aware of
the ADSC, the member will be required to complete the necessary paperwork and have
the ADSC applied to the member’s MilPDS record. (T-1).
4.3.6.3.2. If the member believes the member is receiving an ADSC in error, the
member may follow the provisions in paragraph 4.3.9.
4.3.7. ADSC Waivers. The Secretary of the Air Force or the Secretary’s designee may, in
appropriate cases, waive an unfulfilled ADSC when requested by a member in conjunction
with applying for separation or retirement in accordance with provisions outlined in AFI 36-
3206 and AFI 36-3208. Note: This process is not for Airmen that believe they have had an
ADSC erroneously applied. For those cases, please refer to paragraph 4.3.9.
4.3.8. Failure to Complete the ADSC for Education, Bonus, or Similar Benefit.
4.3.8.1. Members who fail to complete their ADSC may be subject to recoupment, unless
waived in accordance with Title 37 USC § 303a(e), Special pay: general provisions, or §
373, Repayment of unearned portion of bonus, incentive pay, or similar benefit, and
termination of remaining payments, when conditions of payment not met.
4.3.8.2. Unless a waiver is obtained, members remaining on active duty do not have the
option of reimbursing the government in lieu of fulfilling an ADSC. Exception: Members
who must repay Tuition Assistance in full as directed by the government (incomplete
grade, failing grade, or class dropped) may request removal of the ADSC. The MPF or
Education Services Officer will confirm recoupment action and coordinate with
AFPC/DP2LT to remove ADSC from member’s records. (T-2).
4.3.9. Resolving an ADSC discrepancy (Formal Review Process) (OPR: AFPC/DP2LT). It
is vital members and the Air Force quickly resolve ADSC issues surfaced by the member,
record reviews, or other means. The FSS does not make the final decision on ADSC issues,
but should advise members of the information discovered. The FSS and/or the member ensures
a review of the member’s record is complete and at a minimum complete the following actions:
4.3.9.1. Review the member’s ADSC documentation.
4.3.9.2. Contact the Flight Management Office for record of all flying training the member
has completed.
4.3.9.3. Contact the Education Center to verify all ADSCs for tuition assistance are
properly recorded.
4.3.9.4. Ensures the Automated Record Management System contains the appropriate AF
Form 63 and, if missing, follows the steps in paragraph 4.3.4.
4.3.9.5. The FSS, during initial notification sends the supporting documents to
AFPC/DP2LT and requests a review of the ADSC in question.
4.3.9.6. Upon receipt of AFPC/DP2LT’s review response, the FSS notifies the member of
the results and provides a copy to the member.
86 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
4.3.9.7. If the member disagrees with the AFPC/DP2LT ADSC decision, the FSS will
notify AFPC/DP2LT. AFPC/DP2LT will forward the case to AFPC/DP3DA for an
additional review. (T-2).
4.3.9.8. AFPC/DP3DA will then adjudicate the case. If the answer is clear that the
member should incur the ADSC, AFPC’s adjudication is final. However, if there is any
question to applicability, AFPC/DP3DA will forward the case to AF/A1P for further
staffing.
4.3.9.9. AF/A1P will facilitate staffing the request to SAF/MR for final adjudication.
Note: A proper package should include all relevant information regarding why a member
should or should not receive the ADSC.
4.3.9.10. In cases where there is a question regarding applicability of the ADSC, the
decision of SAF/MR is binding.
4.4. ANG Reserve Service Commitments.
4.4.1. Service commitments are needed to ensure the ANG receives a return on its investments
in its members. All service commitments will be served concurrently and not be added together
to increase a member’s obligation to the ANG unless specifically indicated otherwise in this
publication. (T-2).
4.4.2. Service commitment waivers should be approved only when it is in the best interest of
the ANG or for hardship not common to other ANG members. TAG is the waiver authority
for service commitments. This authority may not be delegated below TAG. (T-2).
4.4.3. The FSS will ensure each member is properly and thoroughly briefed on each
commitment incurred as a result of action taken in accordance with Attachment 3. The FSS
will ensure commitment requirements such as extensions or reenlistments are completed to
cover the required period prior to entering into the required or requested action. (T-2). The
remarks section of the DD Form 4, Enlistment/Reenlistment Document - Armed Forces of the
United States, or AF Form 1411, Extension of Enlistment in the Air Force, or AF Form 1411-
1, Cancelation of Extension of Enlistment in the Air Force, will specify the reason and duration
of each service commitment. No member will be allowed to attend a training course that
cannot be expected to meet service commitment requirements, regardless of the reason. (T-2).
4.4.4. All ANG service commitments will be documented. Members will not be allowed to
attend training unless service commitment agreements are completed prior to attendance (see
Attachment 5). (T-2).
4.4.5. All commitments incurred as a result of training begin on the day after that training is
completed. (T-1).
4.5. Reserve Service Commitments (RSCs) (General). RSCs fulfill two very important
functions. They assure the Air Force and the taxpayers receive an appropriate return for their
investment in training and education. RSCs also communicate to Air Force members the periods
of obligated service they must complete before becoming eligible to separate, transfer, or retire
from Selected Reserve (SELRES). SELRES refers to Air Reserve Technicians (ARTs),
Traditional Reservist, IRs and AGRs. All RSCs must be served in the SELRES unless waived.
(T-2). This includes training not provided by the Air Force.
4.5.1. Program Processes specific to AF Reserve.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 87
4.5.1.1. HQ USAF/REP. HQ USAF/REP is the OPR for policy for the RSC Program, and
determines all RSCs.
4.5.1.2. AFRC/CD. Through the Numbered Air Force (NAF)/Wing/DET Groups/Unit
and MPS Commanders ensure the following is accomplished:
4.5.1.2.1. Initiate Implementation instructions and forward to the field. (T-2).
4.5.1.2.2. Ensure members are counseled on their ensuing commitment. (T-2).
4.5.1.2.3. Ensure members have sufficient retainability to attend RSC incurring events.
4.5.1.2.4. Ensure Reserve Service Contracts are properly completed and filed in the
Automated Records Mangement System (ARMS).
4.5.1.2.5. Ensure recall procedures are in effect for those who are identified as
unsatisfactory participants.
4.5.1.2.6. Ensure all (20 weeks or more) orders, to include PCSs, reflect the RSC
associated with the event.
4.5.1.2.7. Adjust the RSC date if course graduation date changes or the member does
not complete the training. (T-2).
4.5.1.3. ARPC/CC will (Applies to IRs only):
4.5.1.3.1. Ensure each detachment commander advises respective members on the
ensuing commitment they incur by entry into any of the events in Table 4.1. or Table
4.2 and member acknowledges same by executing an AF Form 64, Reserve Service
Commitment Acknowledgement/ Declination. (T-2).
4.5.1.3.2. Ensure that all in-residence course orders of 20 weeks or more, to include
PCS, reflect the RSC associated with the event. (T-2).
4.5.1.3.3. Ensure the appropriate office files RSC documentation in ARMS and
updates MilPDS. (T-2).
4.5.1.3.4. Ensure members are not allowed to proceed to training or education
contained in Table 4.1, without a completed AF Form 64. If course graduation date
changes or the member does not complete the training, HQ ARPC will adjust RSC Date
in accordance with Note 2 of Table 4.1. (T-2).
4.5.1.4. ARPC’s Directorate of Assignments (ARPC/DPA).
4.5.1.4.1. Calculates and updates RSCs for health profession officers in accordance
with Table 4.2., Rules 1 through 6.
4.5.1.4.2. Ensures health profession member completes AF Form 64 and maintains a
copy and submits the original for filing in ARMS and MilPDS update.
4.5.1.4.3. If course graduation date changes or the member does not complete the
training, or if the member has a period of non-availability, HQ ARPC/DPA will adjust
RSC Date. In coordination with ARPC/DPA, the MPS (Unit), HQ ARPC (IRs) will
adjust RSC Date.
4.5.1.5. Headquarters Active Guard and Reserve. ARPC’s Directorate of Assignments
(ARPC/DPA):
88 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
4.5.1.5.1. Ensures all AGR members obtaining RSCs are counseled on their ensuing
commitment. Normally AGRs assigned to HQ AFRC or HQ ARPC do not attend a
school 20 weeks or more in duration, except resident PME, but in the event that it is
required, then ARPC/DPA must be notified. (T-1).
4.5.1.5.2. Ensures that all (20 weeks or more) orders, to include PCS, reflect the RSC
associated with the event. (T-2).
4.5.1.5.3. Monitors in coordination with servicing personnel offices that members
have sufficient retainability to attend the RSC-incurring events. (T-1).
4.5.1.5.4. Coordinates with servicing personnel office to ensure members are not
allowed to proceed to training or education contained in Table 4.1 without a completed
AF Form 64.
4.5.1.5.5. Processes requests for formal RSC reviews (see paragraph 4.3.9.).
4.5.1.5.6. Forwards RSC documentation to the responsible force support unit for filing
in Electronic Records Managements (ERM) or placed in ARMS. (T-1).
4.5.1.5.7. Updates MilPDS. (T-1).
4.5.1.5.8. If course graduation date changes or the member does not complete the
training, ARPC/DPA will adjust RCSD in coordination with servicing personnel office.
4.5.1.5.9. Ensures AGR Tour curtailments are processed in accordance with
procedures in accordance with AFI 36-2110 and that RSCs are maintained following
tour curtailments (as applicable).
4.5.1.6. Servicing MPS/CC for unit members (includes unit AGRs) will:
4.5.1.6.1. Ensure members are counseled on the ensuing commitment. (T-2).
4.5.1.6.2. Ensure that all (20 weeks or more) orders, to include PCS, reflect the RSC
associated with the event. (T-2).
4.5.1.6.3. Ensure that members have sufficient retainability to attend the RSC-
incurring events. (T-2).
4.5.1.6.4. Ensure all individuals attending Air Force Training have a completed AF
Form 64 on the first day of training. (T-2).
4.5.1.6.5. Process requests for formal RSC reviews (see paragraph 4.3.9). (T-2).
4.5.1.6.6. Ensure RSC documentation is filed in Electronic Records Managements
(ERM) or placed in ARMS. (T-1).
4.5.1.6.7. Adjust RSC Date in accordance with Table 4.1., Note 2for course
graduation date changes or if the member does not complete the training. (T-2).
4.5.1.7. Unit Commander (Unit Program): Ensures members who are directed to attend
an RSC- incurring event process through the MPS for RSC counseling and completion of
the AF Form 64.
4.5.1.8. Detachment Commander for IR Members will:
4.5.1.8.1. Ensure members are counseled on the ensuing commitment. (T-1).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 89
4.5.1.8.2. Ensure that members have sufficient retainability to attend the RSC-
incurring events. (T-1). When a member cannot obtain the retainability for a Reserve
Service Commitment incurring event, the detachment commander must notify the
selection authority and the member may apply for a waiver of retainability. (T-1).
Enlisted members who lack the necessary retainability must obtain it, if eligible,
through reenlistment or extension. (T-1).
4.5.1.8.3. Ensure that the AF Form 64 is forwarded to the office at HQ ARPC
responsible for the RSC incurring event program (e.g., careering for enlisted
promotions, education and training for formal schools), so that the contract can be filed
in Electronic Records Management (ERM) or placed in ARMS. (T-1).
4.5.2. The Air Force Reserve establishes RSCs for all SELRES members who participate in
RSC-incurring events. As such, it is imperative that RSCs and associated policies in this
manual be clearly communicated by responsible officials and fully understood by SELRES
members. In the event of a conflict, commitments set by law, DoD, or other Air Force
Instructions take precedence over time commitments established in this manual. (T-0).
4.5.3. Officers in the grades of colonel and below and all enlisted personnel incur RSCs when
they complete all or a portion of RSC-incurring events. Two or more RSC-incurring events
are served concurrently, not consecutively. When two or more RSC-incurring events overlap,
the RSC-incurring event with the longest remaining obligation will take precedence. AF Form
64 must be completed and filed in Electronic Records Management (ERM) or placed in ARMS.
The AF Form 64 with the greatest expiration date is adjusted or waived, the RSC expiration
date is then adjusted to the next longest intervening contract. (T-2).
4.5.4. An RSC does not establish a DOS.
4.5.4.1. Enlisted personnel serve in accordance with their enlistment and/or extension
contracts. (T-1).
4.5.4.2. Officers serve indefinitely by appointment of the President and must request
release or discharge from their appointment from the Secretary of the Air Force after
serving their RSC. (T-0).
4.5.5. AGRs who receive (voluntary or involuntary) tour curtailments may still have a
commitment to fulfill the RSC and procedures are outlined in AFI 36-2110.
4.5.6. Needs of the Air Force Reserve may require continued service beyond an RSC such as
mobilization.
4.5.7. The Air Force may release the member from the obligations of the AF Form 64 when
in the best interests of the Air Force.
4.5.8. Members who decline to incur an RSC should do so by filling Section II of the AF Form
64. (T-1).
4.5.9. RSC-Incurring Events. Tables 4.1 and 4.2 identify RSC-incurring events.
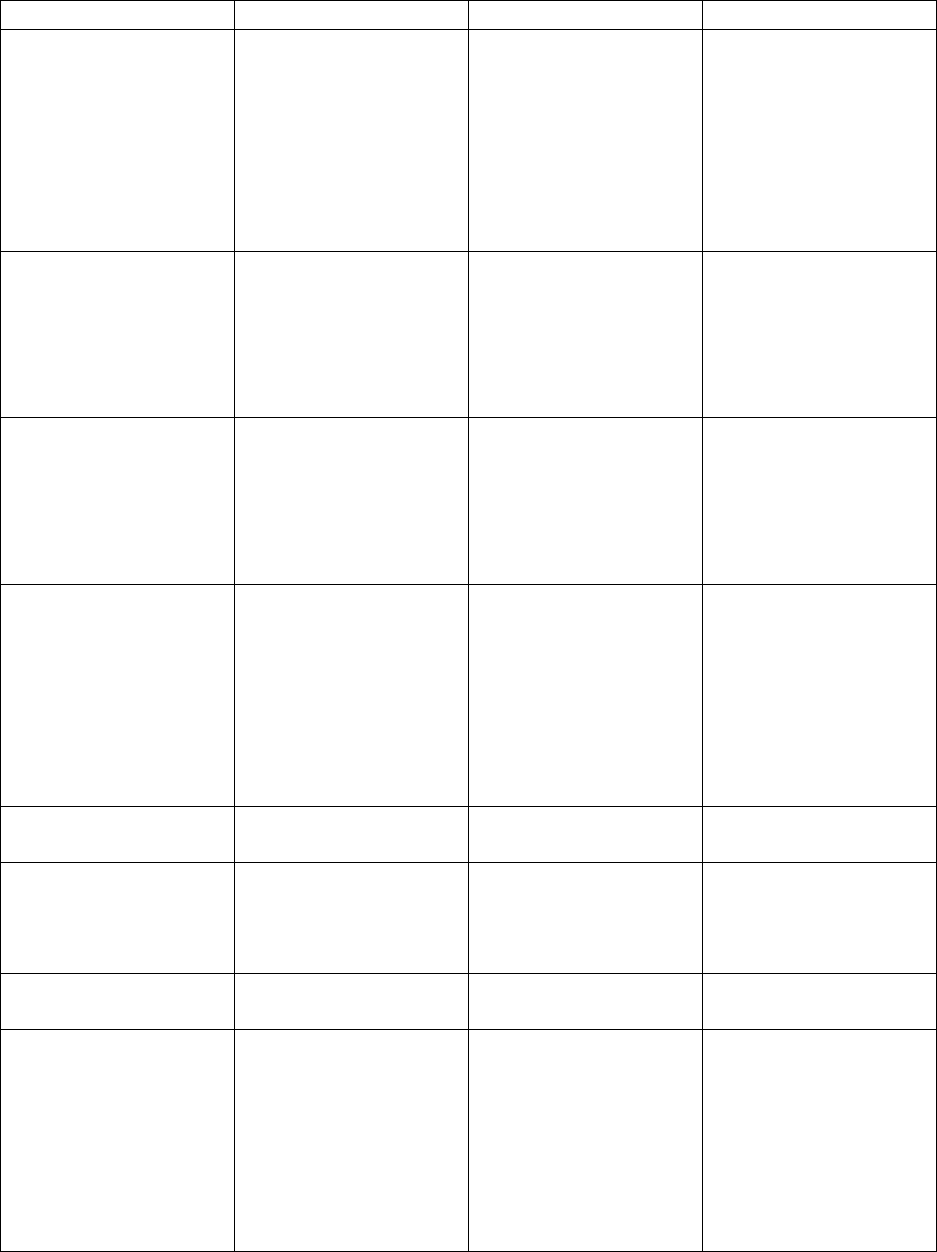
90 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 4.1. Line, Chaplain, Judge Advocate General Officer, and All Enlisted RSCs (T-1).
R U L E
A
B
C
If the RSC
incurring event is
for:
Then the RSC is
served concurrently
unless otherwise
noted: (this only
applies to members
accepting an RSC
on or after 1
October 03) (Note 1)
Reason Code
1
Officer Training
School
4 years, plus one
month for each
additional month of
scholarship benefits
beyond 4 years (Note
2)
81
2
Air Force Reserve
Officer Training
Corps (AFROTC)
4 years, plus one
month for each
additional month of
scholarship benefits
beyond 4 years (Note
2)
31
3
Promotions: AGRs,
Unit Reservist, and
IR
2 years, Time in
Grade for grades E-7,
E-8, and E-9.
Commissioned
officers: Per Reserve
Officer Personnel
Management Act
(Note 3)
10
4
Undergraduate Pilot
Training
10 years (Notes 2 and
4)
80
5
Undergraduate
Navigator Training &
ABM Undergraduate
Training
6 years (Notes 2 and
4)
04
6
Undergraduate RPA
Training
6 years (Note 2)
37
7
Advanced Flying
Training (AFT)
(follow on), Test
Pilot School Pilot,
Navigation, Engineer
Career Enlisted
Aviators (CEA major
weapons system
3 years (Note 2)
05

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 91
(MWS Qual)
1AXXX or 1UXXX
AFSCs) Major
Weapons System
Qualification (PIQ,
TX1 and IQT-B
Course), Applicable
AFT courses must be
listed in ETCA at
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/s
ites/app10-
ETCA/SitePages/Ho
me.aspx Initial
qualification. RSC
applies to in-
residence only.
8
USAF Weapons
Instructor Course in-
residence
3 years for
Intermediate and
Senior schools) (Note
2)
76
9
Instructor
Qualification courses
in- residence. Only
those courses listed in
the ETCA at
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/s
ites/app10-
ETCA/SitePages/Ho
me.aspx
(Applies to PIT, TX-
2 and TX-3)
RSC applies to in-
residence only.
2 years (Note 2)
77
10
Any formal schools
and in-residence
education less than
16 calendar days
receive a 1-year RSC;
courses exceeding 16
calendar days,
receive a 2-year RSC
and courses which
are 20 or more
weeks, receive a 3-
year RSC. This RSC
only applies in the
1-3 years (Notes 2
and 5)
78

92 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
event this
publication, the
ETCA or applicable
course guidance does
not prescribe a
specific commitment
requirement.
11
Officer PME in-
residence
(Notes 2 and 6)
07
12
NPS Enlistment
6 years, Term of
Enlistment (Note 7)
82
13
Officer Tuition
Assistance
2 years per AFI 36-
2670
09
14
Enlisted PME in
residence
2 years
07
Notes:
1. Members who decline to sign the RSC event will sign an AF Form 64. All formal training
will incur a RSC. (T-1).
2. Individuals withdrawn or eliminated from education or training program will incur a 2-year
RSC from the date the member was withdrawn or eliminated. (T-1). NPS members are not
required to sign a contract for training, however, reference AFMAN 36-2136, Reserve
Personnel Participation, for recall procedures. (T-1).
3. Members who are demoted will have RSC-incurred in Rule 2 removed. (T-1).
4. Pilot RSC: 10 years, NAV/CSO RSC: 6 years, Undergraduate ABM RSC: 6-Years,
Undergraduate RPA Training (URT) RSC: 6. (T-1).
5. In the event that a Chaplain's ecclesiastical endorsement is withdrawn, the discharge
authority outlined in AFI 36-2110, will take precedence over the RSC. (T-1).
6. The Reserve Service Commitment will be 3 years for intermediate and senior service
schools. (T-1). It will be one year for primary service schools. (T-1).
7. This applies to all NPS enlistees regardless of school length. (T-1). NPS members are not
required to sign an AF Form 64, however, RSC code 82 will be updated in MilPDS with an
expiration date equal to their term of enlistment. AFMAN 36-2136, gives the authority for
recall of NPS unsatisfactory participants for up to 45 days. Recall procedures are to be
accomplished in accordance with RSC recall procedures as outlined in this guideline. (T-1).

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 93
Table 4.2. Health Profession Officer and Enlisted Education/Training (T-1).
R U L E
A
B
C
If the RSC
incurring event is
for
Then the RSC is
(Note 6)
RSC Reason for
code
1
Direct Accession
and/or Minimum
Term of Service
3 years
12
2
Ready Reserve
Health Professions
Stipend Program (See
Notes 1-4)
1 year in the Selected
Reserves for each 6
months, or part
thereof for which
stipend is paid (Note
4)
32
3
Graduate Medical
Educationor Graduate
Dental Education
Residency (deferred
or re-deferred)
1 year for each year,
min 2 years (Notes 1
and 2)
45
4
Military Physician
Assistant Training
4 years (Notes 1and
3)
81
5
Any In-residence
formal training in
duration of 20 weeks
or more
3 years concurrent
with other RSCs (5
years for Doctoral
programs)
78
6
Officer PME in-
residence
3 years for
intermediate and
senior service
schools, 1 year for
primary service
schools (Note 5)
07
7
Promotions: AGRs,
Unit Reservists, and
IRs
2 years, Time in
Grade for grades E-7,
E-8, and E-9,
Commissioned
officers: Per Reserve
Officer Personnel
Management Act
10
8
Incentive Pay,
Accession Bonus,
1 year per payment
(Note 4)
47
9
Retention Bonus
In accordance with
FY Health
Professions Special &
Incentive (HPS&I)
47

94 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Pay Plan published
by AFRC/SG
Notes:
1. Members who withdraw or are eliminated from school will be processed for discharge due
to their violation of DoDI 1205.21, Reserve Component Incentive Program Procedures. (T-0).
2. Do not use any part of the educational or training program period to satisfy any existing
RSC.
3. Members serve this RSC after fulfilling all previously existing RSCs.
4. Members who received funds are subject to recoupment.
5. Waivable only by HQ USAF/RE. (T-1).
6. Members who decline to sign an RSC event will sign a declination statement (AF Form
64).
4.5.10. Advising Members of RSCs. Prior to the member accepting a RSC, ARPC/DPA
(AGR Assignments), the MPS for unit members, or program manager for IRs, advises
members of RSC commitments and documents RSCs (see paragraphs 3.4 for health
professions officers). (T-3).
4.5.11. AF Form 64 - Officer and Enlisted RSC. Formally documents the member’s
acknowledgement and acceptance with the acceptance of the RSC. Failure to complete the
contract does not relieve the member or the command of the RSC. (T-2). Undergraduate
Flying Training (orders) (T-2), and/or any participation in education or training programs listed
in Tables 4.1 and 4.2 (T-1) also require an RSC.
4.5.12. Enlisted Retainability. Prior to entering an AF Form 64, enlisted members who lack
the necessary retainability to complete their RSC must obtain the time, if eligible, through
reenlistment or extension. (T-2). When an enlisted member cannot obtain the retainability for
an RSC-incurring event, HQ ARPC/DPA, the MPS for unit members, and HQ RIO for IRs,
must notify the selection authority and the member must apply for a waiver of retainability. If
member is within HYT and will not have enough time to fulfill the RSC incurring event,
member will have to apply for an HYT waiver, if approved, then member can obtain necessary
retainability. (T-2). Unit member’s requests for waivers must be processed through the
member’s chain of command to the NAF/CC for approval or disapproval. (T-2). For IRs the
request must go through their RIO/Dets to HQ RIO/CC, who will then forward the request to
HQ ARPC/CC for approval/disapproval. (T-2). Unit member’s requests for waivers must be
processed through the member’s chain of command to the NAF/CC. (T-2). For AGRs, the
approval authority for waivers is the AFRC/CD.
4.5.13. RSC Waivers. AFRC/CD or designated representative may, in appropriate cases,
waive an unfulfilled RSC when applying for separation, reassignment, or retirement from the
SELRES (see AFI 36-3203, Service Retirements and AFI 36-2110). Members must request a
RSC to be excused in writing to applicable commander through command channels prior to
submitting request for separation, reassignment, or retirement. (T-2). IRs must process their
request through their program manager to ARPC/CC. (T-2). Intervening command channels
have disapproval authority only. Where more than one AF Form 64 exists, it is important to
understand that waiver of RSC is specific to the RSC event that is being considered for waiver.
Hence, if an individual is seeking waiver of all commitments, a waiver request must address
all existing AF Form 64s. (T-2). The Commander of the Air Force Reserve (or designee) shall
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 95
excuse members from their obligation to serve on Reserve duty for the period specified in their
contract when such authority deems release in the best interests of the Air Force. (T-1).
4.5.13.1. Members with an RSC may seek conditional release to another component or
service (T-1).
4.5.13.2. Period of commitment with another component or service shall be commensurate
with remaining RSC. (T-1).
4.5.13.3. For the purpose of conditional release to another component or service AFRC
NAF/CC or ARPC/CC is the designee for approval for SELRES members. (T-1).
4.5.14. Resolving Administrative RSC issues. It is vital that members and the Air Force
Reserve quickly resolve RSC issues surfaced by the member to include missing documents,
signatures, records reviews, or other means that may preclude the member from meeting RSC
requirements. (T-2).
4.5.14.1. AGRs. ARPC/DPA makes the final decision on RSC issues. (T-2).
4.5.14.2. Unit program. The force support unit makes the final decision on RSC issues.
(T-2).
4.5.14.3. IR program. The Commander, Individual Reserve Readiness and Integration
Organization (RIO/CC) makes the final decision on RSC issues. (T-2).
4.5.15. Sabbaticals. Religious sabbaticals are not an RSC-incurring event. Religious
sabbaticals will necessitate an adjustment to an AF Form 64 upon return to the participating
status. Period of adjustment will be commensurate with the period of the sabbatical. This time
will not count toward a member’s RSC. Members who are approved for a religious sabbatical
will be transferred to the Standby Reserve in accordance with AFI 36-2110. At the end of the
obligation ARPC will send a letter to the member, with a courtesy copy to 367th Recruiting
Group. (T-2). At the end of the sabbatical the member will be placed back into the position
(or an equitable position in the SELRES) from where they were reassigned. (T-2). If the
member fails to report, the gaining commander/Program Manager will be responsible to start
the recall procedures. (T-2).
4.5.16. Recall Procedures. When a member with a current RSC fails to satisfactorily
participate follow procedures in accordance with AFMAN 36-2136, recall procedures under
Title 10 USC § 12303 and Title 10 USC § 10148, (involuntary recall for up to 45 days) will be
initiated. (T-0).
96 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 5
TECHNICAL TRAINING PROGRAMS REQUIREMENTS
5.1. Technical Training Requirements Purpose and Responsibilities.
5.1.1. Purpose. The purpose of this chapter is to manage the Air Force (AF) technical training
program to ensure maximum utilization in support of the AF mission. This chapter defines the
roles, responsibilities, programs, and procedures necessary for technical training management
across the planning, programming, budgeting, and execution cycle. All individuals and
organizations involved in the technical training requirements process are subject to the
directive guidance and procedures established in this publication and those generated by
AETC. This chapter provides directive guidance to ensure Air Force meets both Air Force and
applicable non-Air Force technical training requirements. Some non-Air Force requirements
are applicable due to industry standards (e.g., set by US government agencies or certification
requirements). Other non-Air Force training requirements may become applicable when Air
Force personnel are assigned outside the Air Force, or when non-Air Force personnel are
assigned to the Air Force.
5.1.2. Program Procedures.
5.1.2.1. AFPC Chief, Personnel Sustainment Division (AFPC/DP1S). Manages the
overall development and integration of the MilPDS/OTA and provide AETC/A3LZ/A3LR
with utilization data needed for monitoring and/or reallocating funded class allocations.
5.1.2.2. AFPC/DP2LWD is the OPR for all training requester quota identifier system
access.
5.1.2.3. Force Development Resources Branch (AETC/A3LR) will:
5.1.2.3.1. Along with AETC/A3LZ, use the program requirements document as a
planning tool to prioritize funding requirements for submission throughout the
planning, programming, budgeting, and execution cycle and to submit Air Force
requirements into the sister services’ and other US government agencies’ training
processes.
5.1.2.3.2. Build the mission readiness training program budget requirements in
program objective memorandum submissions, funding a specific number of allocated
training quotas.
5.1.2.3.3. Work in conjunction with the Financial Management Analysis Division
(AETC/FMA) to establish unfunded requirements during the operations and
maintenance execution plan, initial distribution, quarterly program execution review
and mid-year execution review.
5.1.2.3.4. Develop proposed distribution of mission readiness training program funded
allocations with AETC/FMA coordination. Initiates and coordinates action with the
AF/A1PT to amend the mission readiness training program guidance letters to resolve
any associated disconnects in the program objective memorandum with program
requirements, e.g., when funds approved by the Air Force corporate structure will not
support execution of training requirements. (See AFMAN 65-605, Volume 1, Budget
Guidance and Technical Procedures).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 97
5.1.2.4. Technical Training Requirements Branch (AETC/A3LZ) will:
5.1.2.4.1. Develop the programmed technical training documents, which serve as
planning documents for the number of entries or seats resourced, scheduled and
executed in technical training to meet the requirements in the program guidance letters
and program requirements documents. Will staff the programmed technical training
for schoolhouse capacity assessment to include course level schoolhouse capacity,
aggregate installation level base operating support, and basic military training capacity.
5.1.2.4.2. For initial skills, AETC/A3LZ will work in conjunction with AF/A1PT to
ensure the accession levels are balanced with the enlisted initial skills program
guidance letters and the programmed technical training. AETC/A3LZ works with Air
Force Personnel Center and AF/A1PT to ensure accession levels are balanced with the
officer initial skills program guidance letters and programmed technical training.
5.1.2.4.3. For mission readiness training, trained dog requirements, field training
detachment, and non-resident programs, AETC/A3LZ will collect, develop and
forward the emergent FY training requirements documents to AF/A1PT, in accordance
with the annual AF/A1PT technical training data call message. Will ensure user
requirements fall within the maximum baselines of the program guidance letters and
program requirements documents by the data call message suspense date.
5.1.2.4.4. Serve as Air Force quota management authority (including language training
and sister service and/or other agency training) to ensure effectiveness and efficiency
of technical training programs. For quota management details, refer to AETCI 36-
2651, Basic Military and Technical Training.
5.1.2.4.5. Determine if and when available technical training allocations may be
utilized by unscheduled users. Users may allow use of unscheduled seat that will go
unfilled by the original user. For quota management details, refer to AETCI 36-2651.
5.1.2.4.6. When Air Force members are trained by a sister service, AETC/A3LZ will
work in conjunction with Army and Navy to ensure the Air Force requirements are
scheduled and executed based on enlisted initial skills and officer initial skills
programmed technical training documents and mission readiness training programmed
technical training documents.
5.1.2.4.6.1. For initial skills programs, AETC/A3LZ will receive and forward user
requirements turn-in requests to AF/A1PT for consideration and approval.
5.1.2.4.6.2. Upon AF/A1PT approval, AETC/A3LZ forwards approved turn-in(s)
to Second Air Force or applicable organization (e.g., USAF School of Aerospace
Medicine, Air Force Personnel Center, etc.) who disseminates to the appropriate
schoolhouse for action with a courtesy copy to the training requester quota
identifier. Then, AETC/A3LZ updates the programmed technical training to reflect
the approved turn-in(s).
5.1.2.4.6.3. Upon disapproval, AETC/A3LZ returns the turn-in request to the
training requester quota identifier with AF/A1PT’s decision.

98 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.1.2.4.7. After scheduling and resourcing the program guidance letters, users submit
change requests to AETC/A3LZ. AETC will work the requirements(s) and elevate any
related recommendations, concerns, or questions to AF/A1PT.
5.1.2.4.7.1. For mission readiness training, trained dog requirements, field training
detachment and non-resident programs, AETC/A3LZ can adjust the number of
quotas allocated to conform to the AF/A1PT program guidance letters or to initial
distribution of mission readiness training program funds. Proper coordination with
the training requester quota identifier manager will be made to ensure accurate
accountability and tracking.
5.1.2.4.7.2. For mission readiness training, trained dog requirements, field training
detachment and non-resident programs, AETC/A3LZ will validate, coordinate and
track all program users’ AF Form 3933, MAJCOM Mission Training Request
actions. Will ensure that any AF/A1PT approved changes to program guidance
letters and program requirements documents are adhered to by program
administrators and users.
5.1.2.5. Financial Management Analysis Division (AETC/FMA) will:
5.1.2.5.1. Prepare the AETC budget submission for mission readiness training, in
coordination with AETC/A3LR, for operations and maintenance execution plan, initial
distribution, quarterly program execution review, mid-year execution review, end-of-
year spend plan, end-of-year close out, and various cost exercises (e.g., impact of
lodging and per diem increases).
5.1.2.5.2. Track mission readiness training program expenditures, funded execution
rates and the actual allocations used per travel orders. AETC TDY-to-school centrally-
funded orders for RegAF trainees are certified through the following web site:
https://tdytoschool.us.af.mil/login/.
5.1.2.5.3. Compute the average cost to send a student TDY to an AETC owned,
operated or controlled formal training course.
5.1.2.5.4. Convert funds into allocations based on funding approved by the Air Force
corporate structure and average cost per student. Releases to AETC/A3LZ in
coordination with AETC/A3LR.
5.1.2.5.5. Prepare a funded mission readiness training program letter and sends to the
Second Air Force mission readiness training office at initial distribution.
5.1.2.5.6. Identify execution year funding shortfalls, which may drive the reduction of
quotas to AETC/A3LR.
5.1.2.6. 502d Comptroller Squadron will issue fund-cites for travel, per diem and lodging
for non-pipeline students. (T-2).

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 99
5.1.2.7. The following roles and responsibilities are related to the mission readiness
training, trained dog requirements, field training detachment, and non-resident programs:
5.1.2.7.1. Second Air Force (2 AF) will:
5.1.2.7.1.1. Produce the monthly execution report tracker. This AF/A1PT
requested report identifies the mission readiness training program funding level-1
baseline execution rates during the year of execution. Forwards monthly to
AF/A1PT, AETC/A3LR/A3LZ/FMA. Forwarded quarterly to the following
training requester quota identifiers and users: Air Force directed, AFPC/DP2LWD,
MAJCOMs (warfighters and support), and non-Air Force users.
5.1.2.7.1.2. Produce mission readiness training program funding level-2 annual
execution report. This AF/A1PT requested report is produced at the end of each
FY; identifies mission readiness training program funding level-2 execution rates.
Forwards report by 1 November to AF/A1PT, AETC/A3LR/A3LZ/FMA, as well
as the following training requester quota identifiers and users: Air Force directed,
AFPC/DP2LWD, MAJCOMs (warfighters and support), and non-Air Force users.
5.1.2.7.1.3. Assist with the day-to-day management, oversight, and accountability
of the mission readiness training program during the year of execution, to include
managing special authorizations (see paragraph 5.5.3.).
5.1.2.7.1.4. Ensure maximum utilization of allocations. Unexecuted quotas may
be redistributed quarterly by the training requester quota identifier manager within
30 days of notification (i.e., unexecuted quotas are quotas that have not been sub-
allocated). If not sub-allocated by the training requester quota identifier manager,
the Second Air Force mission readiness training office will notify the training
requester quota identifier manager at the time of redistribution. Exception:
Though the total baselines may appear on the mission readiness training program
guidance letter, redistribution of officer and enlisted initial skills quotas must be
approved by AF/A1PT through the chain of command before implementation.
5.1.2.7.1.4.1. No earlier than 60 days from the class start date for course types:
5, 8, 9, A, B, C, D (2nd position of the course number “Training type
designator”).
5.1.2.7.1.4.2. No earlier than 45 days from the class start date for course types:
4 or 7 (2nd position of the course number “Training type designator”).
5.1.2.7.1.4.3. No earlier than 30 days from the class start date for course types:
2 or 3 (2nd position of the course number “Training type designator”).
5.1.2.7.1.4.4. Second Air Force monitors, on a monthly basis, total program
execution of allocations (Air Force directed and MAJCOM mission) to prevent
over or underutilization by program users.
5.1.2.7.2. MAJCOMs, ANG, AFR, Direct Reporting Units, Forward Operating
Agencies, Sister Services, or Other US government agencies.
5.1.2.7.2.1. MAJCOM/CC (or equivalent) will ensure a rigorous review and
validation of annual requirements and maximum utilization of limited training
resources.

100 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.1.2.7.2.2. Director of Manpower and Personnel (A1) or equivalent (i.e., the
agency’s manpower and personnel office when the customer is not a MAJCOM)
will:
5.1.2.7.2.2.1. Establish command process involving base-level units,
functional managers, and commanders in identifying and validating mission
essential, executable training requirements.
5.1.2.7.2.2.2. Notify functional managers, wing commanders, and unit
commanders of the annual screening for formal training requirements.
5.1.2.7.3. MAJCOM functional managers or equivalent. Examples: For the AFR,
these functions are performed by the AFR Command Education and Training
Operations Support (AFRC/A1KE). For the ANG, these functions are performed by
the ANG Force Development Division (NGB/A1D).
5.1.2.7.3.1. Serve as liaison between AFPC/DP2LWD, the training requester quota
identifier manager, and the base-level functional manager and/or unit training
manager.
5.1.2.7.3.2. Maintain awareness of available training for respective career field
using the Education and Training Course Announcements (ETCA) website
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/app10-ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx.
5.1.2.7.3.3. Monitor current FY allocations.
5.1.2.7.3.3.1. Execute quotas, both funded and unfunded.
5.1.2.7.3.3.2. Move or release funding, if unable to fill or use quota.
5.1.2.7.3.3.3. Seek funding for quotas if needed.
5.1.2.7.3.3.4. Utilize program out-of-cycle process for unforeseen requirement
needs. Obtain worksheets from the Second Air Force Quota Management
SharePoint® site at https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/app10-
ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx. Refer to AETCI 36-2651.
5.1.2.7.3.3.5. Submit training requests using the Air Force Personnel Center’s
Workforce Development organizational email box at
[email protected], (Exception: lateral training, retraining, officer
crossflow training, NPS training, accessions, craftsman, PALACE ACQUIRE,
PME, and recruiting (refer to myPers)). Prior to submitting requests to
AFPC/DP2LWD, the MAJCOM or Air Reserve Component, the functional
manager will ensure the trainee meets all mandatory prerequisites for course
eligibility. (T-3). If the member reports to school without a valid training line
number or without meeting prerequisites, the schoolhouse has the option to
return the member to the parent organization without attending the training, and
the parent organization will incur any and all associated costs. Prerequisites are
listed on the Education and Training Course Announcements SharePoint® site
at https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/app10-ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx.
5.1.2.7.3.3.6. Approve and/or validate each S-record (force gain) for the quota
type loaded by the schoolhouse by the designated suspense date. Upon approval

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 101
or disapproval action, notify the AFPC/DP2LWD training requester quota
identifier manager. If the MAJCOM functional manager disapproves the S-
record as it is reflected on the OTA report, MAJCOM functional manager will
notify the schoolhouse and request deletion of the current record. Once the
schoolhouse deletes the records, the force-gain will be resubmitted with the
appropriate quota type.
5.1.2.7.3.4. Conduct annual screening process for respective career field training.
5.1.2.7.3.4.1. Validate projected FYs’ training requirements during annual
screening.
5.1.2.7.3.4.2. Program new FY training based on requirements received from
the base-level functional manager.
5.1.2.7.3.4.3. Do not over estimate program requirements. MAJCOM
functional managers should know the historical execution success rate. Justify
any requirement increases clearly and accurately based on projected mission
changes or emerging missions.
5.1.2.7.3.4.4. Consolidate requirements from each base-level functional
manager or unit training manager, and forward to the training requester quota
identifier manager.
5.1.2.7.4. Base-Level functional managers will:
5.1.2.7.4.1. Identify training requirements that exceed the mission readiness
training program guidance letter’s baseline using AF Form 3933. (T-1). Ensure the
AF Form 3933 is prepared, certified, and coordinated per the detailed instructions
provided in the AF/A1P technical training data call message. (T-1).
5.1.2.7.4.2. Forward training requirements through the commander (as designated
by the MAJCOM, but no lower than unit level) to the MAJCOM functional
manager. Base requirements on the actual number of personnel that require the
training and can be released to attend the requested courses (i.e., the executable
requirement). (T-2).
5.1.2.7.5. Training Requester Quota Identifier Managers will:
5.1.2.7.5.1. Provide up-to-date training requester quota identifier manager
(primary and/or alternate) appointment letter to the Second Air Force mission
readiness training office to maintain current points of contact information. Refer
to the mission readiness training program SharePoint® site at
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/12821/default.aspx. (T-2).
5.1.2.7.5.2. Conduct annual screening, including specialized skills training
requirements. (T-2).
5.1.2.7.5.2.1. Based upon provided guidance, training requester quota
identifier managers will consolidate and enter all training requirements into
MilPDS/OTA by the date specified in the AF/A1P data call message. (T-1). If
mission readiness training program funding needs exceed the AF/A1P
prescribed funding level-1/2 program guidance letters’ baseline levels, the

102 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
training requester quota identifier manager may submit a request for increase to
AETC/A3LZ per the detailed instructions in the data call message. Use AF
Form 3933.
5.1.2.7.5.2.2. Involve base-level units, MAJCOM functional managers, and
Air Force CFMs in identifying and validating training needs. Approve training
requirements based on priority and execution history.
5.1.2.7.5.2.3. Consolidate and forward all functional training requirements to
the appropriate MAJCOM, functional manager, forward operating agency, or
direct reporting unit A1 or equivalent for final assessment.
5.1.2.7.5.3. Maintain copy of the functional annual submission until allocations are
received from the MAJCOM, AFPC/DP2LWD, functional managers, forward
operating agency, or direct reporting unit A1s or equivalent.
5.1.2.7.5.4. Monitor the utilization of allocations.
5.1.2.7.5.4.1. Execute allocated requirements or turn-in any unused quotas as
early as possible.
5.1.2.7.5.4.2. Ensure an allocation is not deleted from the system once the
student has entered or been sent to class. Funding is tied to each training line
number and deletion in the MilPDS/OTA will cause the member to not be
reimbursed. A new training line number and allocation must be reissued if the
student is sent again to the same class. (T-3). The student’s home base FSS
must ensure the student is not kept on medical, administrative hold,
reclassification, or washback, etc. for more than seven days without amendment
of orders and prior coordination with AETC/FMA (NGB/A1D for ANG) for
financial impact. (T-3).
5.1.2.7.5.4.3. Process initial scheduling, cancellations, replacements, swaps,
out-of-cycle, and quota movement requests within 10 duty days of receipt from
the MAJCOM functional manager, forward operating agency, direct reporting
unit, or designated training representative. For details, refer to AETCI 36-2651.
5.1.2.7.5.4.4. Process and confirm ‘no-shows’ in OTA.
5.1.2.7.5.4.5. Generate and manage reports for ‘no-shows,’ S-records (force
gains), overdue training line numbers, and open seat rosters at least monthly.
Reports for mission readiness training program courses (except lateral training,
retraining, officer crossflows, NPS training, accessions, craftsman, PALACE
ACQUIRE, PME, and recruiting) will be posted monthly to the Air Force
Personnel Center’s Workforce Development SharePoint® site at
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/11842/default.aspx.
5.1.2.7.5.4.6. Send overdue training line number reports to the formal training
sections at each DoD site for required action and/or confirmation.
5.1.2.7.5.5. Provide assistance, guidance, and training to the MAJCOM or Air
Reserve Component functional managers.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 103
5.1.2.7.5.6. Maintain oversight on quota usage and have final approval authority
on mission readiness training funding issues, baseline distribution of funding and
quota allocations.
5.1.2.8. Training requester quota identifier managers for officer and enlisted initial skills
programs will:
5.1.2.8.1. Execute allocated requirements or turn-in any unused quotas as early as
possible.
5.1.2.8.2. Submit their request to turn-in any unused officer or enlisted initial skills
training requirements to AETC/A3LZ no later than 60 days prior to class start date.
(T-2).
5.1.2.8.2.1. Make an effort to see if other users have a need for the requirements
prior to requesting requirements turn-in. (T-2).
5.1.2.8.2.2. Send a request to AETC/A3LZ to request a change to their
requirements once coordination with other users is complete. (T-3).
5.2. HQ Air Force Technical Training Programs.
5.2.1. Enlisted Initial Skills. Enlisted initial skills reflects the total validated enlisted technical
training requirements necessary for force sustainment in each AFSC. It includes initial skills
technical training requirements for Total Force, international, sister service and Air Force
civilian personnel.
5.2.1.1. Trained Personnel Requirement. Trained personnel requirement states the RegAF
need for trained personnel by AFSC. From this requirement, Air Staff projects the NPS,
PS, and retraining required by FY to keep the active enlisted force at manning levels needed
by the Air Force. Air Staff communicates the trained personnel requirement to AETC as
the total Air Force production requirements for a given AFSC. The trained personnel
requirement does not include ANG, AFR, sister service, international or Air Force civilian
personnel. Note: The process to satisfy trained personnel requirements is not limited to
AETC formal schools.
5.2.1.2. Student Training Requirement. Student training requirement is the sum of ANG,
AFR, sister service, international, and Air Force civilian training requirements for initial
skills training. It represents all resource categories except active duty Air Force NPS, PS,
and retrainees.
5.2.2. Officer Initial Skills. The officer initial skills reflects the non-rated line officer technical
training requirements for force sustainment in each officer AFSC. It includes initial skills
technical training requirements for Total Force, international, and Air Force civilian personnel.
5.2.3. Mission Readiness Training Program. The mission readiness training program reflects
baseline requirements for RegAF directed, component, and MAJCOM (warfighter and
support) technical training (PS, retraining, supplemental, 7-level, etc.).
104 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.2.4. Trained Dog Requirements. Trained dog requirements reflect the military working dog
technical training requirements for sustainment across the DoD and Transportation Security
Administration, based on the outcome of the annual meeting of the Joint Services Military
Working Dog Committee, whose inputs are vetted, consolidated and submitted by the HQ Air
Force Director of Security Forces (AF/A4S) to AF/A1PT.
5.2.5. Field Training Detachment (Type-4). The field training detachment reflects TDY and
TDY en-route funds to achieve mission requirements through technical training at worldwide
field training detachments.
5.2.6. Non-Resident Training (Type-6). The non-resident training reflects requirements to
fund the analysis, design, implementation and maintenance for non-resident courses.
5.2.7. Language Program. The language program reflects validated technical training
requirements necessary for force sustainment in airborne and ground linguist AFSCs, as well
as requirements for basic, intermediate and advanced language training for non-linguists
requiring specialized language skills (e.g., attachés serving outside of the US).
5.2.8. Sister Service. The sister service reflects validated technical training requirements
necessary for force sustainment when Air Force members attend other services’ course(s) of
training. It includes Air Force officer and enlisted initial skills training and mission readiness
training programs.
5.3. HQ Air Force Technical Training Tasking Documents.
5.3.1. Tasking Documents. Technical training requirements must be aligned with the
planning, programming, budgeting, and execution cycle. (T-3). The primary vehicles that
capture and align training requirements to resources are the program requirements documents
and the program guidance letters. See Table 5.1 for program guidance letters and program
requirements documents programs and users.
5.3.2. Technical Training Data Call Message.
5.3.2.1. AF/A1PT disseminates an annual technical training data call message that
provides guidance and timelines for submitting technical training requirements for three
years out.
5.3.2.2. Training requester quota identifier managers input their training requirements into
the MilPDS/OTA. From these inputs, the training manager validates training requirements
and builds class schedules. Those schedules then flow back to OTA to the training
requester quota identifiers for sub-allocation (loading of names) and execution.
5.3.2.3. Specific timelines and deadlines are provided in the data call. Exceptions:
5.3.2.3.1. The process of establishing the Air Force airborne (1A8X1) and ground
linguist (1N3XX) training requirements is different from all other enlisted career fields.
The specific shred and/or suffix and language requirements are established by the Air
Force CFMs in coordination with AF/A1PT.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 105
5.3.2.3.2. The Army is the executive agent for global language training. Therefore,
the Air Force follows the Army’s process and timeline for requesting and updating
language training requirements.
5.3.2.3.3. Air Force language out-year requirements are projected at the annual
Structure Manning Decision Review. In addition, execution year and out year language
training requirements are reviewed and updated on a quarterly basis at the Training
Requirement Arbitration Panel.
5.3.2.4. AETC/A3LZ serves as the Air Force requirements manager for language training
and sister service skills training.
5.3.2.5. The process of establishing sister service and/or other agency training
requirements differs from all career fields where training is provided by Air Force. Where
sister services and/or other agencies are the training providers, AETC/A3LZ serves as the
Air Force requirements manager for sister service and/or other agency training.
5.3.2.6. Air Force must follow the sister service and/or other agency processes and
timelines for requesting and updating training requirements. (T-3).
5.3.3. Program Guidance Letters, Program Requirements Documents, Programs, and Users.
The technical training requirements are identified for each of the programs listed in Table 5.1
below. Each program has a set of requirements documents that is broken down by the training
requester quota identifiers. Training requester quota identifiers are four-character
communication codes within MilPDS/OTA used to convey annual or supplemental training
requirements, quota allocations, quota confirmations, and student-tracking information
between a training user and the training provider (owner). The Air Force assigns training
requester quota identifiers to sister services, components, MAJCOMs, forward operating
agencies, direct reporting units and functional areas to ensure training accountability.

106 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 5.1. Program Guidance Letters, Program Requirements Documents Programs and
Users.
Technical Training Program
Training Requester Quota Identifiers
1
Enlisted Initial Skills
AJ10, AJ30 - RegAF NPS / Follow-On
AJ1J, AJ3J, AMDO, AJ50 - Retrainee
AJ1K - Regular PS
CC10 - ANG NPS, PS (Non-Flying)
CNN0 - ANG NPS, PS (Flying)
RR10 - AFR NPS, PS
A0M0 - AFR ART
DA00 - United States Army
DANG - Army National Guard
DAAR - Army Reserve
DN00 - Navy
DM00 - Marine Corps
DP10 - United States Coast Guard
A2C0 - PALACE ACQUIRE (Civilian)
MX20 - Air Force Security Assistance Training/Royal
Saudi Air Force
2
(Non-Rated Line) Officer
Initial Skills
AM10 - RegAF Accessions
AM11 - RegAF Crossflows
CC10 - ANG Non-Flying
CNN0 - ANG Flying
RR10 - AFR
A0M0 - AFR ART
MX20 - Air Force Security Assistance Training
A2C0 - PALACE ACQUIRE (Civilian)
Multiple Training Requester Quota Identifiers - Civilian or
Other
3
Mission Readiness Training
Wide variety of training requester quota identifiers for
the following categories: warfighter, support, AF
directed, MAJCOM equivalent, special categories.
4
Trained Dog Requirements
Multiple Training Requester Quota Identifiers - RegAF
DA00 - United States Army
DN00 - United States Navy
DM00 - United States Marine Corps
TSA (Transportation Security Administration)
5
Non-Resident Training
Wide variety of training requester quota identifiers for
distance learning (Type-6) courses for the following
categories: warfighter, support, Air Force directed,
MAJCOM equivalent.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 107
Technical Training Program
Training Requester Quota Identifiers
6
Field Training Detachment
AJ40 - Type-4 courses conducted at operational locations
primarily use this training requester quota identifier
CC10 - ANG NPS, PS (Non-Flying)
CNN0 - ANG NPS, PS (Flying)
RR10 - AFR NPS, PS
A0M0 - AFR ART
DP10 - United States Coast Guard
MX20 - Air Force Security Assistance Training/Royal
Saudi Air Force
Note: See the master training requester quota identifier list for an explanation of each code
5.3.4. Reclassification Guidance.
5.3.4.1. Enlisted.
5.3.4.1.1. AF/A1PT provides reclassification guidance to HQ AETC annually based
upon current Department of the Air Force needs.
5.3.4.1.2. The reclassification process is covered in more detail in an AETCI 36-2651.
5.3.4.2. Officers. Line officer initial skills training eliminees, whether elimination was
self- initiated or not, and whether before or after training commences (to include initial
training declination), may be considered for reclassification contingent on current RegAF,
ANG, and AFR requirements. Guidance for initial skills training eliminees is covered in
more detail in Chapter 2, AFI 36-2110, and AFPCI 36-112.
5.4. Capacity Assessment and Constraints.
5.4.1. Tasking. Upon receiving the draft program guidance letters from AF/A1PT, AETC
assesses capacity to determine capability to train stated requirements.
5.4.2. Schoolhouse Capacity Assessment. This assessment includes course level schoolhouse
capacity and aggregate installation level base operating support and basic military training
capacity. Technical training constraints include AETC and sister service and/or other agency
limitations and shortfalls.
5.4.3. Constraints. If entries identified on the programmed technical training exceed existing
schoolhouse capacity, schoolhouse personnel complete a constraint worksheet that identifies
any combination of facility, equipment, base operating support, and/or instructor limitations.
AETC identifies these constraints to AF/A1PT if these resource shortfalls cannot be met within
the MAJCOM. For officer and enlisted initial skills, AF/A1PT uses the constraints identified
(e.g., facility, equipment, base operating support) to advocate for additional resources to
unconstrain the AFSC/course. When the constraint cannot be resolved immediately, AF/A1PT
considers the re-distributing the training requirement delta to other AFSC(s) on the program
guidance letter(s).
5.4.4. AETC Process. The capacity and constraint processes are covered in more detail in
AETCI 36-2651.

108 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.5. Technical Training Requirements Working Groups.
5.5.1. Enlisted Initial Skills. AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ co-chair the annual Training Flow
Management Working Group to provide a forum for timely detailed discussion of all issues
regarding requirements and schoolhouse capacity and to facilitate cross feed of information
between users and providers of initial skills training.
Table 5.2. Training Flow Management Working Group Organization.
Category
Participants
1
Co-chairs
AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ
2
Attendees
Representatives from AETC Personnel Division (A1K), Manpower
and Organization Division (A1M), A3LR, Graduate Flying Training
Division (A3Z), Undergraduate Flying Training Division (A3F),
Surgeon General (SGU), 2 AF, schoolhouses, ANG, AFR, sister
services, internationals, AFPC Retraining, Air Force Recruiting.
Representatives are usually TRQI Managers.
5.5.2. Officer Initial Skills. AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ co-chair the annual Officer Initial
Skills Working Group to provide a forum for timely detailed discussion of all issues regarding
requirements and schoolhouse capacity and to facilitate cross feed of information between
users and providers of initial skills training.
Table 5.3. Officer Initial Skills Working Group Organization.
Category
Participants
1
Co-chairs
AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ
2
Attendees
AFPC Officer Accessions, AFPC Officer Crossflows, HQ
AETC/A1M, 2 AF, schoolhouses, ANG, sister service,
internationals, CFMs. Representatives are usually training
requester quota identifier managers.
5.5.3. Mission Readiness Training Program. AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ co-chair the annual
Mission Readiness Training Program Working Group to provide a forum for timely detailed
discussion of all issues regarding requirements to facilitate cross feed of information between
users and providers. The working group covers training requirements for the following
programs: mission readiness training program, trained dog requirements, non-resident, and
field training. The AF/A1PT technical training data call message triggers a critical data
gathering point for all out-year technical training requirements.
5.5.3.1. AETC/A3LZ works pre-scheduling requirements and prepares the mission
readiness training, non-resident, trained dog requirements, and field training detachment
spreadsheets.
5.5.3.2. Key purposes of the working group are to educate training requester quota
identifier managers and establish out-year requirements to be incorporated into the program
guidance letters and program requirements documents.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 109
Table 5.4. Mission Readiness Training Program Working Group Organization.
Category
Participants
1
Co-chairs
AF/A1PT and AETC/A3LZ
2
Attendees
2 AF, MAJCOMs, forward operating agencies, direct reporting units,
training requester quota identifier managers (Air Force and non-Air
Force).
5.6. Program Guidance Letter Changes (Adjustments and Quota Management).
5.6.1. Program Guidance Letter Adjustments.
5.6.1.1. AF/A1PT transmits budget year and execution year adjustments to AETC
representing AF customer requirements.
5.6.1.2. When AF/A1PT requests proposed adjustments to the program guidance letters,
AETC/A3LZ updates the programmed technical training document(s) to identify the
proposed change to the specific pipeline(s) and publishes to the appropriate electronic
portal site. AETC/A3LZ then staffs an electronic staff summary sheet (with link to
website) with all appropriate organizations (AETC, A-Staffs, Second Air Force, Air Force
Personnel Center, etc.) requesting impacted organizations assess capacity and identify if
all, part or none of the proposed change(s) (increase or decrease) can be implemented with
existing resources. Once notification is received identifying what part of the change(s) can
be supported, AETC/A3LZ updates the applicable programmed technical training with the
portion that can be executed and notifies AF/A1PT of the portion that could not be
supported without additional resources. If additional resources are required, AETC/A3LZ
notifies AETC/A3LR (and/or other users of required unfunded resources). For Total Force,
AETC/A3LR will request that an unfunded requirement submission be placed in the
execution plan to the Air Force corporate structure. For non-AF requirements, AF/A1PT
will work with affected users to resolve resource shortfalls. The applicable programmed
technical training will not be updated with the proposed change until the resources are
procured. Exception: AETC/A3LZ updates applicable mission readiness training
programmed technical training and/or relevant requirements (i.e., trained dog requirements
and non-resident) only after completion of capacity and resource assessments and final
approval from AF/A1PT.
5.6.1.2.1. Total Force Adjustments. RegAF end strength, accession balancing and
overall field sustainment follow the process in paragraph 5.6.1.2.
5.6.1.2.2. Non-Total Force (Other Users’) Adjustments. Follow the quota
management adjustment process in paragraph 5.6.2 when non-Total Force tech
training users request scheduled unfilled seats. This process assumes post-scheduling
activity. If officer and/or enlisted initial skills or mission readiness training changes
and/or adjustments affect resources, multiple FYs, or multiple program guidance
letters, use process in paragraph 5.6.1.2.
5.6.2. Quota Management.
5.6.2.1. Quota management is the operation of swapping or moving scheduled quotas
between non-Total Force users or requesting the use of another non-Total Force training
user’s future scheduled unfilled seats. Air Force customers manage quotas during the
110 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
execution year to ensure the most efficient use of training resources. The quota
management authority requires properly completed worksheets for quota movements and
out-of-cycles promoting a quota management discipline among Air Force customers and
reducing risks of erroneous or unintended actions. All training requester quota identifier
managers are eligible to make quota management requests except for regular training
requester quota identifiers (regular Air Force NPS, PS, and retrainees). The quota
management authority may reallocate scheduled training quotas after coordination with the
training manager for the following resource categories in the execution year: ANG, AFR,
sister services, internationals and civilians. Training requester quota identifier managers
may request quota management actions (except for regular training requester quota
identifiers) to the quota management authority using the prescribed worksheets. The quota
management authority and the affected training manager will coordinate on each request.
(T-3).
5.6.2.2. The training requester quota identifier manager uses the training quota movement
worksheet to request a movement of quota(s) from one class to another class and convert
quota types (whether it is for the first or second digit). This can be done for a class-to-class
move or a same class seat conversion. For officer and enlisted initial skills, the training
requester quota identifier manager’s total number of quotas in the course should not
increase or decrease without AF/A1PT approval.
5.6.2.2.1. For mission readiness training courses under Second Air Force’s purview,
the training requester quota identifier manager sends all completed worksheets
impacting AP, OP, or CP quota types (See paragraph 5.7.4 for definition) and AN,
ON, or CN quota types to the appropriate Second Air Force program manager and all
completed worksheets impacting AT, OT, or CT quota types to the Second Air Force
mission readiness training office execution manager. Note: Ensure the email subject
line includes the course number and class start date. For technical training initial skills
courses, submit change requests to AETC/A3LZ.
5.6.2.2.2. For mission readiness training program, the training requester quota
identifier manager uses the out-of-cycle request worksheet to request the use of another
training user’s unfilled seats or request new seats be added.
5.6.3. AETC Process. For further details on AETC’s role in requirement adjustments and
quota management, refer to AETCI 36-2651.
5.7. Mission Readiness Training Program.
5.7.1. General Information. The mission readiness training program objectives are to develop
and maintain professional and technical skills, knowledge, and abilities to meet Air Force
needs. The mission readiness training program provides travel, per diem, lodging, and special
authorization funds for AETC CONUS formal training courses to aid mission accomplishment
as specified in this chapter. It provides advanced, supplemental, and residential craftsman
technical training for courses of up to 99 academic days (less than 20 calendar weeks), for
officers, enlisted and civilian personnel when other types of training such as on-the-job-
training, unit training, exportable, or mobile training will not satisfy the need.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 111
5.7.1.1. Air Force civilians, foreign direct or indirect hires in validated funded DoD
positions, non-appropriated fund employees in validated (appropriated funded or
unfunded) services manpower positions, or foreign exchange military officers filling Air
Force validated UMD positions are authorized to utilize AETC central funds.
5.7.1.2. The ANG provides active duty training days, travel, per diem, lodging, and special
authorizations funds for formal training courses. These courses support mission
accomplishment through NGB/A1D school day funding authorization or unit level
funding.
5.7.2. Scope and Structure. The mission readiness training program is a key part of the Air
Force’s training resource and plays a vital role in maintaining readiness and a quality force. It
consists of two categories – Air Force-directed training and MAJCOM (warfighter and
support) training. During the identification and validation process, training requirements must
be priority ranked based on levels of training urgency. (T-3). Mission readiness training
program requirements will be categorized as priority level-1 (mission accomplishment),
priority level-2 (mission sustainment) or priority level-3 (mission enhancement). (T-3). The
mission readiness training program functions through a series of processes ensuring mission
accomplishment training (priority level-1) is accomplished first and that there is a maximum
use of funding level-1 (AETC centrally-funded allocations, “T”-allocations). The mission
readiness training program includes the following types of training:
5.7.2.1. Air Force-Directed Training. Training in support of trained personnel
requirements to replenish and balance the force. It ensures enough trained personnel are
in each skill to accomplish the Air Force mission. It also includes training incidental to
assignment action, certain special assignments, upgrade training, promotions, and unique
training as specified by the Air Staff. Air Force-directed training requirements are
categorized as priority level-1 and include:
5.7.2.2. Air Force Legal Services. AETC centrally-funded courses attended by members
of the Air Force Judge Advocate General’s Corps.
5.7.2.3. Colonel’s Group. Training support for officers identified by the colonels’ group.
5.7.2.4. Senior Leader’s Group. Training for general officers and senior executive service
civilians.
5.7.2.5. Lateral Training. Enlisted personnel retraining into a career field that does not
accept active duty Air Force NPS students; such pipelines are called lateral skills.
5.7.2.6. NPS Training (Initial). NPS enlisted personnel who flow from an initial skills
course of 20 calendar weeks or longer into an initial skills course shorter than 20 weeks.
These personnel are still in the training pipeline; however, since their first initial skills
course was 20 weeks or longer and classified as a PCS, any subsequent training at a
different location that is up to 99 academic days (shorter than 20 calendar weeks) entitles
the member to per diem and is classified as a TDY. NPS students attending TDY-length
training (less than 99 days), after being assigned to a PCS-length training course (over 99
days), will attend the subsequent training using a MRT Level 1 quota (unless the
subsequent and/or follow-on training is medical which is funded by the Defense Health
Program (DHP) Appropriation).
112 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.7.2.7. NPS (Follow-On). NPS enlisted personnel (see paragraph 5.7.2.6) continuing
their initial skills training in follow-on courses. These personnel are still in the pipeline;
however, since their first initial skills course is 20 calendar weeks or longer and classified
as a PCS, any subsequent training of up to 99 academic days (shorter than 20 calendar
weeks) entitles the member to per diem and is classified as a TDY. NPS students attending
TDY-length training (less than 99 days), after being assigned to a PCS-length training
course (over 99 days), will attend the subsequent training using a MRT Level 1 quota
(unless the subsequent and/or follow-on training is medical which is funded by the Defense
Health Program (DHP) Appropriation).
5.7.2.8. Officer Accessions. Initial skills training for all new officer accessions following
their commission through OTS, AFROTC or USAFA.
5.7.2.9. Advanced Training. Officer and enlisted advanced training.
5.7.2.10. Officer Crossflows. Initial skills training for all officers crossflowing or
retraining into a new AFSC.
5.7.2.11. PALACE ACQUIRE. Training for newly acquired civilian employees under the
Air Force Personnel Center’s PALACE ACQUIRE intern program.
5.7.2.12. PME Assignments. TDY en-route training for officers requiring prerequisite
language training prior to attending international PME courses. Mission readiness training
program only funds language training, which is up to 99 academic days (or less than 20
calendar weeks), and does not fund any part of the PME course. The majority of officers
attending prerequisite language training attend in a PCS status.
5.7.2.13. Retraining (Initial). Enlisted personnel retraining into new career fields.
5.7.2.14. Retraining (Follow-On). Enlisted personnel continuing their retraining in
follow-on pipeline courses.
5.7.2.15. Active Duty Air Force PS. PS enlisted personnel who require all or part of a
training pipeline to meet career field qualifications leading to award of the Apprentice, 3
skill level.
5.7.2.16. Recruiter and Instructor. Enlisted personnel attending the basic recruiter,
military training instructor, or military training leader course.
5.7.2.17. Secretary of the Air Force Public Affairs. Advanced training for senior non-
commissioned officers or officers in the public affairs career field.
5.7.2.18. Support Officers. Normally, related to embassy and attaché assignments.
5.7.2.19. Seven-Level Craftsman Training. Upgrade training for all active duty military
attending resident 7-Level Craftsman courses.
5.7.3. Mission Readiness Training Program Funding & Priority Levels.
5.7.3.1. Mission Readiness Training Program Funding Levels. Mission readiness training
allocations are divided into two funding categories: funding level-1 and funding level-2.
5.7.3.1.1. Mission readiness training program funding level-1; AETC TDY-to-school
centrally funded quotas identified with a “T” in the 2nd position of the quota type
(Example: AT, OT, or CT).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 113
5.7.3.1.2. Mission readiness training program funding level-2; unit or other than
AETC centrally funded quota; identified with a P or N in the 2nd position of the quota
type (Example: AP, OP, CP, AN, ON, or CN). See quota type definition in paragraph
5.7.4 for detailed breakout information.
5.7.3.2. Mission readiness training must be prioritized by each MAJCOM and/or
organization according to its capabilities to meet the user’s mission. (T-3). Use the
following priority level definitions:
5.7.3.2.1. Priority Level-1 (Mission Accomplishment). Accomplishment of the Air
Force mission objective will not occur if training requirement is not satisfied.
Requestor(s) will fund their requirement(s) if not supported by mission readiness
training program funding. (T-3).
5.7.3.2.2. Priority Level-2 (Mission Sustainment). Training required to sustain the Air
Force readiness posture.
5.7.3.2.3. Priority Level-3 (Mission Enhancement). Training fosters the effective use
of resources to enhance the Air Force mission capability.
5.7.3.3. Funding Level and Priority Level Relationships.
5.7.3.3.1. Funding Level-1 and/or Priority Level-1 (T-Quotas). These quotas are
AETC centrally funded requirements and represent training the user considers essential
to mission accomplishment. This total requirement will not exceed the funding level-
1 baseline stated in the mission readiness training program guidance letters or program
requirements documents issued by AF/A1P. (T-3).
5.7.3.3.2. Funding Level-2 and/or Priority Level-1 (P/N-Quotas). These quotas are
must have requirements, regardless of funding, for training the user considers mission
accomplishment (essential). These quotas represent the requirement needs above the
user’s funding level-1 mission readiness training program guidance letters baseline and
will be reflected on an AF Form 3933. The user acknowledges the certification
statement of AF Form 3933, Section III - this training requirement meets the criteria
for priority level-1 urgency, and if Air Force funds cannot support the request, then unit
funds will be utilized. (T-3).
5.7.3.3.3. Funding Level-2 and/or Priority Level-2/3 (P/N-Quotas). These quotas are
unit funded and represent requirements for training the user considers mission
sustainment (priority-2) or mission enhancement (priority-3) and will be budgeted for
within the unit. The total requirement of funding level 2 and/or priority levels-2/3 (P/N-
quotas) cannot exceed the funding level-2 (unit funded) baseline stated in the AF/A1PT
issued mission readiness training program guidance letters. Quotas above the funding
level-2 (P/N-quota) baseline represent additional requirement needs and will be
reflected on an AF Form 3933, request for increase. (T-3).
5.7.3.3.4. The schoolhouse must accommodate all funding level-1 and/or priority
level-1 requirements before they fulfill any lower funding level and/or priority level
requirements. (T-3).

114 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.7.4. Quota Type. A two-character code within MilPDS/OTA used to indicate the student's
active duty status (i.e., enlisted, officer, or civilian) and the travel funding status (e.g., AETC
centrally-funded, unit-funded, or non-TDY). The particular codes are as follows, with the
understanding that any code in the 1st digit can be paired with any code in the 2nd digit:
Table 5.5. Quota Type Breakdown (Mission Readiness Training Program).
1st Digit (Active Duty Status)
2nd Digit (Travel Funding Status)
A (Enlisted Airman)
T (AETC – Centrally Funded; TDY-to-
School)
O (Officer)
P (Unit Funded, see Note 1)
C (Civilian)
N (Other, see Note 2)
Notes:
1. “P” may be used in the 2nd
digit if the student is co-located with the training location.
2. “N” funding status is usually used for NPS pipeline students, PCS-length schools (20 calendar
weeks or longer), contractors, foreign nationals, or Air Reserve Component users.
5.7.5. Special Funding Restrictions.
5.7.5.1. AETC funds will not be used for RegAF members and Air Force civilian
personnel assigned or on permanent duty outside of Air Force but otherwise within the
DoD, unified commands or Joint Service activities.
5.7.5.2. Students who are not RegAF members are funded by the component or branch of
service or US government agency to which they are assigned.
5.7.5.3. Travel and per diem expenses for students or instructors at command courses are
the funding responsibility of the Air Force activity to which the individual student or
instructor is assigned.
5.7.5.4. ANG students are funded by NGB/A1D or the wing publishing the travel orders.
5.7.5.5. HQ AFRC funds AFR members and ARTs who have military allocations.
However, AETC funds civilians, RegAF members assigned to AFR and ARTs who have
civilian allocations, with the same limitations as for RegAF personnel within their allocated
baseline.
5.7.5.6. The unit training manager and supervisor will ensure students are fully qualified
to attend or enroll in required courses. (T-3). The schoolhouse will contact the servicing
FSS, who will direct the return of the students to their parent organization as a result of
being unqualified to enter an Air Force training program course. (T-3). The member’s unit
will bear all TDY expenses to and from the school. (T-3). If the school finds the member
unqualified for training, the member’s orders issuing authority will immediately amend the
orders. (T-3). The organization selecting and publishing orders on the student concerned
will ensure the orders are amended to reflect the parent unit’s fund citation. A copy of this
amendment must be sent to the 502d Comptroller Squadron, JBSA-Randolph, Texas.
(T-3).

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 115
5.7.5.7. Unqualified ANG students removed from training will only be returned to formal
training once full qualification is obtained using unit level funding.
5.7.5.8. AETC mission readiness training program technical training funds will not be
used for: special contract training (type-1), field training detachment (type-4), distance
learning (non-resident) training (type-6) courses. Authorization to use mission readiness
training funds to travel to attend mobile training team (type-7) courses is handled under the
special authorization process.
5.7.5.9. Courses that are 20 calendar weeks or longer are considered a PCS and AETC
mission readiness training program funds are not authorized for the travel, per diem,
lodging or special authorization expenses. All expenses will be charged to the PCS fund
citation. (T-3). Additionally, students are considered to be in a PCS status when attending
two or more courses at one location and the courses, combined, total 20 weeks or longer in
duration. Secretary of the Air Force is the waiver authority (T-1); UTMs route requests
for waiver through command channels to AF/A1PT for processing. For current list of
approved Secretary of the Air Force waivers, contact AF/A1PT. Refer to AFI 36-2110,
and the JTR.
5.7.5.10. The travel, per diem, lodging, and special authorization expenses for attendance
to Air University, AFIT, flying, survival, medical, and command specific courses are not
funded with AETC mission readiness training program funds.
5.7.6. Special Authorizations.
5.7.6.1. When the RegAF AETC TDY-to-school fund-citation is used on orders, it is only
for normal travel, per diem and lodging for non-initial skills training pipeline student
allowance. The FSS or student must request and receive prior approval from Second Air
Force mission readiness training program for any additional expenditure(s) before
including special authorizations in orders that use the RegAF AETC TDY-to-school central
fund-cite. (T-3). Special authorizations include, but are not limited to, travel to attend type-
7 courses, rental cars and vicinity mileage, when requested as more advantageous to the
government. (T-3). Requests are evaluated on a case-by-case basis and will not be
approved solely for the convenience of the member. (T-3). NGB/A1D processes special
authorization requests for ANG funded orders.
5.7.6.2. The Second Air Force mission readiness training office is the point of contact for
all technical training (to include 7-level and type-7) special authorization requests. All
individuals requesting special authorizations involving the use of AETC centralized funds
will submit their requests through their servicing FSS’s formal training and/or base training
office or commander’s support staff. (T-3). The Second Air Force mission readiness
training office will process the request in order of receipt. (T-3). Note: The Second Air
Force mission readiness training office does not process special authorizations for flying,
medical, survival, AFIT, Defense Acquisition University, and Air University training
because those organizations have their own points of contact and approval processes.
5.7.6.3. Students eligible for training using AETC funds will request a special
authorization memorandum from [email protected]. Requests must be received no later
than seven duty days prior to class start date. (T-2).

116 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
5.7.6.3.1. Students and/or travelers must provide a non-availability letter/statement, if
billeted off base and requesting a rental car or vicinity mileage. (T-3). Approved
vicinity mileage requests will be processed upon the completion of the course. (T-3).
5.7.6.3.2. Students using AETC funds must provide a copy of TDY orders (both front
and back) to the Second Air Force mission readiness training office, if published. (T-3).
5.7.6.3.3. Prior to class start date, students must refer to
https://www.defensetravel.dod.mil/ for the availability of service lodging and dining
facilities at each installation. (T-3).
5.7.6.3.4. Rental cars are issued one per five AETC centrally-funded students per class
and are authorized on a first come, first come, first served basis. AETC centrally-
funded students take passenger precedence over any other student(s). Note: ANG
rental cars are issued at one car per five students per class. ANG CFMs validate rental
car requests and manage car assignment after approval by NGB/A1D.
5.7.6.3.5. If approved, vicinity mileage is paid for training days only and is defined as
the distance to or from school; the distance from the off-base quarters to training
location (e.g., Four miles from hotel to base x 2 = 8 round trip miles x training days.)
5.7.6.3.6. Vicinity mileage may not be authorized if government transportation has
been provided by the Second Air Force mission readiness training office, i.e.,
maximum rental cars have been provided for a class.
5.7.6.3.7. Approval of special authorizations must be received by the Second Air Force
mission readiness training office prior to travel of the trainee and stated in the member's
travel orders (except vicinity mileage requests). (T-3). If not, amendments to member’s
orders will need to be accomplished. (T-3). Note: For NGB funded orders, approval
for special authorizations must be received from NGB/A1DU prior to travel and stated
in the member’s travel order. (T-3).
5.7.6.3.8. Eligible members traveling by air requiring additional clothing may be
authorized excess baggage. This applies when training extends over two seasons or
special circumstances dictate additional gear described in the Education and Training
Course Announcements and justified by the Second Air Force mission readiness
training office. Note: For NGB funded orders, ANG students request excess baggage
authorization through NGB/A1D.
5.7.6.3.9. Eligible members who drive their privately owned vehicles are not
authorized shipment of household goods or do-it-yourself moves. Members who are
PCS with TDY en-route may request shipment of household goods under PCS funds
and not mission readiness training program TDY funds.
5.7.6.3.10. Request for shipping of household goods and/or do-it-yourself moves for
TDY personnel are usually disapproved. All required items should already be at the
training location. Approval may be granted for shipment of household goods and/or
do-it-yourself moves if a member is housed in field conditions.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 117
5.8. Metrics Submissions.
5.8.1. AETC Force Development Planning and Analysis Division (AETC/A3L). Develops
and submits to AF/A1PT semi-annual budget justification books (J-Books) for each calendar
year as prescribed by AF/A1X. Develops and submits to AF/A1PT annual institutional
training readiness report.
5.8.2. Second Air Force. Develops and submits to AETC and AF/A1PT the following:
5.8.2.1. Monthly Execution Report Tracker. Required for the mission readiness training
and/or trained dog requirements, and field training detachment programs. Identifies the
funding level-1 baseline execution rates of the approved training requester quota identifiers
during the year of execution.
5.8.2.2. Annual Funding Level-2 Execution Report. Required for the mission readiness
training and/or trained dog requirements, field training detachment, and non-resident
programs. Identifies the unit funded or co-located execution rates of the programs at the
end of the FY.
5.8.2.3. Reports tasked in the enlisted reclassification rack and stack guidance.
118 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Chapter 6
AIRMAN RETRAINING PROGRAM
6.1. Officer Crossflow and Reclassification Programs.
6.1.1. Purpose.
6.1.1.1. The Nonrated Line crossflow program is a process to more effectively balance
officer inventory to AF requirements. It addresses AFSC manning shortages and over
manning situations, and uses a methodology to facilitate shaping the officer force within
authorized, funded end strength. To execute this process, a crossflow panel is convened
when needed to select the best qualified officers to fill the required vacancies.
6.1.1.2. The Missileer Crossflow Program is a process ensuring the Nuclear and Missile
Operations (13N) AFSC remains balanced for sustainment by crossflowing excess officers
at the 4-year point back to donor career fields. Donor career fields are those who have
provided a portion of their annual accessions to support the 13N community
intercontinental ballistic missile crew force mission needs. During this process the AF
simultaneously selects officers to stay in the 13N AFSC and to crossflow to undermanned
donor career fields.
6.1.1.3. Out-of-cycle crossflow requests from individual officers occur only when
participation in a formal board process is not practical. Approval or disapproval is based
on a variety of factors including gaining and losing career field manning, CFM, Air Force
Personnel Center (AFPC), and AF, Force Management Policy (AF/A1P) coordination.
6.1.1.4. Initial skills training eliminee reclassification occurs when Regular AF (RegAF)
line officers on EAD are eliminated from training in accordance with AFPCI 36-112.
Initial skills training elimination panels convene regularly to consider these officers for
reclassification or separation based on current AF requirements.
6.1.2. Program Processes.
6.1.2.1. AFPC, Special Duty Career Management Section (AFPC/DP2OSS) will:
6.1.2.1.1. Select panel members and execute Nonrated Line crossflow program and
Missileer Crossflow Program. (T-2).
6.1.2.1.2. Serve as approval authority if immediate out-of-cycle crossflow actions are
necessary. (T-1). Action is to be coordinated with AF/A1P and does not require a
crossflow panel or program. (T-2).
6.1.2.1.3. Notify officers of their eligibility. (T-2).
6.1.2.1.4. Prepare results package for AFPC/CC approval and provide courtesy copy
to AF/A1P. (T-2).
6.1.2.2. AFPC/DP2L will serve as initial skills training elimination panel president, selects
panel members, and executes the initial skills training eliminee reclassification process.
(T-2).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 119
6.1.2.3. Wing Commander or equivalent (Nonrated Line Panel and Missileer Crossflow
Panel programs only) will endorse nomination package providing comments on whole-
person concept and recommendation for crossflow. (T-2).
6.1.2.4. AFPC Judge Advocate (AFPC/JA) will perform a legal review of all initial skills
training eliminee cases when documentation in the elimination package indicates that
discharge is for substandard performance of duty or misconduct, moral or professional
dereliction, or for other reasons under AFI 36-3206 as appropriate. (T-2).
6.1.2.5. Applicants will complete nomination packages in accordance with AFPC
instructions, prioritize available AFSC crossflow or reclassification opportunities as
desired, declare volunteer status, and submit documents through the proper channels. (T-2).
For out-of-cycle crossflow requests, applicants will contact their assignments manager for
specific instructions. (T-2).
6.1.3. Nonrated Line Crossflow Program.
6.1.3.1. A panel competitively selects volunteers and non-volunteers from career fields
with overages for crossflow or retraining into shortage career fields using specific
qualification and established selection and scoring criteria.
6.1.3.2. AFPC/DP2OSS will select five AF officers in the grade of colonel as panel
members. (T-1). The panel is held to affect formal training and PCS moves.
6.1.3.3. Crossflow Panel Purpose. The panel’s goal is to competitively select officers who
have the greatest opportunity to gain the experience with the highest potential for success
serving in their gaining career field.
6.1.3.3.1. The panel considers the whole-person concept, including, but not limited to,
the officer’s application, overall record of performance, senior rater recommendations,
academic degrees and transcripts (if required), specific qualifications in accordance
with the AFOCD, officer professional development, career timing to assess the
officer’s relative standing among the officer’s peers, and time on station.
6.1.3.3.2. If necessary, select non-volunteers to crossflow based on a reverse seniority
criteria (most junior officers in a year group first) and the whole-person concept to
maximize return on training.
6.1.3.3.3. Seniority is defined in AFI 36-2501, Officer Promotions and Selective
Continuation. The panel considers the career development of Nonrated Line officers,
however, it does not function as a development team.
6.1.3.4. Eligibility and/or Exemptions:
6.1.3.4.1. AF/A1P will determine eligible AFSCs and year groups based on
sustainment requirements, manning, and other factors. Waiver authority for AFSC and
year group eligibility is also AF/A1P. Field grade officers or officers within the 12-
month period before meeting (prior to) a promotion board to Major in the primary zone
may apply for crossflow but are not involuntarily selected for crossflow. Consideration
for crossflow to the 19ZXA Special Tactics, 19ZXC Combat Rescue, and 19ZXB
Tactical Air Control Party AFSCs is on a voluntary basis only. Officers requesting
crossflow into the above AFSCs are directed to contact the appropriate CFM for
120 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
consideration first but are also vectored by the Nonrated Line crossflow program with
a secondary career field as a back-up.
6.1.3.4.2. Officers meeting the following criteria are exempt from involuntary
crossflow consideration and ineligible to apply for voluntary crossflow consideration.
Only waivers for Total Active Federal Military Service are considered. Waiver
authority for Total Active Federal Military Service is AFPC/DPA.
6.1.3.4.2.1. Officers with an established DOS, including officers not selected for
retention via Force Shaping Board or Reduction in Force.
6.1.3.4.2.2. Officers with quality control indicators (e.g., Unfavorable Information
File, unsatisfactory performance, deferred for promotion, referral performance
reports).
6.1.3.4.2.3. Officers enrolled in and/or selected for AF-sponsored advanced
academic degrees or Education with Industry, or with an ADSC from a completed
advanced academic degrees or Education with Industry program.
6.1.3.4.2.4. Officers who are in-residence graduates of Intermediate
Developmental Education, designated for the next Intermediate Developmental
Education class entry, or Intermediate Developmental Education selects.
6.1.3.4.2.5. Officers already formally selected for reassignment as of panel
convening date.
6.1.3.4.2.6. Officers selected for a 365-day deployment as of panel convening date
or currently serving on a 365-day deployment and redeployment date is after the
first day of the second month of the targeted move cycle; e.g., 1 July for the summer
cycle that starts in June.
6.1.3.4.2.7. Sitting squadron commanders or officers on a Squadron Command
Candidate List.
6.1.3.4.2.8. Officers with cyberspace warfare operations qualifications (17X,
17DXX and 17SXX).
6.1.3.4.2.9. Officers with nuclear qualifications (SEI codes: IWF, MWA, MWB,
MWC, MQT, MQU, MQV; and AFSCs (AFSCs): 21MXN, 21MXI and 31P when
duty experience includes military installations with nuclear missions).
6.1.3.4.2.10. Officers with Psychological Operations qualifications (SEI 9Q).
6.1.3.4.2.11. Officers with 15 or more years Total Active Federal Military Service.
6.1.3.4.2.12. Developmental Engineers who are Test Pilot School graduates.
6.1.3.4.2.13. 38F Field Grade Officers with 2 or more years of manpower
experience.
6.1.3.4.2.14. Officers previously selected for crossflow by any previous panel.
6.1.3.4.2.15. Officers in the Air Force Judge Advocate General’s Corps.
6.1.3.4.2.16. Officers in CONUS with less than 2-years’ time on station at the
beginning of the first month in the targeted move cycle.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 121
6.1.3.4.2.17. Officers assigned Outside of Continental United States with a date
eligible for return from overseas (DEROS) equal to or greater than the first day of
the fourth month beyond the targeted move cycle; e.g., 1 January for the summer
cycle that goes through September.
6.1.3.5. Specific Qualifications for Crossflowing. Officers must be qualified for retraining
in the selected AFSC in accordance with the AFOCD. (T-1).
6.1.3.6. Outcome. AFPC will match officers selected to crossflow to the next available
crossflow training course via the normal assignment process. (T-3). Officers who receive
an assignment selection date or an assignment notification as a result of selection for
crossflow may only decline via 7-day option. Officers who fail their initial skills training
course return to their previous career field. Subsequent panels may be necessary to meet
career field and AF emerging mission requirements. (T-3).
6.1.4. Missileer Crossflow Program.
6.1.4.1. The Missileer Crossflow Program selects volunteers and non-volunteers from the
Nuclear and Missile Operations (13N) AFSC who have completed their initial 4-year
intercontinental ballistic missile crew force tour to crossflow back into donor career fields
or remain in the 13N career field.
6.1.4.2. Colonel representatives from gaining donor career fields with shortages in the year
groups available for crossflowing should, when possible, be part of the Missileer Crossflow
Program, to include participation in the crossflow panel.
6.1.4.3. Crossflow Process Purpose. The Missileer Crossflow Program’s goal is to
simultaneously identify officers to remain in the 13N career field and to crossflow officers
to undermanned donor career fields.
6.1.4.3.1. The process starts with the 13N development team providing AFPC a
stratified list of all eligible officers based on the whole person concept, regardless of
their status as a volunteer or non-volunteer to continue in missile operations. This data
is used to determine quartile distribution for the AFPC classification model.
6.1.4.3.2. AFPC will convene a crossflow panel to determine final AFSC
classification. (T-3). The panel considers the following:
6.1.4.3.2.1. The initial classification results from the AFPC classification model.
6.1.4.3.2.2. The 13N development team-provided list of prioritized officers
approved to continue as 13Ns with enough names to accommodate 1.5 times the
number of officers expected to continue in missile operations for a career.
6.1.4.3.2.3. Senior Rater recommendations, Records of Performance, and officer
preferences.
6.1.4.4. Eligibility and/or Exemptions.
6.1.4.4.1. AF/A1P will determine eligible AFSCs and year groups based on 13N
officers who are completing their initial intercontinental ballistic missile crew force
tour.
122 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.1.4.4.2. Officers have the opportunity to volunteer to crossflow to the following non-
donor AFSCs: 11X Pilot, 12X CSO, 13B ABM, 13C Special Tactics, 13D Combat
Rescue, 13L Air Liaison, and 18X RPA Pilot. Officers requesting crossflow into the
above AFSCs need to contact the appropriate CFM for consideration first but are also
classified by the Missileer Crossflow Program with a secondary career field as a back-
up.
6.1.4.4.3. Officers with an established DOS, including officers not selected for
retention via a Force Shaping Board, do not meet the Missileer Crossflow Program and
remain with the 13N AFSC until separation.
6.1.4.4.3.1. Officers meeting the following criteria are exempt from the Missileer
Crossflow Program. They remain in the 13N AFSC.
6.1.4.4.3.2. Officers with quality control indicators (e.g., Unfavorable Information
File, unsatisfactory performance, deferred for promotion, referral performance
reports).
6.1.4.4.3.3. Officers with 15 or more years Total Active Federal Military Service.
6.1.4.4.3.4. Officers with 6 or more years Total Active Federal Commissioned
Service.
6.1.4.5. Specific Qualifications for Crossflowing. Officers must be qualified for retraining
in the selected AFSC in accordance with the AFOCD. (T-1).
6.1.4.6. Outcome.
6.1.4.6.1. AFPC will match crossflow officers to the first Master Vulnerability List
after completion of the fourth year of their intercontinental ballistic missile crew force
tour. (T-3). Officers who receive an assignment selection date or an assignment
notification as a result of selection for crossflow may only decline via 7-day option.
6.1.4.6.2. AFPC will send crossflow officers to initial skills training en-route to their
first duty assignment whenever practical. (T-3). Officers who fail initial skills training
are considered for retention commensurate with AF needs, or separated from the
service.
6.1.4.6.3. AF, Directorate of Force Development (AF/A1D) will allocate
approximately 100 Missileer Crossflow Program quotas a year to AFPC in the
Squadron Officer School Program Requirement Document or Program Guidance Letter
to provide priority allocation to all Missileer Crossflow Program officers selected to
crossflow out of the 13N career field. AFPC assignment teams will use these quotas
to schedule Missileer Crossflow Program officers for Squadron Officer School with a
priority to the first available class. (T-3).
6.1.5. Out-of-Cycle Crossflows.
6.1.5.1. Out-of-cycle Crossflow Purpose. The goal is to allow officers who are ineligible
to participate in other crossflow programs to request reclassification into another AFSC.
Requests are handled on a case-by-case basis with limited approvals given if crossflowing
is in the best interest of the AF.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 123
6.1.5.2. The process starts with the officer contacting the officer’s current AFPC
assignment team with a request. Disapproval at any step below ends the process with a
notification to the officer. (T-3).
6.1.5.2.1. AFPC assignment team reviews the current officer sustainment matrix to
ensure the crossflow is from an over-manned year group in the current AFSC to an
under-manned year group elsewhere.
6.1.5.2.2. If sustainment supports and the gaining and losing assignment teams believe
the rationale from the officer is in the best interests of the AF, they will seek their
respective CFM’s approvals or disapprovals. (T-3).
6.1.5.2.3. The request with rationale and supporting CFM approvals is forwarded to
AFPC/DPA for review to determine if retraining is in the best interests of the AF based
on training availability, manning, qualification in accordance with the AFOCD, and
other factors as required.
6.1.5.2.4. If AFPC/DPA approves, the crossflow package is forwarded to AF/A1P for
coordination prior to the individual being notified.
6.1.5.3. Outcome. AFPC will match the approved officer to crossflow in the next available
training course via the normal assignment process. (T-2). Officers who receive an
assignment selection date or an assignment notification as a result of selection for crossflow
may only decline via 7-day option. Officers who fail their initial skills training course will
return to their previous career field. (T-2).
6.1.6. Initial Skills Training Eliminee Reclassification
6.1.6.1. An initial skills training eliminee reclassification panel will review and consider
all RegAF line officer eliminees for reclassification or separation based on AF
requirements whether elimination was self-initiated or not, and whether before or after
training commenced (to include initial training declination). (T-2). Exception: Officers
with a previously awarded AFSC, which they are still qualified to hold, will be returned to
that AFSC instead of meeting the panel. (T-2).
6.1.6.2. Panel members will be selected by AFPC/DPS. (T-3). The panel will consist of
five field grade officers in the grade of lieutenant colonel or higher with AFPC/DPS as the
panel president. (T-3).
6.1.6.3. Officer eliminees will complete initial skills training packages for the panel to
review. Guidance on the package contents and instructions on completing are contained
in the Initial Skills Training Elimination Package Guide located on the myPers website,
key word search “IST.” (T-3).
6.1.6.4. The panel will consider the following to determine if reclassification is in the best
interests of the AF:
6.1.6.4.1. A whole-person concept review, which includes the commander’s
assessment on the officer’s commitment to the AF along with any quality force issues.
6.1.6.4.2. Unique or special abilities, degrees, or high demand language skills that
could benefit subject career field or the broader AF in the future.
124 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.1.6.4.3. Consider educational investment already made, officer’s potential to
complete the required training, and the potential payback to the AF. While this should
not be an overriding factor, it must be a consideration.
6.1.6.5. Legal Review. AFPC/JA will perform a legal review of all eliminee cases when
documentation in the elimination package indicates that discharge for substandard
performance of duty or misconduct, moral or professional dereliction, or for other reasons
under AFI 36-3206, as appropriate. (T-3). AFPC/JA will, as appropriate, discuss the case
with the legal office responsible for providing advice to the officer’s commander and make
recommendations to the reclassification panel and the AFPC/CC on whether the case
should be referred to the officer’s command for action under AFI 36-3206. (T-3).
6.1.6.6. Specific Qualifications for Reclassification. Officers must be qualified for
retraining in the selected AFSC in accordance with the AFOCD. (T-2).
6.1.6.7. Outcome.
6.1.6.7.1. The panel president will coordinate on the panel results and forward the
completed recommendations to the reclassification and separation authority. (T-3).
6.1.6.7.2. Based on the panel’s recommendations, the Reclassification and Separation
Authority (AFPC/CC) will approve reclassification or separation of an officer; refer a
case to the officer’s command for processing under AFI 36-3206; or forward the case
to the Secretary of the AF’s Personnel Council (SAF/PC) for action. (T-3).
6.1.6.7.3. Officers approved for reclassification will be matched in the next available
training course via the normal assignment process. (T-2). Officers who receive an
assignment selection date or an assignment notification as a result of selection for
crossflow may only decline via 7-day option.
6.1.6.7.4. Officers not approved for reclassification panel will be separated with
recoupment of educational costs as directed by the Reclassification and Separation
Authority. (T-3).
6.1.6.7.5. If the Reclassification and Separation Authority recommends waiver of
recoupment of an unearned and/or unserved portion of any educational assistance,
bonus, or special pay in excess of $500, the case must be referred to SAF/PC for
decision regarding recoupment liability. (T-3).
6.2. Enlisted Retraining Program Elements.
6.2.1. Retraining Purpose. Retraining is a force management program used primarily to
balance the enlisted force across all AFSCs and ensure sustainability of career fields.
Retraining also provides a means to return disqualified Airmen to a productive status.
Additionally, the program allows a limited number of Airmen the opportunity to pursue other
career paths within the AF. The AF encourages Airmen to voluntarily retrain first, however,
the needs of the AF may require Airmen to be involuntarily retrained to meet sustainment
objectives.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 125
6.2.2. Retraining Advisory. The Retraining Advisory is the primary means to advertise
retraining requirements by fiscal year FY and is maintained on the AFPC myPers website.
Retraining requirements are established via the Program Guidance Letter, identifying the
corporate AF approved training requirements and resources to support execution of training in
accordance with Chapter 5. The retraining advisory advertises two types of requirements:
6.2.2.1. Objective Out. AFSCs where the AF has determined an overage and/or surplus
exists. The AFSCs listed identify by grade the number of Airmen required to retrain out
of these AFSCs. Exception: Does not apply to First Term Airmen.
6.2.2.2. Objective In. AFSCs where the AF has determined shortages exists. The AFSCs
listed identify by grade the number of Airmen required to retrain into these AFSCs. Airmen
use these AFSCs to determine their preferences when applying for retraining.
6.2.2.3. Retraining Advisory Notes. This product is co-located with the Retraining
Advisory on the AFPC myPers website. It provides specific guidelines and special or
unique requirements for each AFSC. Airmen should review the retraining advisory notes
for both retraining in and out AFSCs prior to submitting an application. Applicant should
check these notes closely to avoid delays in the application process.
6.2.3. Personnel Services Delivery Guide. The execution guidance in the myPers website
provides documentation and procedural guidance for personnel processes redesigned as part
of the Personnel Services Delivery Transformation. The execution guidance in the myPers
website is revised continually with additional details for web-based personnel processing
applications to ensure availability of the most current information and guidance.
6.2.4. AFECD. This product is located on AFPC myPers website, Airmen should review the
AFECD prior to applying for retraining to ensure they meet the mandatory AFSC entry
requirements. Each Career Field functional manager is responsible for maintaining the
accuracy of AFSC code entry requirements published within the AFECD and will coordinate
changes with HQ AFPC, Workforce Development and Career Programs Branch
(AFPC/DP3DW). (T-2).
6.3. Enlisted Retraining Program Processes.
6.3.1. AF, Accessions and Training Management Division (AF/A1PT) will:
6.3.1.1. Establish overall AF retraining policy.
6.3.1.2. Monitor and evaluate the Airman Retraining Program.
6.3.1.3. Advise AFPC/DP3DW of policy, procedures, and retraining requirements.
6.3.1.4. Develop the Enlisted Initial Skills Program Guidance Letter on an annual basis
and adjust as necessary.
6.3.1.5. Coordinate retraining requirements with AF, Human Resources Data Analytic and
Decision Support Division (AF/A1XD) to validate against force management sustainment
objectives.
6.3.1.6. Coordinate ETP requests with CFMs and AF/A1XD before approving or
disapproving exception to policies.
6.3.1.7. Coordinate retraining advisory with AFPC/DP3DW before release to the field.
126 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.3.2. AFPC/DP3DW will:
6.3.2.1. Execute established retraining policy, establish procedural guidance, and provide
guidance to the field and manages overall Airman Retraining Program. (T-2).
6.3.2.2. Update and manage the Retraining Advisory and Advisory Notes. (T-2).
6.3.2.3. Monitor disqualified Airmen and quality control standards for retrainees. (T-2).
6.3.2.4. Process ETP requests. (T-2).
6.3.2.5. Identify vulnerable Airmen upon annual implementation of a Noncommissioned
Officer Retraining Program (Phase I and II). (T-2).
6.3.3. AFPC, Formal Training and Retraining Section (AFPC/DP1SST) will:
6.3.3.1. Advise interested Airmen on AF retraining policy. (T-2).
6.3.3.2. Review, process, and approve or disapprove retraining applications. (T-2).
6.3.3.3. Coordinate ETP or waiver requests with AFPC/DP3DW. (T-2).
6.3.3.4. Schedule approved members for formal training. (T-2).
6.3.3.5. Manage class seats, in coordination with AFPC/DP3DW, to include processing
quota movement and quota change requests. (T-2).
6.3.3.6. Review retraining quotas on the Retraining Advisory and ensure the applicant
meets the prerequisites outlined in AFECD, and the Retraining Advisory Notes before
completing the application for enlisted retraining. (T-2).
6.3.3.7. Close all pending retraining applications with no activity within 60 days. (T-2).
6.3.4. AFPC Military Assignments Programs Branch (AFPC/DP3AM) will:
6.3.4.1. Finalize requests for deferment and/or waiver of Assignment Limitation Codes,
Assignment Availability Codes, DEROS window waivers, and waiver of projected
assignment on Airmen applying for retraining. (T-2).
6.3.4.2. Identify CONUS overseas imbalance Airmen returning from overseas for which
no CONUS vacancies exist in the imbalanced AFSC. (T-2).
6.3.4.3. Provide end assignment for retrainees, and reassign Airmen in a PCS status
eliminated from formal training. (T-2).
6.3.5. AFPC/DP3AM will coordinate with AFPC/DP3DW and AFPC, Assignment, Support
Section (HQ AFPC/DP2LWA) on approvable humanitarian and Exceptional Family Member
Program cases when the gaining base does not have authorizations for member’s awarded
AFSCs. (T-2).
6.3.6. HQ AFPC/DP3DW will coordinate Disqualified Airmen actions with AFPC/DP1SST.
(T-2).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 127
6.3.7. AETC Technical Training Strategic Planning and Policy (AETC/A3P) will:
6.3.7.1. Provide AFPC/DP3DW FY requirements upon approval of Enlisted Initial Skills
Program Guidance Letter to allow for the comprehensive program management and student
reporting instructions.
6.3.7.2. Monitor programmed versus actual students and graduates for each FY.
6.3.7.3. Provide AF/A1PT with predicted production statistics for the annual Enlisted
Initial Skills Program Guidance Letter conference.
6.3.7.4. Coordinate quota movement requests and quota change requests.
6.3.7.5. Update class seats in accordance with Enlisted Initial Skills Program Guidance
Letter changes.
6.3.8. Force Support Squadron (FSS).
6.3.8.1. Military Personnel Flight (MPF) will:
6.3.8.1.1. Update Control AFSC (CAFSC) to 1-skill level on member’s scheduled
departure to formal training or start of On-the-Job Training (OJT), whichever applies
as per Chapter 2 (T-2). If an Airman is eliminated from formal training, and is
attending in a temporary duty TDY and return status, update the member’s previously
awarded CAFSC and Primary AFSC.
6.3.8.1.2. Update the Assignment Availability Code 29 to expire 24 months from the
formal training graduation date or the effective date of OJT, whichever applies. (T-2).
Exception: Do not update an Assignment Availability Code 29 on individuals in an
overseas imbalanced AFSC.
6.3.8.1.3. Provide Airman with Retraining RIP. (T-2). Send the original retraining
approval notification RIP for filing in member's personnel record in Automated
Records Management System. (T-2).
6.3.8.1.4. Ensure Airmen obtain required retainability and if the Airman is restricted
by High Year Tenure, notify AFPC/DP3DW immediately. (T-2).
6.3.8.1.5. Process AF Form 964, update applicable Assignment Availability Code,
Assignment Limitation Code, and Reenlistment Eligibility codes for Airman declining
retainability for formal training.
6.3.8.2. Formal Training Office will ensure Airmen have the required retainability 30 days
prior to the class start date. (T-2). Note: If the Airman does not have the required
retainability, request cancellation of retraining to AFPC/DP3DW.
6.3.9. Unit Commander will:
6.3.9.1. Notify AFPC/DP1SST of approved retraining applicants who fail to maintain
quality control standards, or quality factors not visible in MilPDS, prior to attending formal
schools. (T-2).
6.3.9.2. Ensure Airmen comply with all eligibility and reporting instructions. (T-2).
Notify AFPC/DP1SST when Airmen are unable to meet class start date. (T-2).
128 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.3.9.3. Immediately notify AFPC/DP3DW if an Airman approved for retraining is
selected to deploy and the class dates conflict with the deployment. (T-2). Unit CCs must
ensure all requests are submitted at least 30 days prior to scheduled deployment. (T-2).
Failure of notification may result in a lost retraining opportunity for the Airman and/or
class seat.
6.3.10. Airmen applying or identified for retraining will:
6.3.10.1. Apply for retraining via electronic application process. (T-2).
6.3.10.2. Submit required retraining documentation to AFPC/DP1SST as requested. (T-2).
The initial retraining application is not considered complete until all required
documentation is submitted. Update AFPC/DP1SST on documentation status at least
every 30 days for all outstanding documents. (T-2). Note: Failure to update
AFPC/DP1SST for 60 days may result in the pending application being closed.
6.3.10.3. Select up to five AFSCs. (T-2). While five choices are not required, it greatly
increases the member’s chances of getting approved retraining.
6.3.10.4. If selected for promotion, applicant must apply for shortages in projected grade.
(T-2).
6.3.10.5. Obtain the required retainability within 30 days of notification. (T-2).
6.4. Enlisted Retraining Administrative Actions.
6.4.1. Eligibility. AFPC/DP1SST uses the criteria outlined in Table 6.1 in determining
eligibility.
6.4.2. Disqualifying Factors. The below listed factors automatically disqualify Airmen for
retraining. Input of any of the disqualifying factors before class start date results in retraining
cancellation.
6.4.2.1. Under investigation by the Office of Special Investigation or law enforcement
officials (excluding normal security clearance).
6.4.2.2. Most recent Enlisted Performance Report met some but not all expectation or is a
referral.
6.4.2.3. Airmen are currently in a retraining status or not recommended for entry into
upgrade training.
6.4.2.4. Does not possess local network access.
6.4.2.5. Ineligible for promotion or reenlistment. Exception: A disqualified Airman,
awaiting retraining, with a RI of 9A000 or 9A100 may have reenlistment eligibility code
of 4G, in accordance with AFI 36-2606 and may apply for retraining.
6.4.2.6. Does not have current passing physical fitness score, in accordance with AFMAN
36-2905, Air Force Physical Fitness Program, within 30 days of class start date.
6.4.2.7. Airmen with Assignment Limitation Code L.
6.4.2.8. Does not have 24 months retainability beyond class graduation date.
6.4.3. Initial Enlistment Bonus and Selective Retention Bonus and Retraining. Repayment
and Recoupment of a bonus is governed by DoDI 7000.14, DoD Financial Management
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 129
Policy. Retraining into a Selective Retention Bonus skill: Individuals selected for retraining
into a Selective Retention Bonus AFSC should refer to AFI 36-2606, regarding their eligibility
to receive a Selective Retention Bonus. Individuals who received an Initial Enlistment Bonus
or Selective Retention Bonus are identified by Assignment Limitation Code of O.
6.4.4. Class Change Requests. MPF or Airman may send the request to AFPC/DP1SST no
later than 30 days prior to class start date. Class date changes are subject to availability and
should only occur in the same FY. Note: Class change requests for unit manning or readiness
inspections are not considered.
6.4.5. All Exceptions to Policy must be endorsed by the unit commander and per paragraph
6.3.1.6. (T-2). AF/A1PT approves or disapproves ETP requests after coordination with the
appropriate CFM and AF/A1XD. (T-1).
6.4.5.1. If member is attempting to prove miscounseling and/or an injustice occurred, then
the ETP request must include a statement from the organization that provided the
counseling, indorsed by the commander, and explaining the circumstances. (T-2).
6.4.5.2. Exceptions are not granted based on personal convenience (e.g., individual’s
indecision, lack of employment or educational opportunities, etc.).
6.4.5.3. Airman may request to apply for any available AFSC on the Shortfalls
Requirements list.
6.4.6. Disposition of Retraining Formal Training Eliminees. The Technical Training Wing
electronically completes and forwards the elimination source document (e.g., AETC Form
125A, Record of Administrative Training Action or AETC Form 126A, Record of
Commander’s Review Action) to AFPC/DP3DW within 3 duty days of elimination. Note: Not
applicable to pipeline students.
6.4.6.1. If the Airman is attending in a TDY and return status, the Technical Training Wing
returns the Airman to home station. AFPC/DP1SST notifies the Airman if further
retraining actions are required.
6.4.6.2. If the Airman is attending in a TDY en-route or in a PCS status, the Technical
Training Wing holds the Airman in place until receipt of final disposition instructions from
AFPC/DP3DW to return the member to a previously awarded AFSC or retrain.
6.4.7. Retainability Requirements. All Airmen must have 24 months retainability beyond the
class graduation date of the AFSC awarding course or date entered OJT, unless otherwise
specified on the training RIP as directed by the CFM. Airmen selected for retraining may
decline only if they have insufficient retainability.
6.4.8. Withdraw or Cancel Approved Retraining. Airmen may request to withdraw an
approved retraining application prior to receipt of official electronic notification from
AFPC/DP1SST. In addition, they may request cancellation of approved retraining for personal
hardship or other justifiable reasons. Members will submit electronic memorandum, endorsed
by unit commander, requesting withdrawal to AFPC/DP1SST. (T-1).
6.4.9. Directed Travel Status Change Request. Airmen may request specific travel status (for
example, TDY and return, PCS, TDY en-route); however, the needs of the AF take precedence.
Request is sent to AFPC/DP1SST and members are encouraged not to make any financial
commitments until the travel status has been confirmed.

130 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table 6.1. Eligibility for Voluntary and Involuntary Retraining.
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
and Retraining
Advisory
then the applicant
is eligible for
If the
applicant
is a
First
Term
Airmen
(see
Note
1)
is a
Second-
Term
and/or
a
Career
Airman
shows
an
overage
for
current
AFSC
shows a
shortage
for
retraining
AFSC
voluntary
retraining
(see
Note 3)
involuntary
retraining
(see Note 2)
1
is within 2
years of High
Year Tenure
N/A
YES
N/A
N/A
NO
NO
2
selected for an
assignment
YES
YES
N/A
N/A
NO
(see Note 4)
YES
3
selected for
contingency
deployment
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
(see Note 5)
NO
4
is serving in
CONUS on
stabilized tour
(e.g.,
Assignment
Availability
Code 43
or Assignment
Availability
Code 50)
according to
AFI 36-
2110
(see Note 6)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 131
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
and Retraining
Advisory
then the applicant
is eligible for
If the
applicant
is a
First
Term
Airmen
(see
Note
1)
is a
Second-
Term
and/or
a
Career
Airman
shows
an
overage
for
current
AFSC
shows a
shortage
for
retraining
AFSC
voluntary
retraining
(see
Note 3)
involuntary
retraining
(see Note 2)
5
is serving
overseas and
desires
retraining w/
Date
Eligible for
Return from
Overseas.
(see Note 7)
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
6
is a volunteer
for special
duty
assignment,
AF
Educational
Leave of
Absence
Program,
commissionin
g program, or
In-Place
Consecutive
Overseas
Tour
YES
YES
YES
YES
NO (see
Note 8)
YES
7
Holds a
Control
AFSC or has
AFSC on the
Shortfall
Requirements
List (see
Note 9)
Yes
N/A
N/A
N/A
Yes
N/A

132 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
and Retraining
Advisory
then the applicant
is eligible for
If the
applicant
is a
First
Term
Airmen
(see
Note
1)
is a
Second-
Term
and/or
a
Career
Airman
shows
an
overage
for
current
AFSC
shows a
shortage
for
retraining
AFSC
voluntary
retraining
(see
Note 3)
involuntary
retraining
(see Note 2)
Notes:
1. Airmen must not have reenlisted. (T-1).
2. Individuals who have retrained in the past 4 years will be exempt from Noncommissioned
Officer Retraining Program Phase II. (T-1).
3. Airmen eligible under First Term Airman Retraining Program, with an Assignment Limitation
Code O, may apply during their normal retraining window; however, if approved for retraining,
AFPC/DP1SST will schedule Class Start Dates after the expiration date of the code unless
AF/A1XD authorizes an exception. (T-1).
4. If Assignment Selection Date is before the date AFPC/DP1SST receives the completed
retraining application, then assignment remains firm. If the Assignment Selection Date is after the
date AFPC/DP1SST received the completed retraining application, then retraining processing
continues (If retraining is approved, AFPC/DP1SST will request assignment cancellation. (T-1).
Exception: Airmen with approved follow-on and home basing assignments are authorized to
process retraining applications.
5. Airmen eligible during their normal retraining window may apply for retraining. If unable to
complete the application process due to deployment, the member must submit application within 60
days of return. (T-1).
6. All Airmen may apply within 12 months of date of availability and there must be retraining in
objectives on the Retraining Advisory for the FY matching member’s date of availability. Note:
AFPC/DP3AM is the OPR for the stabilized tour program.
7. DEROS coincides with class start date. Airmen with an indefinite DEROS must complete the
original tour length before departing for training. (T-1). Note: DEROS curtailment or extension
request is submitted with completed retraining application, if needed.
8. An Airman may become eligible for voluntary retraining by withdrawing volunteer statement or
application (if otherwise eligible).
9. The Shortfall Requirements List is located on the Personnel Services website.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 133
6.5. Enlisted Retraining Programs.
6.5.1. First Term Airman Retraining Program. The First Term Airman Retraining Program is
designed to retrain First Term Airmen in conjunction with a reenlistment, into skills where
shortages exist and additionally, allows a limited number of Airmen the opportunity to pursue
other career paths in the AF. Airmen maybe selected for involuntary retraining based on AF
needs to balance the force.
6.5.1.1. CONUS assigned Airmen. Airmen may apply not earlier than the 1st duty day of
the month during which they complete 35 months of their current enlistment (59 months
for 6-year enlistees), but not later than the last duty day of the 43rd month of their current
enlistment (67 months for 6-year enlistees). In order to determine if an Airmen is within
their retraining window AFPC/DP1SST utilizes the Total Active Federal Military Service
Date.
6.5.1.2. Airmen may apply for retraining if they are in the same FY and have met the First
Term Airman Retraining Program retraining window (35th month for 4-year enlistee or
59th month for 6-year enlistee) on or before DEROS. Note: If an Airmen has a DEROS
in the months of October to February and have met the service requirement, it is imperative
to establish a DEROS in the months of March through September by requesting a 6 month
DEROS extension on the DEROS option RIP. (T-1). (Guidance is available at the local
military personnel flight.)
6.5.1.3. Selection Process. AFPC/DP1SST will rank the applications on the last duty date
of each month. (T-1). Applications are approved and disapproved NLT the 15th of the
following month. (T-1).
6.5.1.3.1. Applications are prioritized on quality indicators; e.g., current grade;
projected grade; last two years enlisted performance report ratings; date of rank; total
active federal military service date; Aptitude Qualification Examination score in the
applicable area (electrical, mechanical, administrative, general or combination in
accordance with AFECD, Part II, Attachment 4 (Additional Qualifications)); requested
AFSC preferences.
6.5.1.3.2. Available quotas are evenly distributed throughout the FY. Note:
Exceptions are made based on AF needs.
6.5.1.3.3. Applications remain pending a maximum of three months. Each month the
same prioritization is performed; however, there are always new applications updated
as each month more Airmen become eligible or ineligible. Each month, applications
not selected for approval remain pending until the next month for a maximum of three
months, as long as retraining in objectives are available. If no retraining in-objectives
are available, pending applications are disapproved.
6.5.1.3.4. Members may reapply once only under the following conditions:
6.5.1.3.4.1. The Airman is on the AF Career Job Reservation waiting list.
6.5.1.3.4.2. The Airman was removed from the AF Career Job Reservation waiting
list, and is not within 120 days of DOS. Airmen in this category are ranked for the
month in which their retraining application is received.
134 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.5.2. Noncommissioned Officer Retraining Program. The Noncommissioned Officer
Retraining Program is designed to retrain second-term and career Airmen from overage Air
Force Specialties into shortage specialties to optimize the enlisted force to best meet current
and future mission needs. Airmen possessing a secondary, or additional AFSC in a shortage
skill, may be returned to the shortage skill if it is in the best interest of the AF. This program
consists of three phases.
6.5.2.1. Phase I Retraining. The objective of Phase I is to obtain volunteer applicants from
identified overage AFSCs to fill requirements in shortage AFSCs. All Airmen with
retraining out objectives may apply for any available AFSC with retraining in objectives
for which they qualify. Note: Some AFSCs have retraining out restrictions. During Phase
I if sufficient applications are not received and retraining objectives for the FY are not met,
implementation of Phase II is necessary. Note: All Airmen may not be eligible based on
personnel restrictions.
6.5.2.2. Phase II Retraining. Airmen are selected for mandatory retraining based on AF
needs to balance the force. The Master Vulnerability List is used to select Airmen for
mandatory retraining.
6.5.2.3. Phase III Retraining. All remaining objective in (OBJ IN) quotas are opened to
second-term and/or career airmen that were not identified during Phase’s I and II. If
holding a CAFSC not annotated with an objective out (OBJ OUT) quota, member must
submit an ETP, endorsed by respective unit commander requesting release from CAFSC.
(T-1). E.g., 1A8X1 AFSC shows OBJ OUT with the number of members needed to retrain
out is 25 that are at the rank of SSgt. This means that for the current FY, there is an
availability for 25 SSgts to retrain out of that AFSC. 1B4X1 shows OBJ IN with the
number 48 at or under the rank of SSgt. This means for the current FY, there is an
availability for 48 SSgts to retrain into this AFSC.
6.5.3. Disqualified Airmen Retraining Program. AF guidance is to retrain only those Airmen
who have demonstrated the ability to successfully complete training and whose past record
clearly justifies further investment. Retraining is not a guarantee and is subject to quota
availability at the time of disqualification and individual qualification for an AFSC and
retraining eligibility. Note: Not applicable to pipeline students.
6.5.3.1. Disqualified Airman, Awaiting Retraining, Disqualified for Reasons beyond
Airman’s Control (RI 9A000). Airman with a RI of 9A000 and otherwise eligible for
retraining, are considered based on entry requirements, class start date, and availability
date. Airmen are considered for retraining within 180 days of AFSC disqualification
notification from HQ AFPC/DP3DW through their MPF. Those not selected for retraining
after 12 months from disqualification are no longer eligible for retraining consideration.
Exceptions: Medical processing or other reasons deemed appropriate by AFPC/DP3DW
do not result in RI change after 12 months of consideration.
6.5.3.2. Disqualified Airman, Awaiting Retraining-Disqualified for Reasons within
Airman’s Control (RI 9A100). Airmen with a RI of 9A100, are only considered for
available AFSCs for which they qualify and are otherwise eligible with formal training
starting within 60 days.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 135
6.5.4. Humanitarian and Exceptional Family Member Program Retraining.
6.5.4.1. To be eligible, Airman must have a valid humanitarian or Exceptional Family
Member Program application pending AFPC/DP3XAA approval and be a volunteer to
retrain if utilization in an awarded AFSC at the designated location is disapproved. (T-1).
AFSC preferences are not considered.
6.5.4.2. Retraining applications are updated by AFPC/DP3DW using retraining code RF.
6.5.4.3. Humanitarian retraining is via OJT using Career Field Education and Training
Plans and Specialty Training Standard to document three level training.
6.5.4.4. Exceptional Family Member Program retraining is determined on a case by case
basis.
6.5.5. Other Retraining Options. The Shortfall Requirements List consists of those skills
identified with unfilled class seats, short notice class start dates (<60 days), quotas that have
historically been difficult to fill and/or with unique retraining challenges (e.g., demanding entry
requirements, high attrition, etc.).
6.5.5.1. The Shortfall Requirements List is located on the AFPC myPers website. Airmen
must review the AFECD (also available on the AFPC myPers website) and meet mandatory
AFSC entry requirements prior to applying (T-1).
6.5.5.2. Airmen may apply for these AFSCs throughout the year under paragraph 6.4.5.
ETP.
6.5.6. Deployed Overseas Medical Limitations.
6.5.6.1. Some retraining AFSCs require an AF Form 422 that can be completed by the
Medical Group at members’ home station. While other AFSC(s) only require an AF Form
422 for a retraining package.
6.5.6.2. In the deployed area the services to complete an AF Form 422 or other medical
clearances are limited to the available equipment and human resources.
6.5.6.3. This limitation is recognized by the medical community as they try to assist the
Airman with the resources available. Unfortunately, this can be an obstacle when an
Airman is pursuing voluntary retraining before or during a deployment.
6.5.6.4. The Airman Retraining Program does allow Airmen to complete all retraining
actions no later than 60 days after return to home station.
6.6. AFR Retraining Program.
6.6.1. AFR Retraining Program. The purpose of the AFR Retraining Program is to assist in
achieving and maintaining the level of trained personnel resources required to meet AFR
mission requirements. The program allows eligible Airmen a choice of career fields from
which to pursue an AF career and provides a method to return Airmen disqualified from their
current AFSC to a productive status. Continuous efforts should be made to eliminate un-
programmed overages and over-grades and fill positions through recruitment, accessions,
leveling, and both voluntary and involuntary retraining.
6.6.2. Types of Retraining for Unit Program.
136 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.6.2.1. Voluntary Retraining. An application initiated by an eligible Airman into a chosen
specialty where there is a retraining need and mandatory requirements and quality
standards are met. Eligibility:
6.6.2.1.1. All personnel, including ARTs, must meet retraining AFSC entry
requirements as outlined in AFECD or AFOCD, and be in compliance with AFI 36-
2903 and AFMAN 36-2905. (T-1).
6.6.2.1.2. Retraining can only be into an AFSC manned at less than 100 percent or into
an AFSC that is authorized to have overages.
6.6.2.1.3. Personnel must have or attain at least 36 months retainability to voluntarily
retrain. (T-1). If additional retainability is required to meet the requirement in
Education and Training Course Announcements, it must be obtained prior to attending
technical school. (T-1).
6.6.2.1.4. Personnel are ineligible for voluntary retraining for at least 24 months after
completion of technical training and being awarded the Journeyman skill level. Prior
retrainees must also acquire a skill level commensurate with grade. Unit commanders
can make exceptions for humanitarian reasons and for those members who fail a Career
Development Course or End of Course exam twice.
6.6.2.1.5. Generally, personnel will not retrain out of a shortage or critical AFSC.
(T-1). A shortage AFSC is any AFSC below the standard set by AFRC/CC manning
policy. A critical AFSC (established by HQ USAF) is a specialty having unique
requirements or is typically hard to fill. Wing or HQ Reserve Individual Reservist
detachment commander (HQ RIO/Det CC), or designated representatives, may deviate
from this requirement to meet manning level and mission needs. Wing FSSs will
develop local policies in accordance with local needs, budget, and mission. (T-3).
6.6.2.1.6. PS accessions with an awarded and/or convertible AFSC are only retrained
into another AFSC when the AFSC previously held is not authorized or there is no
vacancy and/or authorization in their current AFSC. Convertible AFSCs are new
AFSCs due to establishing a new AFS.
6.6.2.1.7. A PS accession from another service, with a military specialty that does not
convert to an AFSC must attend technical school within 12 months.
6.6.2.1.8. Mobilized personnel and personnel in Stop Loss AFSCs are ineligible to
apply for retraining. Waivers are not accepted. Stop Loss AFSCs are those AFSCs
that are affected by the involuntary extension of a service member’s active duty.
6.6.2.2. Involuntary Retraining.
6.6.2.2.1. Involuntary retraining are actions initiated by unit commander or designated
representative to determine the disposition of personnel who become overages due to
locally generated UMD reductions and/or changes, force structure changes, crew ratio
reduction, medical unit type code reduction, weapons system conversions, withdrawal
of an AFSC because of medical disqualification or the inability of a member to
maintain currency requirements for flying status.
6.6.2.2.2. Involuntary retraining is primarily for the benefit of the AFR and does not
require the concurrence of the member.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 137
6.6.2.2.3. Retraining application (AF Form 3920, Request for Reservist Voluntary
Retraining), is not required.
6.6.3. Responsibilities.
6.6.3.1. AFRC, Personnel Utilization (AFRC/A1KK) will:
6.6.3.1.1. Administer and/or coordinate retraining policies and procedures.
6.6.3.1.2. Monitor and evaluate the AFR Retraining Program in conjunction with
AFRC MAJCOM functional managers
6.6.3.1.3. Coordinate requests for waiver of requirements specified in the AFSC
specialty descriptions contained in the AFECD or AFOCD in accordance with Chapter
2.
6.6.3.1.4. Forward waiver requests recommended for approval to HQ AFPC/DPSIC
when approval level is higher than AFRC.
6.6.3.1.5. Notify MPF of final approval or disapproval.
6.6.3.2. AFRC MAJCOM functional manager provides recommendation or final
disposition on waiver requests using guidelines in Chapter 2, Tables 2.4, 2.5, and 2.6.
6.6.3.3. AFRC Recruiting Service (AFCRS) in conjunction with AFRC, Personnel,
Manpower and Services (AFRC/A1) will establish guidelines to ensure the enlistment
and/or assignment packages on PS retrainees are processed through the Personnel
Employment Element, and approved before accession of the applicant.
6.6.3.4. Wing/ARPC/CC or designated representative will:
6.6.3.4.1. Administer final approval authority for local retraining applications.
6.6.3.4.2. Waive manning level and other requirements as exception when faced with
unique requirements or hard to fill. (T-1). Otherwise, ensure Airmen do not voluntary
retrain out of shortage and/or critical AFSCs or retrain into overages, unless previously
approved. (T-1).
6.6.3.5. Unit Commander will:
6.6.3.5.1. Recommend approval or disapproval of retraining applications and certify
school funds availability. (T-1).
6.6.3.5.2. Delegate, if necessary, this authority to the senior ART at geographically
separated units. (T-1).
6.6.3.5.3. Negotiate the effective date of retraining, as the losing or gaining
commander, provided the member is assigned to the retraining position no later than
30 days prior to the formal school class start date. (T-1).
6.6.3.5.4. Recommend retraining only for those Airmen who can be recommended for
reenlistment and whose behavior, attitude, and record of performance are suited for
subsequent duty assignment and are in compliance with AFI 36-2903, and AFMAN
36-2905. (T-1).
138 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.6.3.5.5. Interview personnel as the gaining unit commander (or designated
representative) applying for retraining to a flying position and makes appropriate
recommendation on the retraining application. (T-1).
6.6.3.5.6. Ensure technical school quotas are requested and certify member's
availability. (T-1).
6.6.3.5.7. Ensure retrainees attend mandatory technical school within 12 months of
approval of the retraining action. (T-1).
6.6.3.6. Unit Commander Support Staff will:
6.6.3.6.1. Verify member’s retraining eligibility prior to initiating retraining
application. (T-1).
6.6.3.6.2. Prepare Section I of the AF Form 3920. (T-1). Ensure a formal school
request is processed. (T-1). Prepare the AF Form 101, Reserve Requirements for
School Tours of Active Duty for Training or SF 182, Authorization, Agreement and
Certification of Training as appropriate, to accompany the AF Form 3920. (T-1).
6.6.3.7. MPF/Personnel Employment Element will:
6.6.3.7.1. Schedule unit applicants for retraining interview. (T-1). Interview should
include at a minimum the information relevant to the retraining processing and the
roles, responsibilities and entrance requirements of AFSC specialty description in the
AFECD.
6.6.3.7.2. Verify member’s retraining eligibility prior to coordinating retraining
application. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.3. Verify AF Form 1288, Application for Ready Reserve Assignment or DD
Form 1966, Record of Military Processing - Armed Forces of the United States,
contains the retraining eligibility statement in the remarks section. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.4. Coordinate voluntary retraining applications. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.5. Develop internal processing controls. (T-3).
6.6.3.7.6. Assist units and/or Airmen in determining eligibility to ensure members are
qualified for duty positions in accordance with all governing classification instructions.
(T-3).
6.6.3.7.7. Ensure classification waivers are processed in accordance with Chapter 2
and identifies the type of waiver required on the cover memorandum when forwarding
waiver requests to higher HQ; e.g., medical, minimum aptitude score(s), AFSC
prerequisites. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.8. Ensure Force Development Flight Education & Training counsels retrainees
on formal school retainability requirements as prescribed in Education and Training
Course Announcements. (T-1).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 139
6.6.3.7.9. Ensure Force Development Flight Education & Training coordinates on the
AF Form 3920 and annotate the respective Training Status Code prior to approval
(T-1).
6.6.3.7.10. Complete final review, interview and forwars the retraining application to
final approval authority for approval. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.11. For internal retraining actions, block position on UMD or the Reserve
Management Vacancy System. (T-1).
6.6.3.7.12. Maintain the approved AF Form 3920 and forward a copy of the approved
retraining action and school request to MPF and/or Education and Training Element
for processing. (T-1).
6.6.3.8. MPF and/or Education and Training Element will:
6.6.3.8.1. Request formal school quota upon receipt of unit request and approved
retraining application. (T-1).
6.6.3.8.2. Review applicant’s technical school waiver documentation when applicable
and ensures completeness prior to forwarding to AFRC/A1. (T-1).
6.6.3.9. MPF/Career Development will:
6.6.3.9.1. Verify member is or is not retraining out of, or into, a bonus AFSC. (T-1).
Individuals retraining from a bonus AFSC into a non-bonus AFSC require a
continuation waiver from AFRC/A1KK in order to continue receiving bonus payments
in their new AFSC. (T-1). However, payments are suspended until the individual is
awarded a three skill-level CAFSC. If continuation is granted, payments are retroactive
(as appropriate) to the retraining effective date. Retraining into balanced or overage
AFSCs is not normally approved for continuation of bonus payments. (T-1).
6.6.3.9.2. Ensure current expiration term of service is a special interest item during the
screening and coordination of the retraining request. (T-1). Applicants, who may be
potentially eligible for bonus program participation, must be within 36 months of
normal expiration term of service upon completion of technical school in order to
remain eligible for a bonus. (T-1).
6.6.3.9.3. If approved, and upon completion of technical school, allow individuals to
reenlist for up to 36 months from current expiration term of service to qualify for a
retraining bonus. (T-1).
6.6.3.10. Reserve Recruiters for new gains to the SELRES will:
6.6.3.10.1. Determine applicant’s eligibility in accordance with the AFSC specialty
descriptions contained in the AFECD, this manual and the current AFRC/CC manning
policy. (T-1).
6.6.3.10.2. Base level recruiters are not required to execute retraining applications.
They will enter the retraining eligibility statement in the remarks section of DD Form
1966 or AF Form 1288. (T-1). The statement reads, "I certify member meets eligibility
for retraining into AFSC_____, from AFSC."
140 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.6.3.10.3. If a waiver is needed, indicate type waiver on cover letter when forwarding
requests to higher HQ, e.g., technical school, medical, minimum aptitude score(s),
AFSC prerequisite. (T-1).
6.6.3.11. Applicant will:
6.6.3.11.1. Ensure all appropriate information for retraining is complete, to include
extending and/or reenlisting for retraining eligibility. (T-1).
6.6.3.11.2. Attend technical school within 12 months of retraining approval date or
return to the position of the previously awarded AFSC, submit technical school waiver
within 6 months of approval of retraining action, or be reassigned to the Inactive Ready
Reserve (IRR).
6.6.4. Retraining Guidelines.
6.6.4.1. Normally Airmen are assigned throughout their enlistment in the AFSC in which
first classified.
6.6.4.2. Airmen are recruited for training and assignment in a specific specialty, based on
the current AFRC/CC manning policy, AFR needs, and the member's qualifications.
6.6.4.3. If additional retainability is needed to meet AF Education and Training Course
Announcements specifications, member will obtain it prior to attending technical school.
(T-1).
6.6.4.4. Chief master sergeants selected to crossflow out of their career ladder are not
considered retraining and do not have to meet minimum retraining eligibility requirements.
Skill level training waivers are submitted in accordance with paragraph 2.3.7 and AFRC,
Education and Training Operations Support (AFRC/A1KE) Automated Training Waiver
Policy.
6.6.4.5. Retraining applications and interviews are only required for voluntary retraining
and used as source documents to approve voluntary retraining actions. The Personnel
Employment Element will maintain retraining applications for a period of 24 months.
(T-1).
6.6.4.6. Once Airmen are approved for retraining, block them in the applicable position in
the Reserve Management Vacancy System but don’t reassign enlisted Airmen until
completion of any technical training required for award of a 3-skill level.
6.6.4.7. Upon approval of the retraining application, the member’s Training Status Code
reflects awaiting technical school (Training Status Code-M).
6.6.4.8. Award a 1-skill level in accordance with Chapter 2, Table 2.10 for officers or
Table 2.11 for enlisted, placed in the position at the time of approval.
6.6.4.9. Prior retrainees must obtain a skill level commensurate with grade. (T-1).
6.6.4.10. Assign personnel who are displaced due to UMD changes either against a valid
authorization in any awarded AFSC, retain them as overages in the current AFSC against
a valid requirement as authorized by the commander, or voluntarily retrain them to fill a
valid authorization. If the member does not voluntarily retrain to fill a valid authorization,
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 141
the commander may initiate involuntary retraining if the Airman has a reserve service
commitment or reassign to IRR if the Airman doesn’t have a reserve service commitment.
6.6.4.11. All new enlisted ART hires or retrainees who meet requirements of the AFSC
specialty description in the AFECD, or obtained appropriate waiver in accordance with
Chapter 2 and have satisfied the minimum Office of Personnel Management standard are
immediately militarily classified at the entry level AFSC.
6.6.4.11.1. The supervisor will conduct an initial evaluation within 60 days from the
date of hire, using the current Career Field Education Training Plan to assess apprentice
skill-level qualifications. (T-2). This includes completion of all mandatory
requirements contained in the AFECD AFSC specialty description.
6.6.4.11.2. After completion of the initial evaluation and the supervisor determines the
member warrants award of the 3-skill level, the AFRC functional manager through
AFPC/DPAT, must sanction the award. (T-1). Waiver requests are submitted through
channels to ARPC/DPAT in accordance with Chapter 2 and USAFR functional
manager Automated Training Waiver Policy. Disapproval by the AFRC functional
manager will require the ART to remain at the entry level AFSC until satisfactory
completion of technical school. (T-1).
6.6.4.11.3. Withdrawing Approved Retraining. An Airman can voluntarily request
withdrawal of approved retraining application up until the time when funds are
expended for technical school. The Wing Commander is final approval authority.
6.6.5. Retraining Formal School Eliminees.
6.6.5.1. Eliminated for reasons not within control.
6.6.5.1.1. Gaining unit commander may retain and return to school previously attended
except for personnel eliminated for academic deficiency.
6.6.5.1.2. Return to previous AFSC if vacancy exists with concurrence of gaining unit
commander.
6.6.5.1.3. Assign to the appropriate subcategory of the IRR or Standby Reserve in
accordance with AFI 36-2110, or administratively discharge in accordance with AFI
36-2110.
6.6.5.1.4. Airmen eliminated for academic deficiency may not request retraining into
an AFSC that requires an identical or higher aptitude score.
6.6.5.2. Eliminated for reasons within control.
6.6.5.2.1. Return to previously held AFSC if vacancy exists with concurrence of
gaining unit commander.
6.6.5.2.2. If member declines any action to qualify for a position, reassign to the
appropriate subcategory of the IRR or Standby Reserve in accordance with AFI 36-
2110.
142 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.6.6. PALACE CHASE and PALACE FRONT Program. Retraining is an option if:
6.6.6.1. The PALACE CHASE applicant holds an AFSC which is not authorized, in the
gaining unit.
6.6.6.2. There is no vacancy and/or authorized overage in the PALACE CHASE
applicant’s current AFSC.
6.6.6.3. A genuine, mission based need exists for the gaining organization to retrain the
PALACE CHASE applicant.
6.6.6.4. PALACE CHASE retraining prohibition outlined in AFI 36-3205, Applying for
the PALACE CHASE and PALACE FRONT Programs is not applicable: Enlisted
personnel who have retrained or who have attended their initial technical training course
of more than ten academic days during the past 12 months may not enter the AFR under
the PALACE CHASE program in a different AFSC from their current control or duty
AFSC.
6.6.7. Retraining Process for IRs. The purpose of the IR retraining program is to assist HQ
RIO/Det CC in achieving and maintaining a level of trained resources required to meet the
needs of the AF. Retraining within the IR program is normally generated due to a reassignment
action. Retraining is solely on a voluntary basis and requires securing a position that requires
the award of an AFSC not currently held. Place emphasis on requesting training waivers if
member has civilian skills applicable to the proposed retraining AFSC. Personnel must have
or attain at least 36 months retainability to voluntarily retrain. (T-1). If additional retainability
is needed to meet requirements in the Education and Training Course Announcements, member
obtains it prior to attending technical school. (T-1). Personnel must submit waiver of technical
training within 6 months of assignment to the position through HQ RIO/Det CC to
ARPC/DPAT. (T-1). The waiver package is forwarded to AFRC/A1.
6.6.7.1. Retraining Guidelines.
6.6.7.1.1. Retrainees must acquire a skill level commensurate with grade. (T-1).
Retraining is only for those Airmen who can be recommended for reenlistment and
whose behavior, attitude, and record of performance are in compliance with AFI 36-
2903 and AFMAN 36-2905.
6.6.7.1.2. All retraining actions are into an AFSC manned at levels less than those
described in the command manning policy. Applicant must not be retraining out of a
shortage or critical AFSC. (T-1).
6.6.7.1.3. Personnel displaced due to UMD changes must either be assigned against a
valid authorization in any awarded AFSC, retrained as an overage in the current AFSC
against a valid requirement as authorized by the HQ RIO/Det CC or voluntarily retrain
to fill a valid authorization. (T-1).
6.6.7.1.4. Retrainees will apply for technical training within 3 months of assignment
to position unless a technical training waiver is submitted. (T-1).
6.6.7.1.5. Applications for technical training include a requested class start date within
12 months of assignment date if a quota is available.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 143
6.6.7.1.6. Personnel must submit technical training waiver if needed and provide
documentation for waiver process in accordance with AFRC/A1 guidelines. Personnel
must submit waivers in sufficient time for waiver to reach AFRC/A1 within 3 months
of assignment to position. (T-1). OJT at home station is not allowed as criteria for a
waiver of technical training. Formal school applications cannot be submitted at the
same time a waiver is being considered.
6.6.7.1.7. If waiver is disapproved, application for tech school is made immediately
upon notification of disapproval and request course attendance within 12 months of
assignment date. (Note: Failure to comply in a timely manner results in applicant
being returned to a position in the previously awarded AFSC or being reassigned to the
IRR if no position is available).
6.6.7.2. Responsibilities.
6.6.7.2.1. HQ Readiness Integration Organization (HQ RIO). Upon receipt of the AF
Form 1288, HQ RIO/Det CC will review qualifications and AFSC requirements to
ensure all waiver packages are complete according to AFRC/A1 guidelines. (T-2).
6.6.7.2.2. HQ RIO/Det CC will:
6.6.7.2.2.1. Administer, coordinate, and monitor retraining policies and
procedures. (T-1). Notify Program Managers of waiver procedures or requirement
for requesting 3-level technical training. (T-1).
6.6.7.2.2.2. Ensure Airmen do not voluntarily retrain out of shortage and/or critical
AFSCs. (T-1). A shortage AFSC is any AFSC below the standard set by the IR
enlisted incentive program manned at less than 100 percent. A critical AFSC within
the AFR is identified within the parameters of the policy set forth by Chief of AF
Reserve (AF/RE) and are normally specialties having unique requirements or are
typically hard to fill. (T-1).
6.6.7.2.2.3. Ensure retraining applicants who may be eligible for the bonus
program be within 36 months of normal expiration term of service upon completion
of technical training in order to remain eligible for a bonus. (T-1).
6.6.7.2.2.4. Ensure funding is programmed. (T-1).
6.6.7.2.3. HQ AFRC/ARPC DPAT will:
6.6.7.2.3.1. Evaluate IR retraining actions in conjunction with HQ ARPC/DPAT
and Headquarter AFRC functional managers.
6.6.7.2.3.2. Receive, evaluate, and process all IR retraining packages or training
waivers, or AF Form 2096. Coordinate with appropriate offices for award of the
entry level (1-skill level) AFSC in accordance with Table 2.13.
6.6.7.2.3.3. Assist HQ RIO/Det CC in determining eligibility to ensure members
are qualified for duty positions in accordance with all governing classification
instructions.
6.6.7.2.3.4. Identify the type of waiver required when coordinating waiver requests
through appropriate channels (i.e., technical school, medical, aptitude score, AFSC
prerequisites).
144 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.6.7.2.3.5. RegAF Unit Training Manager will coordinate with HQ RIO/DET
Training to process requests for school quotas.
6.6.7.3. Eliminated Retrainees.
6.6.7.3.1. No fault of member:
6.6.7.3.1.1. HQ RIO Detachment attempts to place member within AFSC
previously held.
6.6.7.3.1.2. Member will be reassigned to the IRR in accordance with AFI 36-
2110. (T-1).
6.6.7.3.2. With cause (fault of member):
6.6.7.3.2.1. If HQ RIO Detachment recommends member be retained, they attempt
to place member within AFSC previously held.
6.6.7.3.2.2. If member declines any action to qualify for a position, reassign to the
IRR in accordance with AFI 36-2110.
6.7. ANG Retraining Program.
6.7.1. ANG Retraining Program. The purpose of the ANG Retraining Program is to assist in
achieving and maintaining the level of trained personnel resources required to meet ANG
mission requirements. The program allows eligible Airmen a choice of career fields from
which to pursue an AF career and provides a method to return Airmen disqualified from their
current AFSC to a productive status. Continuous efforts should be made to eliminate un-
programmed overages and over-grades and fill positions through recruitment, accessions,
leveling, and both voluntary and involuntary retraining.
6.7.2. Types of Retraining for Unit Program.
6.7.2.1. Voluntary Retraining. ANG members desiring to retrain into a new career field
meet with the Retention Office Manager to discuss opportunities and possibly loss or gain
of additional entitlements. The Retention Office Manager is able to identify vacant
positions and AFECD requirements for AFSCs.
6.7.2.1.1. Eligibility. All personnel, must meet retraining AFSC entry requirements of
Chapter 2, AFECD or AFOCD, and be in compliance with AFI 36-2903, and AFMAN
36-2905. (T-1).
6.7.2.1.2. Retraining can only be into an AFSC manned at less than 100 percent or into
an AFSC that is authorized to have overages. Wing commanders may deviate from
this requirement to meet manning levels and mission needs in accordance with ANG,
Force Management (NGB/A1P) manning policy.
6.7.2.1.3. Enlisted members who have received an incentive who elect to retrain into
another AFSC may be subject to recoupment in accordance with Air National Guard
Instruction (ANGI) 36-2602, Air National Guard Retention Programs.
6.7.2.1.4. Personnel are ineligible for voluntary retraining until any service
commitment for training is met and/or for at least 24 months after completion of
technical training and being awarded the Journeyman skill level. Prior retrainees must
also acquire a skill level commensurate with the skill level of the AFSC from which
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 145
they previously retrained. (T-1). Wing/CC, or designated representative, may deviate
from this requirement to meet manning levels and mission needs.
6.7.2.1.5. Generally, personnel will not retrain out of a shortage or critical AFSC.
(T-1). Wing Commanders, or designated representatives, may deviate from this
requirement to meet manning level and mission needs. Wing FSSs will develop local
policies in accordance with local needs, budget, and mission. (T-3).
6.7.2.1.6. PS accessions with an awarded and/or convertible AFSC identified in the
AFECD Part II, Attachment 6 are only retrained into another AFSC when the AFSC
previously held is not authorized or there is no vacancy and/or authorization in their
current AFSC. Wing/CC, or designated representative, may deviate from this
requirement to meet manning levels and mission needs in accordance with NGB/A1P
manning policy. Wing FSSs will develop local policies in accordance with local needs,
budget, and mission. (T-1).
6.7.2.1.7. Mobilized personnel and personnel in a Stop Loss AFSC are ineligible to
apply for retraining. Waivers are not accepted.
6.7.2.1.8. Guidance for ANG Career Field Service Obligation and Commitments is
covered in more detail in AFI 36-2110.
6.7.2.2. Involuntary Retraining.
6.7.2.2.1. Involuntary retraining are actions initiated by unit commander or designated
representative to determine the disposition of personnel who become overages due to
locally generated UMD reductions and/or changes, force structure changes, crew ratio
reduction, medical unit type code reduction, or weapons system conversions,
withdrawal of an AFSC because of medical disqualification, or the inability of a
member to maintain currency requirements for flying status.
6.7.2.2.2. Involuntary retraining is primarily for the benefit of the ANG and does not
require the concurrence of the member.
6.7.3. Retraining Request Process. A Career Change Worksheet from the AF Recruiting
Information Support System – Total Force (AFRISS-TF) is needed for all voluntary and
involuntary requests for Retraining. Upon completion of worksheet the member will be gained
into new squadron awarded the new AFSC, and scheduled for all required training within 12
months. (T-1).
6.7.4. Responsibilities.
6.7.4.1. ANG, Force Development (NGB/A1D) will:
6.7.4.1.1. Administer and/or coordinate retraining policies and procedures.
6.7.4.1.2. In conjunction with NGB CFMs monitor and evaluate the ANG Retraining
Program.
6.7.4.1.3. Coordinate requests for waiver of AFSC entry requirements in accordance
with Chapter 2 and AFSC specialty description in the AFECD with NGB CFMs.
6.7.4.1.4. Forward waiver requests recommended for approval to HQ AFPC/DPSIC
when approval level is higher than NGB in accordance with Chapter 2.

146 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
6.7.4.2. NGB CFMs will:
6.7.4.2.1. Provide recommendation or final disposition on waiver requests using guidelines in
Tables 2.4, 2.5, and 2.6 and ANG Classification Waiver Guide which can be found at
https://usaf.dps.mil/sites/12866/GUIDANCE/Shared%20Documents/Classification%20
Waiver%20Guide%20Final%201%20Oct%2019%20ASD.pdf.
6.7.4.2.2. Notify MPF of final approval or disapproval.
6.7.4.3. NGB/A1Y and NGB/A1. NGB/A1Y in conjunction with NGB/A1 will establish
guidelines to ensure the enlistment and/or assignment packages on PS retrainees are
processed through the Personnel Employment Element, and approved before accession of
the applicant. The responsibility for the correct completion of recruiter generated
retraining action is with the individual recruiter.
6.7.4.4. Unit Commander Support Staff will verify member’s retraining eligibility prior to
coordinating on career change worksheet and training request. (T-1).
6.7.4.5. Unit Commander will:
6.7.4.5.1. Recommend approval or disapproval of retraining requests and certify
member meets all requirements. (T-1).
6.7.4.5.2. Elevate disagreements between the gaining and losing commander and the
Personnel Employment Element to the group commander for a final decision. (T-3).
6.7.4.5.3. Recommend retraining only for those Airmen who can be recommended for
reenlistment and whose behavior, attitude, and record of performance are suited for
subsequent duty assignment and are in compliance with AFI 36-2903 and AFMAN 36-
2905. (T-1).
6.7.4.5.4. Gaining unit commander or designated representative, interviews all
personnel applying for retraining to a flying position and makes appropriate
recommendation on the retraining application. (T-1).
6.7.4.5.5. Ensure technical training quotas are requested and certify member's
availability (T-1).
6.7.4.5.6. Ensure retrainees attend mandatory technical training within 12 months of
approval of the retraining action. (T-1).
6.7.4.6. Retention Office Manager will:
6.7.4.6.1. Schedule unit applicants for retraining interview. Interview should include
at a minimum the information relevant to the retraining processing and the
requirements of AFSC specialty description in the AFECD and Part II, Attachment 6
on the AFPC myPers website. (T-1).
6.7.4.6.2. Verify member retraining eligibility prior to coordinating career change
worksheet. (T-1).
6.7.4.6.3. Coordinate voluntary retraining requests. (T-1).
6.7.4.6.4. Develop internal processing controls in accordance ANGI 36-2602. (T-1).
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 147
6.7.4.6.5. Ensure Airmen do not voluntarily retrain out of shortage and/or critical
AFSCs, in compliance with current NGB/A1P manning policy, Yearly Recruiting and
Retention Initiatives, and as updates are needed. (T-1). A shortage AFSC is any AFSC
below the standard set by NGB/A1P manning policy. A critical AFSC is a specialty
having unique requirements or is typically hard to fill.
6.7.4.6.6. Verify member is or is not retraining out of, or into, a bonus AFSC. (T-1).
Refer to current FY ANG Incentive Program Operational Guidance for bonus program
implications. (T-1).
6.7.4.6.7. Maintain the approved career change worksheet, within the AFRISS-TF
database. (T-1).
6.7.4.7. FSS or Force Development Office will:
6.7.4.7.1. Assist units and/or Airmen in determining eligibility to ensure members are
qualified for duty positions in accordance with all governing classification instructions.
(T-1).
6.7.4.7.2. Verify member retraining eligibility prior to coordinating career change
worksheet. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.3. Coordinate voluntary retraining requests. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.4. Develop internal processing controls. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.5. Ensure classification waivers are processed in accordance with Chapter 2,
the ANG Classification Waiver Guide and identify the type of waiver required on the
cover memorandum when forwarding waiver requests to higher HQ; e.g., medical,
aptitude score, AFSC prerequisites. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.6. Counsel retrainees on formal school retainability requirements as prescribed
in Education and Training Course Announcements. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.7. Coordinate on the career change worksheet and AF Form 2096 and annotates
the respective training status code prior to approval. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.8. Complete final review, interview, and approve or disapprove formal training
request. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.9. Maintain the approved formal training request. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.10. Request formal school quota upon receipt of unit request and approved
retraining application. (T-1).
6.7.4.7.11. Review applicant’s technical school training waiver documentation when
applicable and insure completeness prior to forwarding to higher HQ. (T-1).
6.7.4.8. Applicant must:
6.7.4.8.1. Ensure all appropriate information for retraining is complete, to include
extending and/or reenlisting for retraining eligibility. (T-1).
6.7.4.8.2. Apply for, and attend technical school within 12 months of retraining
approval date or return to the position of the previously awarded AFSC, submit
148 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
technical school waiver within 6 months of approval of retraining action, be reassigned
or separate from the ANG. (T-1).
6.7.5. Retraining Guidelines.
6.7.5.1. Normally Airmen are assigned throughout their enlistment in the AFSC in which
first classified.
6.7.5.2. Airmen are recruited for training and assignment in a specific specialty, based on
the current NGB/A1P FY manning policy, ANG needs, and the member's qualifications.
6.7.5.3. If additional retainability is needed to meet AF ETCA specifications, member will
obtain it prior to attending technical school. (T-1).
6.7.5.4. Chief master sergeants selected to cross flow out of their career ladder are not
considered retraining and do not have to meet minimum eligibility requirements of ANG
retraining requirements unless specified in ANG Classification Waiver Guide, Table 2..
Chief Enlisted Manager Codes are non-interchangeable. Skill level training waivers are
submitted in accordance with paragraph 2.3.27 and ANG Classification Waiver Guide.
6.7.5.5. Career Change Worksheets are required for all retraining actions and used as
source documents to approve all retraining actions. (T-1). The Retention Office Manager
will maintain them. Once members are approved for retraining and AF Form 2096 is
completed, block them in the position on the UMD. (T-1).
6.7.5.6. Upon approval of the retraining application, AF Form 2096 is initiated to change
the member’s training status code to reflect awaiting technical school (training status code
M) and AFSCs as necessary.
6.7.5.7. Award a 1-skill level in accordance with Table 2.11 for personnel placed in the
position at the time of approval.
6.7.5.8. Assign personnel who are displaced due to UMD changes either against a valid
authorization in any awarded AFSC, retain them as overages in the current AFSC against
a valid requirement as authorized by the commander, or voluntarily retrain them to fill a
valid authorization.
6.7.5.9. If the member does not voluntarily retrain to fill a valid authorization, the
commander may initiate involuntary retraining.
6.7.5.10. If member declines any action to qualify for a position, commander must review
for separation actions. (T-1).
6.7.5.11. Withdrawing Approved Retraining. An Airman can voluntarily request
withdrawal of approved retraining requests up until 45 days prior to the class start date of
formal training. The Wing Commander is final approval authority.
6.7.6. Retraining Formal School Eliminees.
6.7.6.1. Eliminated for reasons not within control.
6.7.6.1.1. Gaining unit commander can retain and return to school previously attended
except for personnel eliminated for academic deficiency or identified on AETC Form
125A.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 149
6.7.6.1.2. Return to previous AFSC if vacancy exists with concurrence of gaining unit
commander.
6.7.6.1.3. Assign to the appropriate subcategory of the IRR or Standby Reserve in
accordance with AFI 36-2110, or administratively discharge in accordance with AFI
36-2110.
6.7.6.1.4. Airmen eliminated for academic deficiency may not request retraining into
an AFSC that requires an identical or higher aptitude score. (T-1).
6.7.6.2. Eliminated for reasons within control.
6.7.6.2.1. Return to previously held AFSC if vacancy exists with concurrence of
gaining unit commander.
6.7.6.2.2. If member declines any action to qualify for a position, commander must
review for potential separation. (T-1).
ALEX WAGNER
Assistant Secretary of the Air Force
(Manpower and Reserve Affairs)
150 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 1
GLOSSARY OF REFERENCES AND SUPPORTING INFORMATION
References
Executive Order 9397, Numbering System for Federal Accounts Relating to Individual Persons
10 USC § 653, Minimum service requirement for flight crew positions
10 USC § 708, Educational leave of absence
10 USC § 972, Members: effect of time lost
10 USC § 1168, Discharge or release from active duty: limitations
10 USC § 1734, Career development
10 USC § 2004, Detail as students at law schools; commissioned officer; certain enlisted
members
10 USC § 2005, Advanced education assistance: active duty agreement; reimbursement
requirements
10 USC § 2006, Department of defense education benefits fund
10 USC § 2007, Payment of tuition for off-duty training or education
10 USC §§ 2101-2111b, Senior reserve officers’ training corps
10 USC § 2114, Students: selection, status, obligation
10 USC § 2603, Acceptance of fellowships, scholarships, or grants
10 USC § 9013, Secretary of the Air Force
10 USC § 9063, Designation: officers to perform certain professional functions
10 USC § 9448, Cadets: agreement to serve as officer
10 USC § 10148, Ready reserve: failure to satisfactorily perform prescribed training
10 USC § 12301, Reserve components generally
10 USC § 12303, Ready Reserve: members not assigned to, or participating satisfactorily in,
units
10 USC § 12319, Ready Reserve: muster duty
32 USC § 502, Required drills and field exercises
32 USC §709, Technicians: employment, use, status
37 USC § 303a(e), Special pay: general provisions
37 USC § 373, Repayment of unearned portion of bonus, incentive pay, or similar benefit, and
termination of remaining payments, when conditions of payment not met
38 USC § 3319, Authority to transfer unused education benefits to family members
DoDI 1200.18, The United States Property and Fiscal Officer (USPFO) Program, 15 April 2020
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 151
DoDI 1205.18, Full Time Support (FTS) to the Reserve Components, 5 June 2020
DoDI 1235.09, Management of the Standby Reserve, 5 May 2020
DoDI 1235.13, Administration and Management of the Individual Ready Reserve (IRR) and the
Inactive National Guard (ING), 30 April 2020
DoDI 1300.28, Military Service by Transgender Persons and Persons with Gender Dysphoria, 4
September 2020
DoDI 1315.18, Procedures for Military Personnel Assignments, 28 October 2015
DoDI 1322.06, Fellowships, Legislative Fellowships, Internships, Scholarships, Training-With-
Industry (TWI), and Grants Provided to DoD Or DoD Personnel for Education and Training, 12
October 2016
DoDI 1322.10, Policy on Graduate Education for Military Officers, 29 April 2008
DoDI 1327.07, Career Intermission Program (CIP) For Service Members, 18 October 2018
DoDI 5154.31, Volume 5, Commercial Travel Management: The Per Diem, Travel and
Transportation Allowance Committee (PDTATAC), 16 October 2015
DoDI 5200.02, DoD Personnel Security Program (PSP), 21 March 2014
DoDI 6000.13, Accession and Retention Policies, {rograms, and Incentives for Military Health
Professions Officers (HPOs), 3 May 2016
DoDI 6000.13_DAFI 41-110, Medical Health Care Professions Scholarship Programs, 23
December 2020
DoDI 7000.14, DoD Financial Management Policy, 10 August 2020
Joint Travel Regulations (JTR), Uniformed Service Members and DoD Civilian Employees
Education and Training Course Announcement (ETCA)
DoDM 5200.02_AFMAN 16-1405, Air Force Personnel Security Program, 1 August 2018
AFPD 36-20, Recruiting Programs and Accession of Air Force Military Personnel, 19 February
2019
AFPD 36-21, Utilization and Classification of Air Force Military Personnel, 22 August 2019
AFPD 36-26, Total Force Development and Management, 18 March 2019
AFPD 41-1, Health Care Programs and Resources, 3 October 2018
DAFI 33-360, Publications and Forms Management, 1 December 2015
AFI 33-322, Records Management and Information Governance Program, 23 March 2020
AFI 35-101, Public Affairs Operations, 20 November 2020
AFI 36-2008, Voluntary Limited Perior of Active Duty (VLPAD) for Air Reserve Component
(ARC) Service Members and the Career Intermission Program, 1 February 2021
AFI 36-2110, Total Force Assignments, 5 October 2018
AFI 36-2406, Officer and Enlisted Evaluation Systems, 14 November 2019
152 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
AFI 36-2501, Officer Promotions and Selective Continuation, 16 July 2004
AFI 36-2502, Enlisted Airman Promotion/Demotion Programs, 12 December 2014
AFI 36-2606, Reenlistment and Extension of Enlistment in the United States Air Force, 20
September 2019
AFI 36-2670, Total Force Development, 25 June 2020
AFI 36-2903, Dress and Personal Appearance of Air Force Personnel, 7 February 2020
AFI 36-3003, Military Leave Program, 24 August 2020
AFI 36-3012, Military Entitlements, 23 August 2019
AFI 36-3203, Service Retirements, 29 January 2021
AFI 36-3205, Applying for the Palace Chase and Palace Front Programs, 10 October 2003
AFI 36-3206, Administrative Discharge Procedures for Commissioned Officers, 9 June 2004
AFI 36-3208, Administrative Separation of Airmen, 09 July 2004
AFI 36-3209, Separation and Retirement Procedures for Air National Guard and Air Force
Reserve Members, 14 April 2005
AFI 36-3212, Physical Evaluation for Retention, Retirement, and Separation, 15 July 2019.
AFI 41-117, Medical Service Officer Education, 25 March 2015
AFI 48-133, Duty Limiting Conditions, 7 August 2020
AFI 51-101, The Air Force Judge Advocate General’s Corps (AFJAGC) Operations, Accessions,
and Professional Development, 29 November 2018
AFI 63-101/20-101, Integrated Life Cycle Management, 30 June 2020
AFMAN 11-202, V1, Aircrew Training, 27 September 2019
AFMAN 11-402, Aviation and Parachutist Service, 24 January 2019
AFMAN 31-115, Volume 1, Department of the Air Force Corrections System, 22 December
2020
AFMAN 36-2032, Military Recruiting and Accessions, 27 September 2019
AFMAN 36-2102, Base-Level Relocation Procedures, 16 December 2020
AFMAN 36-2136, Reserve Personnel Participation, 06 September 2019
AFMAN 36-2664, Personnel Assessment Program, 16 May 2019
AFMAN 36-2905, Air Force Physical Fitness Program, 11 December 2020
AFMAN 36-3004, Aviation Bonus (AVB) Program, 3 May 2019
AFMAN 65-605, Volume 1, Budget Guidance and Technical Procedures, 16 August 2012
DAFMAN 48-123, Medical Examinations and Standards, 8 December 2020
AFPCI 36-112, Line Officer Initial Skill Training Reclassification Procedures, 31 January 2019
AFH 33-337, The Tongue and Quill, 27 May 2015
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 153
AETCI 36-2651, Basic Military and Technical Training, 08 August 2019
Training Administration, 20 August 2018
Air Force Enlisted Classification Directory (AFECD)
Air Force Officer Classification Directory (AFOCD)
ANGI 36-2602, Air National Guard Retention Programs, 14 June 2019
Prescribed Forms
AF Form 63, Active Duty Service Commitment (ADSC) Acknowledgement Statement
AF Form 64, Reserve Service Commitment Acknowledgement/ Declination
Adopted Forms
AETC Form 125A, Record of Administrative Training Action
AETC Form 126A, Record of Commander’s Review Action
AF Form 8, Certificate of Aircrew Qualification
AF Form 101, Reserve Requirements for School Tours of Active Duty for Training
AF Form 964, PCS, TDY, Deployments, or Training Declination Statement
AF Form 1056, Air Force Reserve Officer Training Corps (AFROTC) Contract
AF Form 1288, Application for Ready Reserve Assignment
AF Form 1411, Extension of Enlistment in the Air Force
AF Form 2096, Classification/On-the-Job Training Action
AF Form 2098, Duty Status Change
AF Form 3933, MAJCOM Mission Training Request
AF Form 3920, Request for Reservist Voluntary Retraining
AF Form 422, Notification of Air Force Member’s Qualification Status
AF Form 847, Recommendation for Change of Publication
AF Form 964, PCS, TDY, Deployment, or Training Declination Statement
AF Form 1411-1, Cancellation of Extension of Enlistment in the Air Force
AFIT Form 9, Initial or Change to Reporting Instructions
SF 182, Authorization, Agreement and Certification of Training
DD Form 4, Enlistment/Reenlistment Document - Armed Forces of the United States
DD Form 785, Record of Disenrollment from Officer Candidate-Type Training
DD Form 1966, Record of Military Processing - Armed Forces of the United States
DD Form 2992, Medical Recommendation for Flying or Special Operational Duty
154 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Abbreviations and Acronyms
2 AF—Second Air Force
ABM—Air Battle Manger
ADSC—Active Duty Service Commitment
AETC—Air Education and Training Command
AFAEMS—Automated Education Management System
AFECD—Air Force Enlisted Classification Directory
AFI—Air Force Instruction
AFIT—Air Force Institute of Technology
AFOCD—Air Force Officer Classification Directory
AFOSI—Air Force Office of Special Investigations
AFPD—Air Force Policy Directives
AFR—Air Force Reserve
AFRC—Air Force Reserve Command
AFRCI—Air Force Reserve Command Instruction
AFROTC—Air Force Reserve Officer Training Corps
AFS—Air Force specialty
AFSC—Air Force Specialty Code
AFSOC—Air Force Special Operations Command
AFT—Advanced Flying Training
AGR—Active Guard and/or Reserve
ALO—Air Liaison Officer
ANG—Air National Guard
ANGI—Air National Guard Instruction
ARC—Air Reserve Component (both Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve)
ARMS—Automated Records Management System
ARPC—Air Reserve Personnel Center
ART—Air Reserve Technician
CAFSC—Control AFSC
CFM—career field manager
CIP—Career Intermission Program
CONUS—Continental United States
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 155
CRO—Combat Rescue Officer
CSO—Cobat System Operator
DEROS—date eligible for return from overseas
DET—––Detachment
DoD—Department of Defense
DoDI—Department of Defense Instruction
EAD—extended active duty
ELP—Excess Leave Program
ETCA—Education and Training Course Announcements
ETP—exception to policy
FBI—Federal Bureau of Investigation
FLEP—Funded Legal Education Program
FSS—force support squadron
FY—fiscal year
GPE—graduate professional education
HAF—Headquarters Air Force
HQ—headquarters
IR—individual reservist
IRR—inactive ready reserve
JA—judge advocate
JBSA—Joint Base San Antonio
JTR—Joint Travel Regulations
KLP—key leadership position
MAJCOM—Major Command
MilPDS—Military Personnel Data System
MPF—military personnel flight
MPS—military personnel section
MWS—major weapons system
myPers—My Personnel Services
NAF—Numbered Air Force
NGB—National Guard Bureau
NPS—non-prior service
156 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
OBJ IN—objective in
OBJ OUT—objective out
OJT—on-the-job training
OPR—office of primary responsibility
OTA—Oracle Training Announcement database
OTS—Officer Training School
PCA—permanent change of assignment
PCS—permanent change of station
PDS—permanent duty station
PIT—Pilot Instructor Training
PME—Professional Military Education
PS—prior sevice
RegAF—Regular Air Force
RI—reporting identifiers
RIO—Readiness and Integration Organization
RIP—report on individual person
RPA—Remotely Piloted Aircraft
RSC—reserve service commitment
SDI—Special Duty Identifier
SEI—Special Experience Identifier
SELRES—Selected Reserve
SG—Surgeon General
SRB—selective retention bonus
STO—Special Tactics Officer
TAG—The Adjutant General
TFCS—Total Federal Commissioned Service
TDY—temporary duty
UFT—Undergraduate Flying Training
UMD—Unit Manpower Document
UPT—Undergraduate Pilot Training
US—United States
USC—United States Code
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 157
USAFA—United States Air Force Academy
USAFR—United States Air Force Reserve
USAF—United States Air Force
USUHS—Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
Terms
Accession—Newly commissioned officer or new enlisted recruit entering EAD with no prior
military service. Refers to student entries rather than graduates.
Accessions Program Guidance Letter—AF/A1PT document identifying aggregate enlisted
(NPS and PS) and officer (rated and non-rated; line and non-line) accession levels for a given FY.
Active Component—Any organization of a regular component or defense agency to which an IR
is assigned.
Active Duty—Full-time duty in the active military service of the United States, including active
duty or full-time training duty in the Reserve Component. The term active duty for a period of
more than 30 days means active duty under a call or order that does not specify a period of 30 days
or less.
Active Duty Service Commitment (ADSC)—A period of active duty a member must serve
before becoming eligible for voluntary separation or retirement.
Active Guard and Reserve (AGR)—National Guard and Reserve members who are on voluntary
active duty providing full-time support to National Guard, Reserve, and Active Component
organizations for the purpose of organizing, administering, recruiting, instructing, or training the
Reserve Components. Members of a reserve component who are on active duty pursuant to 10
USC § 12301(d), or a member of the Air National Guard, on full-time National Guard duty
pursuant to 32 USC § 502(f) and who is performing AGR duty. The Secretary of the Air Force
may order a member of the AFR to active duty at any time, or retain him or her on active duty,
with the consent of that member, to perform AGR duty organizing, administering, recruiting,
instructing, or training the reserve components.
Administrative Control—Direction or exercise of authority over subordinate or other
organizations in respect to administration and support. Also called ADCON, including
organization of service forces, control of resources and equipment, personnel management, unit
logistics, individual and unit training, readiness, and mobilization, demobilization, discipline, and
other matters not included in the operational missions of the subordinate or other organizations.
ADSC-Incurring Event—Any event for which a member incurs an ADSC.
Advanced Training—Formal course that provides individuals who are qualified in one or more
positions of their Air Force specialty with additional skills and knowledge to enhance their
expertise in the career field. Training is for selected career Airmen at the advanced level of the
Air Force specialty.
Agency—A military organization constituted by directives issued by United States Air Force.
Air Force Specialty (AFS)—A group of positions requiring common qualifications. Each AFS
has a title and a code.
158 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC)—A combination of numbers and letters used to identify an
AFS. Officer AFSCs consist of four characters and/or digits. Airmen AFSCs consist of five
characters and/or digits. When more specific identification of position requirements and individual
qualifications is needed, alpha prefixes and suffixes are used with the numerical codes.
Air Reserve Component—An overarching term used when referring to both the ANG and AFR
together.
Airman or Airmen—A member or members of the US Air Force, which include officer and
enlisted and civilian members.
Aptitude Index—A number that represents the percentile score made on a single cluster.
Assignment—The permanent change of an Airman’s duty station from one location to another.
Also refers to duties performed. (Used alternately with the term “reassignment.”)
Awarded AFSC—An AFSC awarded to an individual as primary, second, third, or fourth AFSC
after certification of ability to perform in positions of an Air Force Specialty at a certain skill level.
Fourth AFSC applies only to enlisted personnel.
Basic Military Training—Training provided to NPS Airmen to effect an orderly transition from
civilian to military life.
Career Airman (Enlisted)—An enlisted Airman serving on the Airmen’s second or subsequent
enlistment.
Career Enlisted Aviator—An enlisted Airman awarded and performing permanent duty in
AFSCs 1AXXX/1UXXX.
Career Field—A group of closely related Air Force Specialties (or a single Air Force Specialty
when there are not related specialties) requiring basically the same knowledge and skills. A career
field includes subdivisions and ladders.
Career Field Ladder—A division of a career field in which closely related Air Force specialties
are arranged in one or more ladders to indicate lateral functional relationships merging at the 7- or
9-skill level.
Career Field Manager—Office of primary responsibility appointed to ensure assigned Air Force
specialties are trained and utilized to support Air Force mission requirements. Works in concert
with MAJCOM, forward operating agency, direct reporting unit, ANG, and AFRC functional
managers as required.
Category One processing discrepancy—A discrepancy found in the PCS process of an Airman
and/or a discrepancy found in the Personnel Reliability Program.
Chief Enlisted Manager Code—A five-digit code ending in ”00“ to identify Chief Master
Sergeant and Chief Master Sergeant selectees as top enlisted managers in both highly technical
skills and in broad areas of managerial competence.
Command—and/or Commander—The authority that a commander in the armed forces lawfully
exercises over subordinates by virtue of rank or assignment. A commissioned officer who, by
virtue of rank and assignment, exercises command authority over a military organization or
prescribed territorial area, which under pertinent official directives is recognized as a command.
This designation is used in all AF units authorized to be led by a commander except the USAF
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 159
Academy, which is commanded by a superintendent, and school and/or academic units, which may
be commanded by commandants.
Commander—An Air Force Specialty that identifies jobs of broad responsibility for command,
direction, and planning or staff supervision of diverse activities across several functional areas.
Emphasis on the command, managerial, and executive levels of duties and responsibilities.
Competitive Category—A group of officers who compete among themselves for promotion. The
established categories are: Line of the Air Force, Line of the Air Force-Judge Advocate, Medical
Corps, Dental Corps, Chaplain, Medical Service Corps, Biomedical Sciences Corps, and Nurse
Corps.
Control AFSC—A management tool used to make enlisted Airman assignments, to assist in
determining training requirements, and to consider individuals for promotion.
Convertible AFSC—Change in basic mission, weapon system, or equipment may require changes
to authorized AFSCs and reevaluation of training and individual qualifications for individual
AFSCs. Establishing a new AFS or revising existing ones usually requires changes to accession
targets, training courses and requirements, initial and selective reenlistment bonus applicability,
and manning documents as well as reevaluating entry, award, and retention qualification criterion.
Corporate Structure—Embodies the corporate review process for HQ Air Force. The primary
groups of the corporate structure are the Air Force Council, the Air Force Board, the Air Force
Group, the fourteen mission and mission support panels, and integrated process teams. This
structure increases management effectiveness and improves cross-functional decision making by
providing a forum in which senior Air Force leadership can apply their collective judgment and
experience to major programs, objectives, and issues. This process balances programs among
mission areas, between force structure and support, and between readiness and modernization.
Only military or DoD civilian personnel assigned to the Air Staff or Office of the Secretary of the
Air Force may serve as members of the corporate structure.
Craftsman Course—Course required by the Career Field Education Training Plan to attain the 7-
skill-level within an Air Force specialty.
Data Call—Process of polling users of Air Force training programs to capture their technical
training requirements triggered by the data call message.
Date Eligible for Return From Overseas (DEROS)—Date established for a member to complete
the member’s overseas tour and be eligible to return from overseas.
Date of Separation (DOS)—Date established by law and/or policy for the termination of active
or Reserve duty.
Development Team—Development teams are the responsibility of individual career field
functional authorities, functional managers, and the Deputy Chief of Staff, Manpower, Personnel
and Services (AF/A1). Development teams identify and provide vectors for education, training,
and experiences appropriate for personnel within each functional community based on current and
future requirements.
Direct Accession—The accession of individuals who receive their commission prior to attending
OTS when they are in a professional discipline like health professions, chaplaincy, or law.
160 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Disqualified Airman—An Airman whose skill has been withdrawn due to not meeting the
mandatory AFSC award and/or retention requirements in the AFECD Directory, or who cannot
maintain the skill according to Chapter 2 and has no other awarded skill.
Drill Status Guardsman—A unit member who participates in unit training assemblies,
traditionally one weekend per month and a two-week annual training period. Member's status can
be verified through member's servicing personnel office. Also known as Traditional Guardsman.
Dual Status—An individual simultaneously assigned to a position number in excess and over
grade status.
Duty AFSC—The AFSC denoting the specialty in which the individual is performing duty.
Duty Station—The place where an Airman performs military duty. Also see the JTR, Appendix
A.
Eliminee—Member who has been eliminated from training.
Emolument—A salary, fee, or profit from employment or office.
Enlisted Initial Skills Training—A formal training pipeline that results in the attainment of the
3-skill-level in an Air Force specialty.
Entitlement—As used in manning considerations, an alternate form of “Requirement.”
Entry AFSC—An AFSC showing potential or partial qualification in the Air Force Specialty.
The 4th digit of this code is always 1.
Evaluation Official—A disinterested field grade officer, Chief Master Sergeant, Senior Master
Sergeant, or Master Sergeant appointed to evaluate facts and circumstances surrounding a
recommendation to downgrade or withdraw an AFSC based on substandard performance.
Evaluation officials must be senior in grade to the person being evaluated.
Exception—A request involving guidance, procedures, or other actions in this manual which is
prohibited; is not addressed; a criterion is not met and there are no waiver provisions established;
or, there are waiver provisions but that criteria is not met. A circumstance that does not conform
to the normal rules, standards, usual occurrences, general principles, or the like.
Extended Active Duty—A tour of active military service (usually for more than 90 active duty
days) performed by a member of the Air Reserve Component when strength accountability
changes from the ARC to the active Air Force.
Feeder AFSC—The awarded AFSC from which an individual has progressed to the 5-, 7-, or 9-
skill level AFSC or Chief Enlisted Manager code when two or more AFSCs combine.
Field Training—Technical, operator, and other training either a training detachment or mobile
training team conducts at operational locations on specific systems and associated direct-support
equipment for maintenance and aircrew personnel.
First Term Airman—Individuals who are on their: (1) first enlistment (including Airmen who
have extended their enlistments for 23 months or less); (2) first EAD tour, or; (3) first enlistment
with prior active service of less than 24 months.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 161
Force Support Squadron—This squadron provides personnel, manpower, morale and recreation
services, food service and lodging support, child care, training, education and family readiness
functions to military personnel, their dependents and other eligible parties.
Fourth AFSC—The awarded AFSC in which an individual is fourth best qualified to perform
duty (enlisted only).
Full Time Support—Members of the Reserve component assigned to organize, administer,
instruct, recruit and train; maintain supplies, equipment and aircraft; and perform other functions
required on a daily basis in the execution of operational missions and readiness preparation as
authorized in 10 USC § 12301, Reserve components generally. Collectively, Full Time Support
personnel consist of five categories that are Traditional Reservist, AGR, ART, Active Component
personnel and civilian employees.
Functional Manager—Senior leader designated by the appropriate functional authority, who
provides day-to-day management responsibility over specific functional communities at the
MAJCOM, forward operating agency, direct reporting unit, or Air Reserve Component level.
While they should maintain an institutional focus on resource development and distribution,
functional managers are responsible for ensuring their specialties are equipped, developed, and
sustained to meet the functional community’s mission, as well as encouraging force development
opportunities in order to meet future needs of the total Air Force mission.
Headquarters Active Guard and Reserve—AGRs at the seat of government (or office that
exercises its authority to govern), and at HQ responsible for reserve affairs, to participate in
preparing and administering the policies and regulations affecting those reserve components
Health Professions Officer—Includes Medical Corps, Dental Corps, Medical Service Corps,
Nurse Corps, and Biomedical Sciences Corps officers, and applicants selected for or undergoing
training or schooling to qualify them for service in those corps.
Health Professions Scholarship Program—Members appointed as officers in the Ready
Reserve, who have completed their 4-year college degree, and are attending an accredited health
professions school. They receive a scholarship from the Air Force in return for pay back via active
and Reserve service.
Individual Mobilization Augmentee (IMA)—An individual reservist attending drills who
receives training and is preassigned to an Active Component organization, a Selective Service
System, or a Federal Emergency Management Agency billet that must be filled on, or shortly after,
mobilization.
Individual Ready Reserve—A manpower pool consisting of individuals who have had some
training or who have served previously in the Active Component or in the Selected Reserve, and
may have some period of their military service obligation remaining. This section consists of both
participating and non-participating members. Some of these members are those who completed
their 4 years of AD and serve the remainder of their 8 year obligation in the IRR. These members
are subject to involuntary recall by the President and Congress, and are also required to participate
in Muster or Push-Pull screenings.
Individual Reservist—An individual who is either an Individual Mobilization Augmentee or a
Participating Individual Ready Reserve member.
162 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Initial Qualification—A course of instruction which qualifies any rated officer to be an instructor
at a Formal Training Unit, or qualifies Career Enlisted Aviators to perform instructor duties on the
Major Weapon System.
Initial Skills Training—An overarching term for enlisted initial skills and (non-rated line) officer
initial skills technical training. For enlisted, it refers to a formal school pipeline, comprised of one
or more courses, that results in the award of the 3-skill-level in an Air Force specialty. For officers,
it refers to a formal school pipeline comprised of one or more courses of mandatory training needed
to become qualified in their Air Force specialty.
Instructor Qualification—Course of instruction qualifying any rated officer to be an instructor,
or qualifies Career Enlisted Aviators to perform instructor duties on the Major Weapon System.
Judge Advocate Officer—An officer of the Judge Advocate General’s Corps of the Army, Air
Force, or Navy, or officers of the Marine Corps or Coast Guard designated as a judge advocate.
Officers designated as judge advocates do so in accordance with AFI 51-101 and serve in the Judge
Advocate General’s Corps. Selectees and officers in training are not judge advocates until
designated by The Judge Advocate General. By statute, only attorneys qualified and designated
by TJAG as judge advocates may perform judge advocate functions. 10 U.S.C. § 9063(g); AFI 51-
101, Chapter 6.
Lateral AFSC—An AFSC that requires prior qualification at the semiskilled or higher skill level
as specified in the specialty description in AFECD, Airman Classification.
Lost Time—Time during which a member is in desertion, absent without leave, in confinement,
or incapacitated due to alcohol, drugs or disease or injury resulting from the member’s misconduct.
(See 10 USC § 972, Members: effect of time lost).
Major Command—A major subdivision of the Air Force, directly subordinate to HQ US Air
Force.
Major Command Functional Managers—Serve as MAJCOM liaisons for their respective Air
Force CFM. Monitor the health and manning of their career fields within their command and
elevate concerns to the Air Force CFMs while managing command training for their career field
and coordinate command training and personnel issues across their MAJCOM staff and with Air
Force CFMs.
Medical Service Officers—Includes officers of the Medical Corps, Dental Corps, Medical
Service Corps, Nurse Corps and Biomedical Sciences Corps.
MilPDS—A collective term encompassing the total vertical computerized MilPDS. It is used
when a specific subsystem is not being referenced. The system is designed to provide capability
for equitable, responsive, uniformly administered, and cost effective management and
administration of active duty military, ANG, USAFR, retired, and civilian personnel.
Military Personnel Section—Is the strategic advisor for military personnel policies and
programs. The mission of the MPS is to provide quality personnel support in both peacetime and
wartime to commanders, Air Force members and their families.
Military Technicians (Dual Status)—A Federal civilian employee providing full-time support to
a National Guard, Reserve, or Active Component organization for administration, training, and
maintenance of the Selected Reserve. ART and accepted Civil Service employees who are
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 163
members of the AFR or ANG (Title 32 USC § 709, Technicians: employment, use, status) unit
hired as technicians.
Mission Readiness Training—Formal training courses to aid mission accomplishment. Mission
readiness training provides advanced, supplemental and residential craftsman technical training
for courses of up to 99 academic days (less than 20 weeks), for officers, enlisted and civilian
personnel when other types of training (on-the-job-training, unit training, and exportable and
mobile training) will not satisfy the need.
Mission Readiness Training Program Working Group—Annual working group co-hosted by
AF/A1PT and AETC, focusing on the education of training requester quota identifier managers,
MAJCOM functional managers, and/or their representatives. In addition, the working group is the
forum where training requester quota identifier baseline adjustments can be made. Finally, it offers
an opportunity for all parts of the mission readiness training program process to interact and share
new information, while addressing any areas of concern, i.e., increased mission requirements or
emerging missions that may impact execution rates.
Muster—Formal gathering of IRR troops, especially for inspection, display or training, or military
exercise purposes. Under regulations prescribed by the Secretary of Defense, a member of the
Ready Reserve may be ordered without consent to muster duty one time each year. A member
ordered to muster duty under this section shall be required to perform a minimum of two hours of
muster duty on the day of muster in accordance with 10 USC § 12319, Ready Reserve: muster
duty.
Objective In—the number of members needed to retrain into a given AFSC based on the current
FY PGL
Objective out—the number of members needed to retrain out of a given AFSC based on the
current FY PGL
Officer Core ID—Initially based on the AFSC into which the member is classified at the time of
accession, approved for retraining, or approved for Competitive Category Transfer in accordance
with AFMAN 36-2032, Military Recruiting and Accessions. For officers accessed to the Ready
Reserve under an inter-service program, the Core ID will be determined utilizing the Defense
Manpower Data Center Occupational Database unless approved for retraining in conjunction with
accession to the USAFR.
Officer Initial Skills Training—Provides skill sets required to be successful in awarded AFSC.
Officer initial skills training is not AFSC awarding, but is used in conjunction with experience,
on-the-job-training, and other supplemental training to provide required skill sets.
Officer Sustainment Matrix—Spreadsheet provided by A1XD identifying shortfalls and
overages in the non-rated line officer inventory by AFSC and Commissioned Years of Service.
Out-year—The year(s) beyond a current FY.
Participating Individual Ready Reserver—Individual reserve members that participates for
points only status. Eligible to perform Military Personnel Appropriation man-days.
Permanent Change of Assignment (PCA)—The permanent change of assignment of an Airman
from one unit to another (with or without concurrent change of PDS).
164 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Permanent Change of Station (PCS) Notification—Official notification that Airmen have been
selected for reassignment. Airmen receive notification by accessing the Virtual Military Personnel
Flight after receiving an email advising they have been selected for an assignment. Alternatively,
commanders or other authorized officials notify Airmen by requiring them to sign the PCS
notification report on individual person notification message or notification memorandum
acknowledging assignment selection. When Airmen are TDY or on leave, notification is the date
they receive the notice.
Permanent Duty Station (PDS)—A service member’s official station or a civilian employee or
invitational traveler’s permanent workplace.
Personnel Data System—A collective term encompassing the total vertical computerized
personnel data system. It does not refer to a specific subsystem. The system provides capability
for equitable, responsive, uniformly administered and cost effective management, and
administration of active duty military, ANG, AFR, retired, and civilian personnel.
Pipeline—The strength accounting status of those members of the ANG assigned to a Student
Flight who are not qualified for mobilization and/or operational assignment because of training
not yet completed.
Pipeline Student—Newly accessed Airman undergoing processing, orientation, basic training, or
formal training immediately following Basic Military Training and have not PCSed to an
operational unit as a permanent party member.
Primary AFSC—The awarded AFSC in which an individual is best qualified to perform duty. It
will always be the AFSC with the highest skill level.
Program Guidance Letter(s) Adjustment—HQ Air Force-directed changes that modify a
program guidance letters baseline (e.g., increases) because of out-of-cycle training requests that
occur during budget or execution year. Also may include HQ Air Force-directed changes made to
training requirements resulting in a change to AETC aggregate funding. May be driven by force
management actions and user-requested changes.
Program Guidance Letters—Establishes training requirements for AETC execution. Program
Guidance Letters are the official tasking documents enabling AETC planners and programmers to
acquire the necessary resources for accomplishment of the tasking. The Program Guidance Letters
align the AF requirements with the Planning, Programming, Budgeting, and Execution process.
Includes Enlisted Initial Skills, Officer Initial Skills, Trained Dog Requirements, Mission
Readiness Training, Field Training, and Non-Resident training. If the funding changes in the DoD
Program Objective Memorandum process, AF/A1 determines how the changes will affect the
Program Guidance Letters and publishes official amendments as necessary.
Program Objective Memorandum—Office of the Secretary of Defense, service developed
document identifying money, people and equipment requirements and allocations over a specified
period of time, covering a five year period, e.g., FY 13-17. Program objective memorandum
funding baselines are used to develop budget level detail for distribution of resources during
budget execution years. The program objective memorandum is developed by individual services
to set objectives for their forces, weapon systems and logistical support within the fiscal limits
assigned to them by the Secretary of Defense.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 165
Programmed Technical Training—AETC documents reflecting training requirements by
training requester quota identifier and course. For enlisted, the documents include projected
elimination rates for active duty Air Force NPS students. Unlike the program guidance letters,
which reflect graduate requirements into the field for each Air Force specialty, the programmed
technical training documents reflect entries (or allocations, or class seats) by Air Force specialty,
course, and training requester quota identifier.
Push-Pull—A reserve action that is typically conducted every other year and is designed to
exercise and evaluate the mobilization process and crisis action procedures of indivduals.
Ensuring the nation has an adequate source of deployable, highly skilled reservists to support any
contingency is critical. Occasional reorientation or re-bluing is required for Airmen who are no
longer actively serving but still have a commitment to the Air Force.
Qualified AFSC—An officer AFSC showing full qualification in the Air Force Specialty. The
4th digit is always "3" and is authorized at any level.
Quota Management—The operation of swapping or moving scheduled quotas between non-Total
Force users or requesting use of another non-Total Force training user’s future scheduled unfilled
seats.
Quota Type—A two-character code within MilPDS/OTA used to indicate the student's duty status
(i.e., Airman, officer, or civilian) and the travel funding status (i.e., AETC centrally-funded, unit-
funded, or non-TDY).
Rated AFSC—Aircrew AFSCs (11XX, 12XX, 13BX, and 18XX) identify aircrew members
serving in, or qualified to serve in, Pilot, CSO, flight test positions, astronaut, ABM, and RPA
Pilot.
Requirement (Enlisted)—A shortage that exists at a unit or location when the 7th month
projected manning level in the AFSC ladder, skill level, and grade under consideration is below
the world-wide level, or 100 percent, whichever is lower. When the ladder manning is adequate
only because of overmanning at the 3 or 5-skill level, Career Field Managers may identify
requirements at the 7 or 9-skill level.
Requirement (Officer)—An actual or projected vacancy of a funded manpower authorization.
Requirements—The documented number of graduates by user as identified on the enlisted initial
skills, officer initial skills, trained dog requirements, mission readiness training, field training,
distance learning or language training program guidance letters, program requirements documents,
or corresponding planning spreadsheets.
Reserve Service Commitment (RSC)—A period of SELRES duty a member must serve before
becoming eligible for voluntary separation or retirement.
Reserve Service Commitment Date—The date the RSC expires.
Reserve Service Commitment Incurring Event—Any event for which a member incurs an RSC.
Resource—Airmen who possess a required skill and who are available for assignment to meet
manning requirements.
Retainability—Obligated military service. Time remaining on an overseas tour (including any
extensions) or time remaining in the Air Force SELRES.
166 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Retrainee—A previously trained enlisted Airman in the process of gaining qualifications in a new
AF specialty under an approved retraining program.
Retraining Advisory—An application in the MilPDS used at all levels of management that shows
AF retraining needs. AFPC/DP3DW manages the MilPDS Retraining Advisory folder.
Retraining AFSC—The AFSC for which an Airman is approved. It is not an awarded AFSC and
does not reflect the individual's qualification level.
Retraining—Either formal school or on-the-job training which qualifies an Airman for award of
a new AFSC or AFSC shred and/or suffix, to include lateral AFSCs.
Sabbatical—A temporary obligation of a member that does not allow participation in the
SELRES. The most common example is that of a church or denominational missionary tour
requirement. This is usually a period of two years. These members are placed in the Active
Standby while they serve their missionary obligation. The member will resume participation
immediately following the obligation.
Schoolhouse—Primarily refers to: Air University, AFIT, Goodfellow AFB, JBSA-Lackland,
JBSA-Fort Sam Houston, Keesler AFB, Sheppard AFB, Vandenberg AFB, USAF Academy, and
the USAF School of Aerospace Medicine.
Secondary AFSC—The awarded AFSC in which an individual is second best qualified to perform
duty.
Second-Term Airman (Enlisted)—See Career Airmen.
SELRES—A member of the Selected Reserve who is an actively serving Airmen and is currently
assigned to an Air Force Reserve, Air National Guard, or active duty unit (Traditional Reservists,
ARTs, IRs, and AGR members).
Separation—A general term encompassing discharge, retirement or release from reserve duty.
Separation and discharge are frequently simultaneous but not identical actions. A discharge severs
all ties to the military and occurs in accordance with the requirements of 10 USC § 1168, Discharge
or release from active duty: limitations. Release occurs when a member leaves one status and
goes to another (e.g., active to Reserve; release from ANG to Reserve; release from Reserve to
non-participating). Retirement places a member into an inactive reserve status potentially subject
to recall.
Shreds—positions within an AFSC associated with a particular airframe, piece of equipment, or
functions within that specialty
Sister Service—Another branch of military service within the DoD, i.e., Army, Navy, Marine
Corps, and Coast Guard.
Sister Service—and/or Other Agency Capacity—When Air Force members attend sister service
and/or other agency training, the number of seats given to Air Force can be a limiting factor that
can drive a capacity constraint. Air Force must follow the sister service and/or other agency
processes and timelines when requesting training seats.
Skill Level—The level of qualification within an awarded enlisted AFS, shown by the fourth
character of an enlisted AFSC.
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 167
Special Duty Identifier—A four- or five-digit code and title used to identify manpower positions
and persons performing duties not clearly within a specific career field. Has a complete specialty
description. Examples: 83RO Recruiting Service (Officer), 8P000 Courier (Enlisted).
Specialty Description—A description of an Air Force Specialty or SDI that includes a title, code,
specialty summary, duties and responsibilities, qualifications, other specialty data, and, when
established, suffixes.
Staff AFSC—Identifies an officer position above wing level specifically on the duty requirements
of the role performed, not the fact that the authorization is on a staff above wing level. Use staff
AFSCs (XXX4) to identify planning and policy-making positions above wing level. It requires
the same skills as those for the qualified AFSC (XXX3), but applied to developing broad policies,
plans, and procedures. Management responsibility increases without a corresponding increase in
knowledge of the technical aspects of the function. Officers filling or who have filled such
positions are awarded the staff AFSC.
Stop Loss AFSCs—Those AFSCs that are affected by the involuntary extension of a service
member’s active duty under the enlistment contract in order require to retain them beyond their
intial end of term of service (ETS) date and up to their contractually agreed end of active obligated
service.
Standby Reserve—Those units and members of the Reserve Component (other than those in the
Ready Reserve or Retired Reserve) who are liable for active duty only, as provided in the Title 10
USC §§ 10151, 12301, and 12306. Comprised of Reserve members who have no military Reserve
obligation, or those who have been temporarily excused from Reserve participation, or those who
have been designated as key or essential in their present civilian position. It is also used to place
members who have reached Reserve Sanctuary, Non-Affiliated Reserve Section-NC (18 but less
than 20 years satisfactory service for retirement) and are unable to participate in the SELRES.
Strength Aptitude—An individual's strength ability as measured by the Air Force Strength
Aptitude Test. The AFECD lists strength requirements for each AFSC.
Sub-allocation—Refers to a user’s allocation or class seat after a student name has been assigned.
Supplemental Training—Formal Air Force specialty specific training (post initial skills training)
on new equipment, methods or technology that are not suited for on-the-job training.
Surplus—When there are Airmen assigned to a location that has zero manpower authorizations in
a career field (Example: Senior Master Sergeant and below in 3S0X1). A surplus does require
assignment action because either there are no authorizations for the career field, manning at that
location will not support them to remain due to manning and/or requirements at other locations, or
they have been disqualified for duties. An overage does not require assignment action since there
are authorizations for the career field and the manning at that location, as well as overall manning
in the career field, allows them to remain. An overage or surplus situation may be impractical or
unnecessary to resolve by reassignment when it is the result of intentional action (possible plus up,
change in mission, career field manned at 133%) which has been approved by the assignment OPR
and functional assignment manager.
Sustainment—The provision of logistics and personnel services required to maintain and prolong
operations until successful mission accomplishment. Required number of officers throughout the
career field to accomplish the mission. Accounts for authorized versus assigned billets, retention
168 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
rates, career broadening and PME assignments drawing officers from core AFSC billets.
Calculations for sustainment incorporate career field health considerations.
Technical Advisor—Any military person awarded the AFSC at the 5-skill level or above that can
evaluate an individual’s specialty qualifications. Does not require formal designation.
Temporary Duty (TDY)—For assignment purposes, non-contingency duty performed at a
location other than an Airman’s permanent duty station. Also see JTR, Appendix A and DoDI
1315.18, Glossary.
Third AFSC—The awarded AFSC in which the individual is third best qualified to perform duty.
Total Force—Overarching term used when referring to the combination of RegAF, ANG, AFR,
and DoD civilians.
Trained Personnel Requirement (TPR)—A statement by AFSC of projected training and
retraining required by FY to keep the active Airman force at manning levels supportive of the Air
Force mission. The active duty Air Force Trained Personnel Requirement categories are NPS, PS,
and retrainees. It does not include ANG, AFR, sister service, international or civilian personnel.
Training Detachment—AETC detachment that provides technical training, at an operational
location, on specific systems and aerospace ground equipment. A training detachment aims to
qualify personnel on new equipment or in new techniques and procedures, maintain proficiency
and to increase skill and knowledge, acquaint personnel with specific systems, and keep personnel
aware of changing concepts and requirements.
Training Flow Management Working Group—Annual conference focused on refining enlisted
initial skills training requirements while addressing course capacity, constraints and shortfalls.
Training Requester Quota Identifier—A four-character communication code within Oracle®
Training Administration used to convey annual or supplemental training requirements, quota
allocations, allocation confirmations, and student-tracking information between a user of training
and the provider (owner) of training. Training requester quota identifiers are assigned to a service
branch, component, MAJCOM, forward operating agency, direct reporting unit, or functional area
to ensure training accountability. Only one training requester quota identifier is assigned to a
functional entity or training category.
Training Requester Quota Identifier Manager—Person(s) appointed to gather and report
annual training requirements and manage quotas. While only one training requester quota
identifier code is assigned to a functional entity, there can be multiple managers handling courses.
Training—Instruction and applied exercises for the acquisition and retention of skills, knowledge,
and attitudes required to accomplish military tasks.
Transaction—Any computer action and/or process used to create and/or change an Airman’s
personnel data.
Unit—Any military element whose structure is prescribed by competent authority. 2.An
organization title of a subdivision of a group in a task force. A separate and distinct functional
organization. In most cases, a unit is defined in manpower and personnel data systems by a
Personnel Accounting Symbol code. However, operating locations and detachments, which have
their own Personnel Accounting Symbol codes are not separate units, but are integral parts of their
parent unit. Combat Readiness Training Centers will be treated as units
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 169
Utilization Field—A group of Air Force officer specialties, related by required skills and
knowledge. A utilization field can consist of only one specialty if the skills and knowledge
required are unique and do not relate to other officer specialties.
Vector—The development team’s recommendation for training or education opportunities (e.g.,
resident Developmental Education, advanced functional training), assignments (e.g., Joint Staff,
Air Staff, MAJCOM, base level, etc.) or position type (e.g., flight commander, division chief,
instructor, special duty, etc.) a member is considered for in the next or subsequent assignments.
Voluntary Retraining—An application by an eligible Airman into a chosen skill where there is a
retraining need and mandatory quality standards.
Volunteer—An Airman who formally states the desire to accept a defined assignment.
Vulnerability—The relative standing of an Airman among the Airman’s peers for assignment
selection.
Waive or Waiver—To refrain from insisting upon compliance, enforcement; voluntarily give up
or relinquish; put aside or put off for a time or permanently. To allow deviation from a policy,
procedure, provision, standard, requirement, limitation, minimum, maximum, etc.

170 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 2
OFFICER AND ENLISTED ADSCS AND HEALTH PROFESSIONS OFFICER ADSCS
A2.1. Officer and Enlisted ADSCs. Specific ADSC information for training courses are listed
in the ETCA website (https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/app10-ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx) or via the
OTA database within MilPDS.
A2.2. Contact the Air Force Personnel Center, Accessions Branch (AFPC/DP3DA) for any
questions regarding this table or ETP request.
Table A2.1. Officer and Enlisted ADSCs.
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
1
EAD from a service
academy (10 USC §
9448)
5 years (T-0).
29
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur an ADSC of 2 years.
2
EAD from AFROTC
4 years (T-1).
31
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33 as defined
in AFMAN 36-2032.
2. If one accepted extended
scholarship entitlements, the
member will serve an
additional ADSC equivalent
to the entitlement extension.
The additional ADSC runs
consecutively not
concurrently to the original 4
year ADSC.
3
EAD for all other
commissioning sources
(see Table A2.2 for
Medical)
4 years for
Line of the
Air Force
(including
Judge
Advocate
General
Corps)
officers (T-1).
31
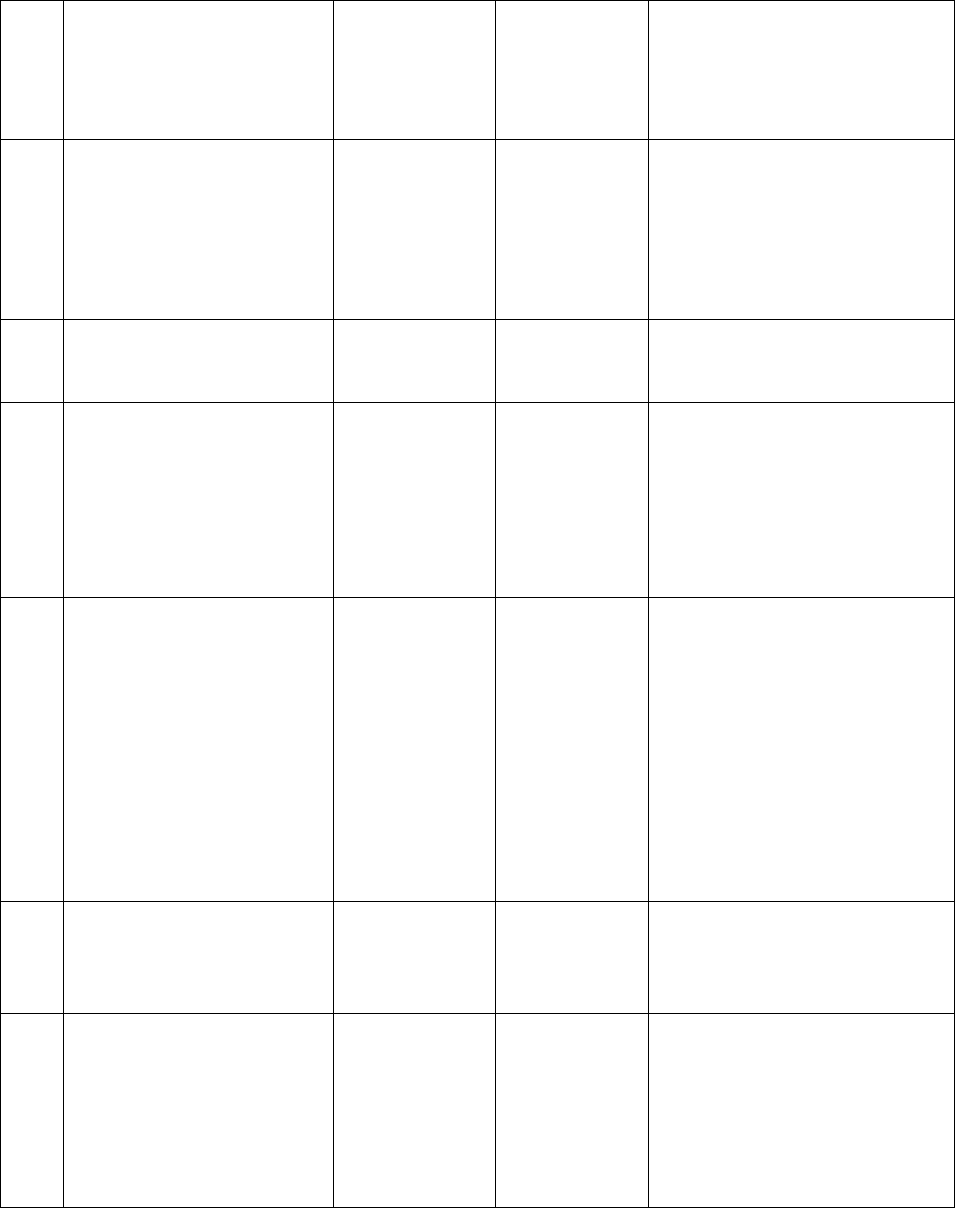
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 171
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
3 years for
Chaplains
(T-1).
4
EAD for recall to active
duty
Equal to DOS
on EAD
orders (T-1).
31
5
Direct Accession (i.e.,
the accession of a
individual in a
professional disciple
prior to OTS), Minimum
Term of Service, and
Constructive Credit
3 years (T-1).
12
6
PCS (CONUS to
CONUS)
(DoDI 1315.18 and AFI
36-2110)
2 years (T-1).
11
1. Excludes “low cost” and
“no cost” PCS. See AFI 36-
2110 for additional details.
2. Permissive and
Humanitarian PCS still incur
an ADSC. However, the
humanitarian PCS ADSC
may be reduced to a six-
month commitment if a
hardship condition exists
after PCS move.
7
PCS (Overseas to
CONUS)
(DoDI 1315.18 and AFI
36-2110)
1 year (T-1).
11
1. No AF Form 63 required
for this PCS
8
PCS (CONUS to
Overseas or Overseas to
Overseas)
(DoDI 1315.18 and AFI
36-2110)
Equal to
initial
DEROS; or
subsequent
changes to
DEROS
(T-1).
11
1. As an example: If a
curtailment or extension
occurs to the DEROS, the
ADSC will be adjusted to
match the new DEROS.
2. No AF Form 63 required
for this PCS
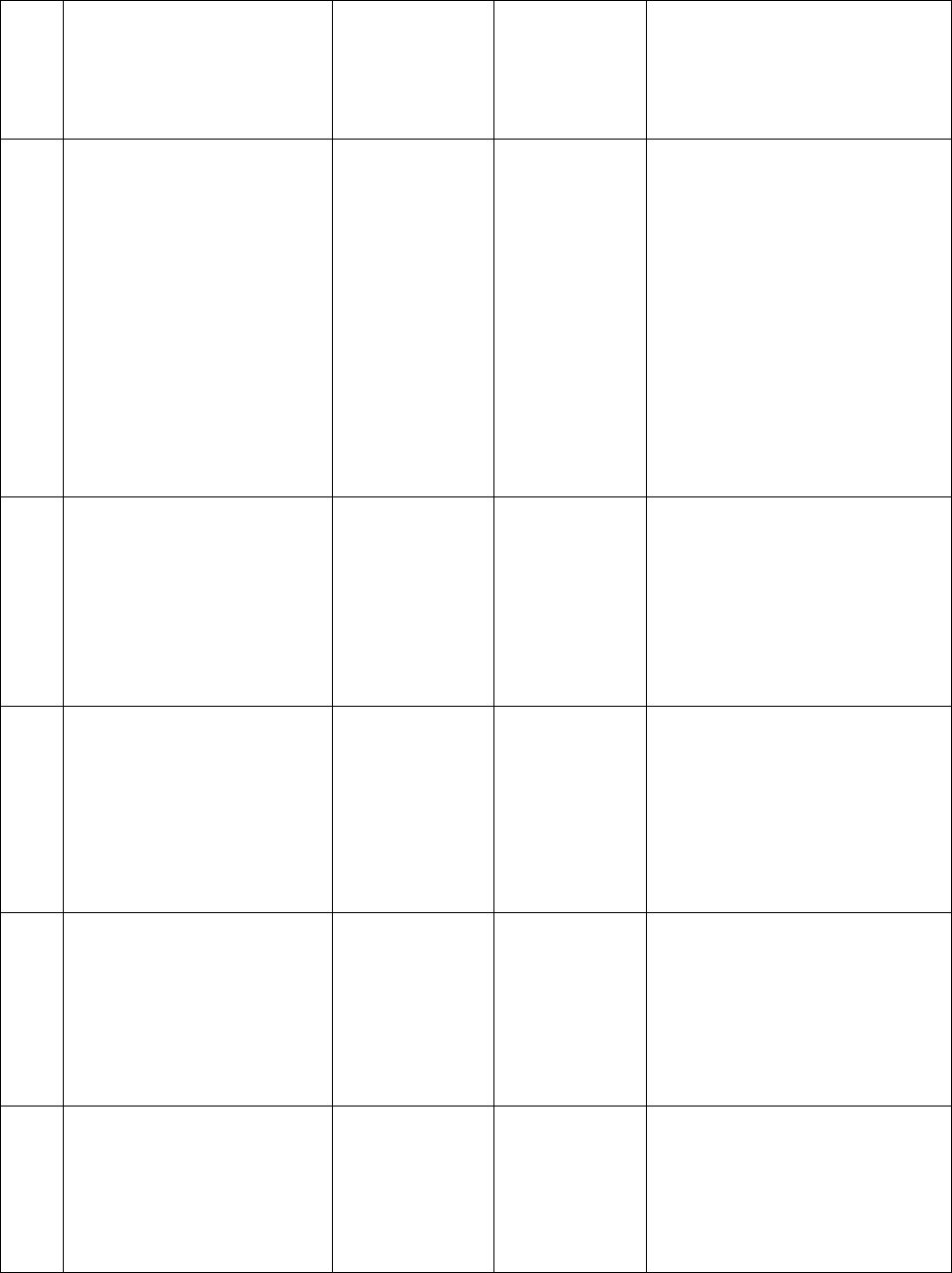
172 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
9
Promotions
2 years for
promotion to
Master
Sergeant,
Senior Master
Sergeant
(T-1).
3 years for
promotion to
Chief Master
Sergeant
(T-1).
10
1. There is no ADSC for
officer promotions.
2. There is no ADSC for
enlisted promotions from
Airman Basic through TSgt.
3. See AFI 36-3203 for
retired grade requirements.
4. Demotion action does not
automatically relieve an
enlisted member of an ADSC
previously incurred for
promotion.
10
Undergraduate Pilot
Training (UPT)
(10 USC § 653,
Minimum service
requirement for flight
crew positions)
10 years
(T-1).
80
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
11
Undergraduate Navigator
Training and Combat
Systems Officer (CSO)
(10 USC § 653)
6 years (T-0).
04
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
12
Undergraduate ABM
Training
6 years (T-1).
35
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
13
Undergraduate RPA
Training
6 years (T-1).
37
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 173
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
14
AFT: courses in the
following categories:
- Initial qualification (any
fixed, rotary wing
aircraft, or unmanned
aerial system RPA)
- Requalification (any
fixed, rotary wing
aircraft, or unmanned
aerial system RPA),
including senior officer
qualification courses as
defined in AFMAN 11-
202 V1, Aircrew
Training
- AETC Pilot Instructor
Training (PIT), including
senior officer
qualification courses as
defined in AFMAN 11-
202v1
- Rated Non-
Commissioned Officer
Aircrew members
attending AFT (Enlisted
Pilots)
No ADSC
05
1. Owning MAJCOM of the
course can make exceptions
to the No ADSC
requirement.
2. HAF/A3 will ensure
updated ADSCs are
warranted and do not cause
any unforeseen issues.
3. The ADSC will be
updated in ETCA for the
AFT courses that are covered
by this rule; if there are
changes to this rule, they will
require an ETP. (T-1).
4. ETPs have an expiration
date (not to exceed 10 years).
15
Test Pilot School (all
AFSCs)
Please see
ETCA (T-1).
05
1. Owning MAJOM/CC of
the course can prescribe
ADSC requirement.
2. HAF/A3 will ensure
updated ADSCs are
warranted and do not cause
any unforeseen issues.
3. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
training, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC from
the course elimination date,
using Reason Code 33.
4. Test Pilot School
graduates do not incur an

174 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
ADSC for initial
qualification, requalification,
or PIT training if the training
is in direct support of Flight
Test or Test Pilot School
Instructor duty. For these
occurrences, AFMC will
coordinate with AFPC for
adjudication of these
ADSCs.
16
USAF Weapons
Instructor Course (all
AFSCs)
Career Enlisted Aviator
Advanced Instructor
Courses
Please see
ETCA (T-1).
76
1. Owning MAJOM/CC of
the course can prescribe
ADSC requirement.
2. HAF/A3 will ensure
updated ADSCs are
warranted and do not cause
any unforeseen issues.
3. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33.
4. Members selected for
formal in-unit or unit funded
courses that are listed in
ETCA
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/ap
p10-
ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx
will still incur the ADSC.
This rule is not intended to
drive an ADSC for a non-
formal course.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 175
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
17
Flying Instructor
Qualification courses
No ADSC
77
1. Owning MAJOM/CC of
the course can prescribe
ADSC requirement.
2. HAF/A3 will ensure
updated ADSCs are
warranted and do not cause
any unforeseen issues.
3. The ADSC will be
updated in the ETCA for the
AFT courses that are covered
by this rule; if there are
changes to this rule, they will
require an they will require
an ETP (T-1).
4. ETPs have an expiration
date (not to exceed 10 years).
18
TG-16A Pilot and
Mission or Instructor
Pilot (applies only to the
306th Flying Training
Group)
No ADSC
89
1. Owning MAJOM/CC of
the course can prescribe
ADSC requirement.
2. HAF/A3 will ensure
updated ADSCs are
warranted and do not cause
any unforeseen issues.
3. The ADSC will be
updated in the ETCA for the
AFT courses that are covered
by this rule; if there are
changes to this rule, they will
require an they will require
an ETP (T-1).
4. ETPs have an expiration
date (not to exceed 10 years).
19
TG-15A/B Pilot and
Mission or Instructor
Pilot (applies only to the
306th Flying Training
Group)
No ADSC
89
20
Power Flight Program
Pilot and Mission or
Instructor Pilot
Qualification (applies
only to the 306th Flying
Training Group)
No ADSC
91
21
T-41 Pilot and Mission or
Instructor Pilot (applies
only to the 306th Flying
Training Group)
No ADSC
87
22
T-51, T-52, T-53A Pilot
and Mission or Instructor
Pilot (applies only to the
No ADSC
87

176 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
306th Flying Training
Group)
23
UV-18 Pilot Initial
Qualification
No ADSC
92
24
Initial Training: Combat
Rescue Officer (AFSC
13DX), Air Liaison
Officer (AFSC 13LX),
and Special Tactics
Officer (AFSC 13CX)
6 years
84
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
2. The ADSC for CRO will
be associated with the AETC
Combat Rescue Officer
course. The ADSC for STO
will be associated with the
Air Force Special Operations
Command
(AFSOC) Advanced Skills
Training course. The ADSC
for ALO will be associated
with the AETC Air Liaison
Officer Basic course.
25
Combat Aviation
Advisor initial Mission
Qualification Course
(applies only to AFSOC)
4 years
93
1. Due to operational
requirements, Combat
Aviation Advisor aircrew
members may be required to
crossflow and/or retrain into
aircraft or airframes for
AFSOC and/or Special
Operations Command
-directed missions.
Therefore, they will not incur
any additional AFT ADSCs
while they are serving as
Combat Aviation Advisors.
2. AFSOC will notify
AFPC/DP2LT of the
effective date of the ADSC.
26
Career Enlisted Aviators
attending AFT
4 years (T-2).
05
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 177
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
-Initial qualification (any
fixed, rotary wing
aircraft, or unmanned
aerial system RPA)
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33.
2. This rule does not apply
to NPS Accessions attending
initial and/or mission
qualification training into
their first major weapons
system.
27
Joint Interface Control
Officers
2 years
39
ACC/A3 will notify
AFPC/DP2LT of the
effective date of the ADSC.
28
Federally-sponsored
fellowships and
educational programs
lasting 10 weeks (approx.
70 calendar days) or
longer including, but not
limited to,
all advanced graduate
programs,
in-residence PME,
Education with Industry,
Advanced Studies Group
programs, technical
training, Air Force
funded industry training
and AFIT non-clinical
fellowships
(10 USC § 2005,
Advanced Education
Assistance: Active Duty
Agreement;
Reimbursement
Requirements & DoDI
1322.10, Policy on
Graduate Education for
Military Officers)
3 years
For Master’s
Degrees, 3
times the
length of the
period of the
education or
training with a
maximum of a
4.5 year
ADSC (T-1).
For Doctoral
programs, 5
years (Health
Professions
Officers
follow Table
A2.2
guidance)
(T-1).
78
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
2. Members selected for in-
unit or unit funded courses
will still incur the ADSC.
3. Examples of federally-
sponsored fellowships
include, but are not limited
to, Secretary of Defense
Corporate Fellowships,
National Defense
Fellowships, RAND
Research Fellowships, White
House Fellowships,
Legislative Fellowships,
Council on Foreign Relations
Fellowships, and National
Security Fellowships.
4. AFIT students who are
attending AFIT on a part-
time basis will not incur an
ADSC for completion of
AFIT courses.
5. For AFIT students
attending civilian

178 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
institutions, this ADSC will
normally begin upon
graduation. However, failure
to complete a thesis or
dissertation is not considered
formal elimination or
withdrawal if all requisite
coursework has been
completed and will not
excuse a member from
serving the full prescribed
ADSC.
29
Corporate, foundation, or
educational institution
sponsored fellowships,
scholarships, and grants
(10 USC § 2603,
Acceptance of
fellowships, scholarships,
or grants)
3 times the
length of
training
(Health
Professions
Officers
follow Table
A2.2
guidance)
(T-0).
32
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 2-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33, in
accordance with Rule 38.
30
Computer Network
Operations Development
Program
5 years
38
1. The ADSC begins on the
Course Graduation Date.
2. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur an ADSC using Reason
Code 33 for 1 year or
equivalent to the time spent
in training, whichever is
greater.
31
Remote Interactive
Operator Training or
National Security
Agency or United States
Cyber Command training
equivalent
3 years
38
1. The ADSC begins 24
months from the start of the
first (1 of 3) course date.
2. The ADSC will be
adjusted to reflect the Course
Graduation Date from course
3 of 3 if the individual
graduates prior to the 24
month mark.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 179
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
32
Tuition assistance of any
length or cost
(commissioned officers
only) (10 USC § 2007,
Payment of tuition for
off-duty training or
education)
2 years (T-1).
09
1. The ADSC begins after
the last date of the term
33
Post-911 GI Bill transfer
of education
(38 USC § 3319,
Authority to Transfer
Unused Education
Benefits to Family
Members)
4 years (T-0).
85
34
Legal education--
FLEP/ELP
(10 USC § 2004, Detail
as students at law
schools; commissioned
officers; certain enlisted
members)
ELP
FLEP: 2
years for each
year of
education
(T-0);
ELP: 4 years
(T-1);
FLEP/ELP
combined:
minimum of 5
years (T-0).
79
1. ADSC begins upon
completion of any other
unfulfilled ADSC (e.g.,
EAD). Additionally, no
portion of the education
period (including legal
internship) may satisfy any
existing ADSC. Exception:
The ADSC for initial PCS to
Law School is fulfilled
during the education period.
2. FLEP students who
withdraw or eliminate must
serve one year for each year,
or part thereof, of
participation in the program.
3. ELP students who
withdraw or eliminate must
serve one month for each
month of participation in the
program.
35
Air Force educational
leave of absence
(10 USC § 708,
Educational Leave of
Absence)
2 months for
each month of
the period of
the leave of
absence
08

180 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
program
(T-1).
36
Assignment to a critical
acquisition position
under the Acquisition
Professional
Development Program
(10 USC § 1734, Career
Development, and AFI
63-101/20-101,
Integrated Life Cycle
Management)
3 years from
effective duty
date; 4 years
from effective
duty date for
program
manager or
deputy
program
manager
(T-0).
72(3yrs),
73(4yrs)
37
Assignment to a KLP
(AFI 63-101/20-101)
Determined
by the Service
Acquisition
Executive
prior to
selection of
position
(T-0).
86
1. ADSC will begin from
effective duty date into KLP
position. If member is
transferred and/or removed
from the KLP position, the
ADSC incurred will be
adjusted and/or removed on
the effective date to a non-
KLP position.
38
Eliminated, withdrawal,
or resignation of training
2 years or the
length of the
program
ADSC,
whichever is
less
33
Note: ADSC is calculated
from the original projected
course graduation date.
39
Aviation Bonus
Reference
Aviation
Bonus
Agreement
70
See AFMAN 36-3004
40
Blended Retirement
Continuation Pay
4 years
55
41
Judge Advocate
Continuation Pay
ADSC is
stipulated by
AFI 51-101
90
42
Inter-Service Transfers
6 years for
rated officers
98 (3 years)
31 (4 years)

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 181
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring
event is for: (Rules
apply to all personnel
unless otherwise
indicated)
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code (see
Attachment
4)
Remarks:
3 years for
Chaplains
4 years for all
others
98 (6 years)
43
Career Intermission
Program (CIP)
(10 USC §710 and DoDI
1327.07
2 months for
every 1 month
in CIP (T-0).
08
1. This ADSC is consecutive
to other service
commitments
44
World Class Athlete
Program
3 years
98
1. Member will incur a 2-
year ADSC for voluntary
withdrawal from the WCAP,
except in the case where an
injury results in the member's
inability to continue training.
2. AFSVA/SVOR will
notify AFPC/DP2LT when a
member is selected for
WCAP to ensure the AF
Form 63 is completed.
45
Career Enlisted Aviators
attending AFT
- Requalification (any
fixed, rotary wing
aircraft, or unmanned
aerial system RPA)
- Transition Courses
(CEAs cross-flowing to a
different airframe within
their current AFSC)
2 years (T-1).
05
1. Upon formal withdrawal
or elimination from the
program, the member will
incur a 1-year ADSC using
Reason Code 33.
2. Members selected for
formal in-unit or unit funded
courses that are listed in
ETCA
https://cs2.eis.af.mil/sites/ap
p10-
ETCA/SitePages/Home.aspx
will still incur the ADSC.
This rule is not intended to
drive an ADSC for a non-
formal course.

182 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table A2.2. Health Professions Officer ADSCs.
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring event is
for
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code
Legal Citation
1
EAD from a service academy
5 years (see Notes 1 and
3) (T-1).
29
10 USC § 9448
2
Direct Accession and/or
Minimum Term of Service
2 years following
internship for physicians
(T-1).
3 years for all other
Health Professions
Officers (T-1).
12
DoDI 1322.10
3
EAD from AFROTC
4 years (see Notes 1 and
3) (T-1).
50
10 USC §§ 2107,
2101-2111b
AF Form 1056
4
Uniformed Services University
of the Health Sciences (USUHS)
Doctor of Medicine degree
awarding program only
7 years (see Notes 1, 3, 4,
5 and 7) (T-1).
53
10 USC § 2114,
Students: selection,
status, obligation
5
Armed Forces Health
Professions Scholarship
Program
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years; concurrent with
minimum term of service
(see Notes 3, 4, 5, 7 and
9) (T-1).
52
DoDI 6000.13
6
Initial One Year Advanced
Education in General Dentistry
and General Practice Residency
(Dental Corps)
Participation in these two
skill enhancement
programs incurs no
additional ADSC for the
officer and does not fulfill
any existing ADSC.
(T-1).
45
DoDI 6000.13
7
Graduate Professional Education
(GPE) internship and/or
residency (in a military training
program)
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years (see Notes 1, 3, 5,
6, 7, 9 and 10) (T-1).
45
DoDI 6000.13

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 183
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring event is
for
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code
Legal Citation
8
GPE internship and/or residency
(sponsored in a civilian training
program, e.g., AFIT)
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years (see Notes 1, 3, 4,
5, 7, 9 and 10) (T-1).
45
DoDI 6000.13
9
GPE internship and/or residency
(deferred or re-deferred)
Existing ADSC, minimum
2 years (see Notes 1, 3, 7
and 10) (T-1).
45
DoDI 6000.13
10
Financial Assistance Program
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years; concurrent with
minimum term of service
(see Notes 3, 5, 7 and 9)
(T-1).
45
DoDI 6000.13
11
GPE (clinical) fellowship (in a
military training program)
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years (see Notes 1, 3, 5,
6, 9 and 10) (T-1).
32
DoDI 6000.13
12
GPE (clinical) fellowship
(sponsored in a civilian training
program, e.g., AFIT)
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof, minimum
2 years (see Notes 1, 3, 4,
5, 9 and 10) (T-1).
32
DoDI 6000.13
13
Federally-sponsored fellowships
and educational programs
lasting 20 weeks (140 calendar
days) or longer including, but not
limited to, all advanced graduate
programs, in-residence PME,
Education with Industry,
Advanced Studies Group
programs, technical training, and
AFIT non-clinical fellowships
3 years (see Notes 1, 3, 4
and 8) (T-1).
78
DoDI 1322.10
AFPD 36-26
AFPD 41-1,
Health Care
Programs and
Resources
14
Inter-Service Physician Assistant
Program and Nurse Enlisted
Commissioning Program
3 years for 1st
year, then
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof. (see
Notes 1, 3 and 4) (T-1).
98
DoDI 1322.10

184 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
If the ADSC incurring event is
for
ADSC is
ADSC
Reason
code
Legal Citation
15
Full-time Masters or Doctorate
program – AFIT or Air Force
Medical Service sponsorship
3 years for 1st year, then
½ year for each ½ year or
portion thereof. (see
Notes 2, 4, 8 and 12)
(T-1).
02
DoDI 1322.10
AFPD 41-1
16
Health Professions Loan
Repayment Program– accession
& retention
Minimum 2 years, or 1
year for each annual
repayment, whichever is
greater (see Notes 3 and
11) (T-1).
44
DoDI 6000.13

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 185
Notes:
The ADSCs for all health care provider special and incentive pays, and accession and retention
bonuses which require contractual agreements, shall be in accordance with 37 USC § 335 and as
implemented through AFPD 36-20, Recruiting Programs and Accession of Air Force Military
Personnel.
1. Members who withdraw or eliminate incur an ADSC of 2 years or the length of time in
training, whichever is greater, not to exceed the ADSC for program completion. (Exception:
AFROTC cadets who withdraw or eliminate incur the ADSC set out in AFMAN 36-2032.
USUHS medical students who withdraw or eliminate incur an ADSC equal to the period
participated in the program, minimum of 1 year.)
2. Members who withdraw or eliminate incur an ADSC of 3 years or the length of time in
training, whichever is greater, not to exceed the ADSC for program completion.
3. Do not use any period of an educational or training program to satisfy ADSC.
4. Members serve this ADSC after fulfilling all previously existing educational or initial accession
ADSCs.
5. Extensions of training (beyond original approved completion date) will incur ½ year ADSC for
each ½ year extension or portion thereof.
6. Members serve this ADSC consecutively with other ADSCs incurred for GPE training.
7. Required to fulfill 3 year minimum term of service or 2 year minimum term of service
following internship for Medical Corps.
8. For AFIT students attending civilian institutions and USUHS students, this ADSC will
normally begin upon graduation. However, failure to complete a thesis or dissertation is not
considered formal elimination or withdrawal if all requisite coursework has been completed and
will not excuse a member from serving the full prescribed ADSC.
9. Do not use any period without possession of a current, valid unrestricted license or approved
waiver, if a health care provider, to satisfy ADSC.
10. GPE is the education that begins after completion of the basic professional degree. It is
comprised of internships, residencies, and fellowships completed by physicians, dentists,
veterinarians, or other health care specialists in their respective professional fields. For Nurse
Corps, clinical fellowships may authorize sub-specialization suffix to the parent (primary) 4-digit
AFSC upon completion of the clinical fellowship program. Nurse Corp fellowship training may
be limited to only a single 3-digit AFSC career field; whereas non-clinical fellowships do not
provide sub-specialization suffix to the parent (primary) 4-digit AFSC upon completion of the non-
clinical fellowship program. Nurse Corps fellowship training may be open to more than one 3-
digit AFSC career field.
11. ADSC for accession Health Professions Loan Repayment Program will be served first when
combined with an existing medical education or training ADSC. ADSC for contractual multiyear
pay, to include multiyear incentives will be served consecutively and after the Health Professions
Loan Repayment Program ADSC.
12. ADSC incurred for participation in a military clinical psychology internship program may be
served concurrently with an ADSC incurred for the Armed Forces Health Professions Scholarship
Program.

186 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 3
SERVICE COMMITMENTS (ANG ONLY)
Table A3.1. Airman Service Commitments.
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
Airman
Service Commitment
(Notes 1,6)
Beginning
Source
Document
1.
Attends aircrew
courses conducted
by AETC and the
operational
commands
Three months for each
academic week or part
of academic week but
no less than six months
and no more than 36
months (Note 2). (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Training
Certificate and/or
Orders
2.
Attends field
training detachment
courses
Six months. (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Training
Certificate and/or
Orders
3.
Attends technical
training of less than
20 weeks (Note 3)
Six times the length of
training but not less
than six months. (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Any official
document bearing
the date training
was completed
such as
certificate, special
orders, or training
report.
4.
Attends technical
training of 20
weeks or more but
less than 12 months
(Note 3)
Three years (Note 4).
(T-2).
Day after course
completion
Any official
document bearing
the date training
was completed
such as
certificate, special
orders, or training
report.
5.
Attends technical
training of 12
months or more
(Note 3)
Four years. (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Any official
document bearing
the date training
was completed
such as
certificate, special
orders, or training
report.
6.
Attends any type of
enlisted PME in-
residence only
12 months. (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Training Cert
and/or Orders

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 187
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
Airman
Service Commitment
(Notes 1,6)
Beginning
Source
Document
7.
Promotion to the
grade of Master
Sergeant
Drill Status Guardsman
and military technician
– 12 months
AGR - 24 months.
(T-2).
Date of promotion
Promotion orders
or AF Form 2096
8.
Promotion to the
grade of Senior
Master Sergeant
Exceptional Promotion
Program 36 Months
(Note 5)
All Others- 24 months.
T-2).
Date of promotion
Promotion orders
or AF Form 2096
9.
Promotion to the
grade of Chief
Master Sergeant
Exceptional Promotion
Program - 36 Months
(Note 5)
All Others- 24 months.
(T-2).
Date of promotion
Promotion orders
or AF Form 2096
10.
Attends Air Force
Basic Military
Training
36 Months. (T-2).
Day after course
completion
Any official
document bearing
the date training
was completed
such as
certificate, special
orders, or training
report.
Notes:
1. Service commitments incurred as a result of two or more rules of this table are served
concurrently.
2. Except for the instructor survival-training course, the service commitment for all survival
training is six months.
3. Formal training not identified in other rules of this table.
4. Minimum service commitment of six months and a maximum of 36 months for training with
an academic length of 20 weeks or more. Computation for six times the length of training:
academic length x 1.4 (length in calendar days) x 6 divided by 30 equals service commitment in
months (always round up).
5. Non waivable.
6. TAG is the waiver authority for service commitments. This authority may not be delegated
below TAG. (T-2).

188 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Table A3.2. Officer Service Commitments.
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
Type Training
Qualifiers
Service
Commitment
(Notes 1, 11)
Is effective
Supporting
Document
1.
UPT,
Undergraduate Pilot
Training-Helicopter
(UPT-H),
Specialized
Undergraduate Pilot
Training (SUPT),
Specialized
Undergraduate Pilot
Training-Helicopter
(SUPT-H), Joint
Specialized
Undergraduate Pilot
Training (JSUPT)
(Note 2)
N/A
Seven years
Date of the
original
aeronautical
rating
Aeronautical
order
2.
UPT, UPT-H,
SUPT, SUPT-H,
JSUPT (Note 2)
Entering
training on or
after 1 October
99
Ten years.
(T-2).
3.
Undergraduate
Navigator Training
(UNT), Joint
Undergraduate
Navigator Training
(JUNT),
Specialized
Undergraduate
Navigator Training
(SUNT)
Entering
training on or
after 1 October
99
Six years.
(T-2).
4.
Undergraduate Air
Battle Manager
Training
N/A
Six years.
(T-2).
Day after
completion of
ABM course
Any official
document
bearing the
date training
was
completed
such as
certificate,
special orders,
5.
Fixed Wing
Qualification
N/A
Six years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
6.
Receives initial
training in an
aircraft major
weapons system
N/A
Five years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 189
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
Type Training
Qualifiers
Service
Commitment
(Notes 1, 11)
Is effective
Supporting
Document
(MWS) group
(Note 3)
or training
report.
7.
Receives initial
training in a
different aircraft of
the same MWS
group (Note 4)
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
8.
Receives initial
training in an
aircraft (not a
MWS) (Note 5)
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
9.
Receives
qualification
(upgrade or
mission) training in
current aircraft
(Note 6)
N/A
Two years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
10.
Receives re-
qualification
training in an
aircraft (Note 7)
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
Any official
document
bearing the
date training
was
completed
such as
certificate,
special orders,
or training
report.
11.
Attends USAF
Weapons School
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
12.
AETC Initial Pilot
Instructor Training
(PIT), in-unit re-
qualification for
T- 37, T-38, AT-38,
T-43, or T-1
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
13.
Attends Squadron
Officer School
and/or Armed
Forces Staff
College
N/A
One year.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion

190 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
Type Training
Qualifiers
Service
Commitment
(Notes 1, 11)
Is effective
Supporting
Document
14.
Attends
Intermediate
Service School,
Senior Service
School (In-
residence) or
completes training
at comparable
schools of other
armed services
N/A
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
15.
Attends technical
training of less than
20 weeks, includes
Advanced
Instrument School
(Note 8)
N/A
Six times the
length of
training but not
less than 6
months (Note
9). (T-2).
Day after
course
completion
Any official
document
bearing the
date training
was
completed
such as
certificate,
special orders,
or training
report.
16.
Attends technical
training of 20
weeks or more but
less than 12 months
(Note 8)
NA
Three years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
Any official
document
bearing the
date training
was
completed
such as
certificate,
special orders,
or training
report.
17.
Attends technical
training of 12
months or more
(Note 8)
N/A
Four years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
18.
Survival school
courses
N/A
Six months.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion
19.
Attends off duty
education with
tuition assistance
(AGR only)
N/A
Two years.
(T-2).
Day after
course
completion

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 191
R
U
L
E
A
B
C
D
E
Type Training
Qualifiers
Service
Commitment
(Notes 1, 11)
Is effective
Supporting
Document
20.
Field Training
Detachment
courses
N/A
Six months.
(T-2).
21.
Service
commitment cannot
be determined in
accordance with
rules above. (Note
10)
Notes:
1. Service commitments incurred as a result of two or more rules of this table are served
concurrently.
2. Applicants and commanders who provide proper documentation of a seven year commitment
signed and dated prior to 1 Dec 98 for SUPT classes starting in FY 00, will be recognized and
honored by the NGB.
3. This is the first training experience in an aircraft of a major weapons system group, such as,
fighter or bomber systems (F-15, F-16, A-10, B-1), tanker systems (KC-135), airlift systems (C-
5, C-41, C-130, C-17), and special duty aircraft (EC-130, HC-130, HH-60, counter drug
aircraft). Cross-flow from fighter to non-fighter and non-fighter to fighter incurs a 5-year
commitment.
4. This is training in a different type aircraft within the same MWS group, such as an F-16 pilot
undergoing F-15 training. For this purpose all non-fighter aircraft are considered one group.
5. Examples: C-9, C-12, C-20, C-21, C-22, C-23, C-26, C-27, C-29, C-32, C-37, C-38, C-135,
C-140, CASA 212 and T-39 aircraft.
6. This is training to update the qualifications of aircrew members in the same aircraft, such as a
copilot upgrading to aircraft commander, aircrew members upgrading to instructor status, and
aircrew members receiving mission qualification training.
7. This is training to re-qualify an aircrew member in an aircraft in which previously qualified.
8. Includes AU/AFIT continuing education courses, weather courses, education or professional
training not specifically shown in other rules of this table.
9. Minimum service commitment of 6 months and a maximum of 36 months for training with
an academic length of 20 weeks or more. Computation for 6 times the length of training:
academic length x 1.4 (length in calendar days) x 6 divided by 30 equals service commitment in
months (always round up).
10. Contact NGB/A1P to determine appropriate service commitment.
11. TAG is the waiver authority for service commitments. This authority may not be delegated
below TAG. (T-2).
192 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 4
PREVIOUS AND CURRENT ACTIVE DUTY SERVICE COMMITMENT REASON
CODES WITH CLEAR TEXT TITLES
01 Air Force Institute of Technology (Education with Industry)
02 Air Force Institute of Technology
03 Technical Training
04 UPT (prior to 1 October 99), UNT, Undergraduate RPA Training
05 Advanced Flying Training
06 Thunderbirds
07 Professional Military Education
08 Education Absence of Leave
09 Tuition Assistance
10 Promotion
11 Permanent Change of Duty Station
12 Minimum Term of Service
13 Selective Continuation
14 1st Manned Space-flight Control Squadron (MSFSG/HQ AFSCF Tour)
15 FBI Academy
16 Air Force Intern Program
17 Airborne Warning and Control System Course (AWACS)
18 Initial Missile Qualification
19 Air Traffic Control Upgrade Training Officer Program
20 Junior Officer Cryptologic Career Program
21 Air Force Office of Special Investigation Senior Investigation Course
22 White House Fellowship Program
23 Funded Legal Education Program
24 Excess Leave Program (ELP)
25 AFMC Scientist and Engineering Exchange Program
26 Research Associate Program
27 Miscellaneous Education or Professional Training
28 Accept Indefinite Reserve Status
29 USAF Academy
30 Recalled to Active Duty
31 Extended Active Duty
32 Fellowship, Scholarship, Grant, TNG # include Health Svc Officers
33 Eliminate, withdraw, resign, TNG # include Health Svc Officers
34 Educational Leave of Absence
35 Airborne Battle Manager Ground Training
36 Airborne Battle Manager Initial Flying Training Qualification Training
37 Undergraduate Remote Pilot Aircraft Training
40 Internship Health Services Officer
41 Medical, Dental or Veterinarian Student Program
42 Senior Medical, Dental or Veterinarian Student Program
43 Post Graduate or Graduate Health Services Professional Education Training
44 Health Professions Loan Repayment Program
DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 193
45 Residency Training
46 Additional Special Pay
47 Health Professions Incentive Special Pay
48 Health Professions Multi-year Special Pay or Retention Bonus
49 Continuation Pay for Dental Corps in Training or Payback Status
50 ROTC Pre-Health
51 ROTC Education Delay
52 Health Professions Scholarship Program
53 Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences
55 Blended Retirement Continuation Pay
60 Engineering or Scientific Career Continuation Pay
61 Manned Space Flight Engineer or Payload Specialist
62 Laboratory Associates Program
63 Minute Man Education Program
64 Defense Advanced Language Area Studies Program
65 Special Agreement with Specified Period of Time Contracts
66 Medical Unique Situations
67 Medical Personnel Over 60
68 Intelligence Program
69 Critical Skills Retention Bonus (CSRB) or Zone E (SRB)
70 Aviator Continuation Pay (ACP)
71 Pilot Bonus Transition
72 Critical Acquisition Position (3 years)
73 Critical Acquisition Position Program Manager (4 years)
74 Health Professions Accession Bonus
76 USAF Weapons Instructor Course (WIC)
77 Instructor Qualification (Other than PIT)
78 All In-residence Education, including all AFIT Programs
79 Funded Legal Education Program (FLEP) and Excess Leave Program (ELP)
80 Undergraduate Pilot Training (UPT)
84 Combat Rescue Officer (CRO), Special Tactics Officer (STO), or Air Liaison Officer (ALO)
85 Post 9-11 GI Bill Transfer of Education Benefits
86 Key Leadership Position
90 Specialty Pay Legal Officers
98 Other
99 Unknown

194 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 5
SERVICE COMMITMENT STATEMENTS OF AGREEMENT
Active Duty Service Commitment (ADSC) Statement of Agreement Sample (RegAF).
If selected for a Pilot, Remotely Piloted Aircraft Pilot, Combat Systems Officer, or Air Battle
Manager training slot by the Undergraduate Flying Training Selection Board, I accept the
appropriate ADSC as specified in Table A2.1 in AFMAN 36-2100.
(Signature and Date)
Name (last, first, middle)
Grade
Social Security Number (Social Security Number)
Witnessed by MPF official:
Reserve Service Commitment (ANG) Statement of Agreement (SAMPLE)
MEMORANDUM FOR RECORD FOR TAG
I accept the appropriate service commitment as specified in Attachment A9X, Rule XXX.
This statement must be signed, dated by the applicant and witnessed by a servicing 3F0X1 in the
FSS.
(Signature and Date)
Applicant’s Rank and Full Name
(Signature and Date)
Witness’s Rank and Full Name

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 195
Attachment 6
DELETED
A6.1. DELETED.
A6.2. DELETED.
Table A6.1. DELETED.
Table A6.2. DELETED.
Table A6.3. DELETED.
Table A6.4. DELETED.
Table A6.5. DELETED.
Table A6.6. DELETED.
Table A6.7. DELETED.

196 DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021
Attachment 7
DELETED
Table A7.1. DELETED.
Table A7.2. DELETED.

DAFMAN36-2100 7 APRIL 2021 197
Attachment 8
DELETED
*DELETED
