
How to generate tables
using SAS
Liying (Lily) Wu
Research Analyst
Health Quality Council of Saskatchewan

Outline
• Process to generate table
• Proc tablulate and examples
• Proc report and examples
• A comparison of Proc tablulate and
Proc report

Generating table process
Step1. Design the table
• Specification of classification variables and analysis variables,
• definition of dimensions of the table,
• Identification of desired statistics etc..
Step2. Generate the SAS code
Step3. Customize the table.
Label, format, style, font, weight

Proc tablulate
Proc Tabulate is used to build tabular reports containing descriptive information,
including hierarchical relationships among variables.
This procedure provides flexible report writing features such as:
flexible table construction
multiple dimensions
use of labels and formats

Proc tablulate
The general syntax
PROC TABULATE <option(s)>;
BY <DESCENDING> variable-1 <...<DESCENDING>variable-n> <NOTSORTED>;
CLASS variable(s) </options>;
CLASSLEV variable(s)/ STYLE=<style-element-name| <PARENT>><[style-attribute-specification(s)] >;
FREQ variable;
KEYLABEL keyword-1='description-1'<...keyword-n='description-n'>;
KEYWORD keyword(s)/ STYLE=<style-element-name|<PARENT>><[style-attribute-specification(s)]>;
TABLE <<page-expression, > row-expression,> column-expression< / table-option(s)>;
VAR analysis-variable(s) </ options>;
WEIGHT variable;

Proc tablulate-Example 1
proc tabulate data=asthma1 order=data ;
class region;
var number ;
table number*mean*region;
run;

Proc tablulate-Example 2
proc tabulate data=asthma1 order=data ;
class region;
var number ;
table region, number*mean ;
run;

Proc tablulate-Example 3
proc tabulate data=asthma order=data ;
class region time;
var number;
table time, region , number*mean ;
run;
. . . . portions of the table not shown . . .
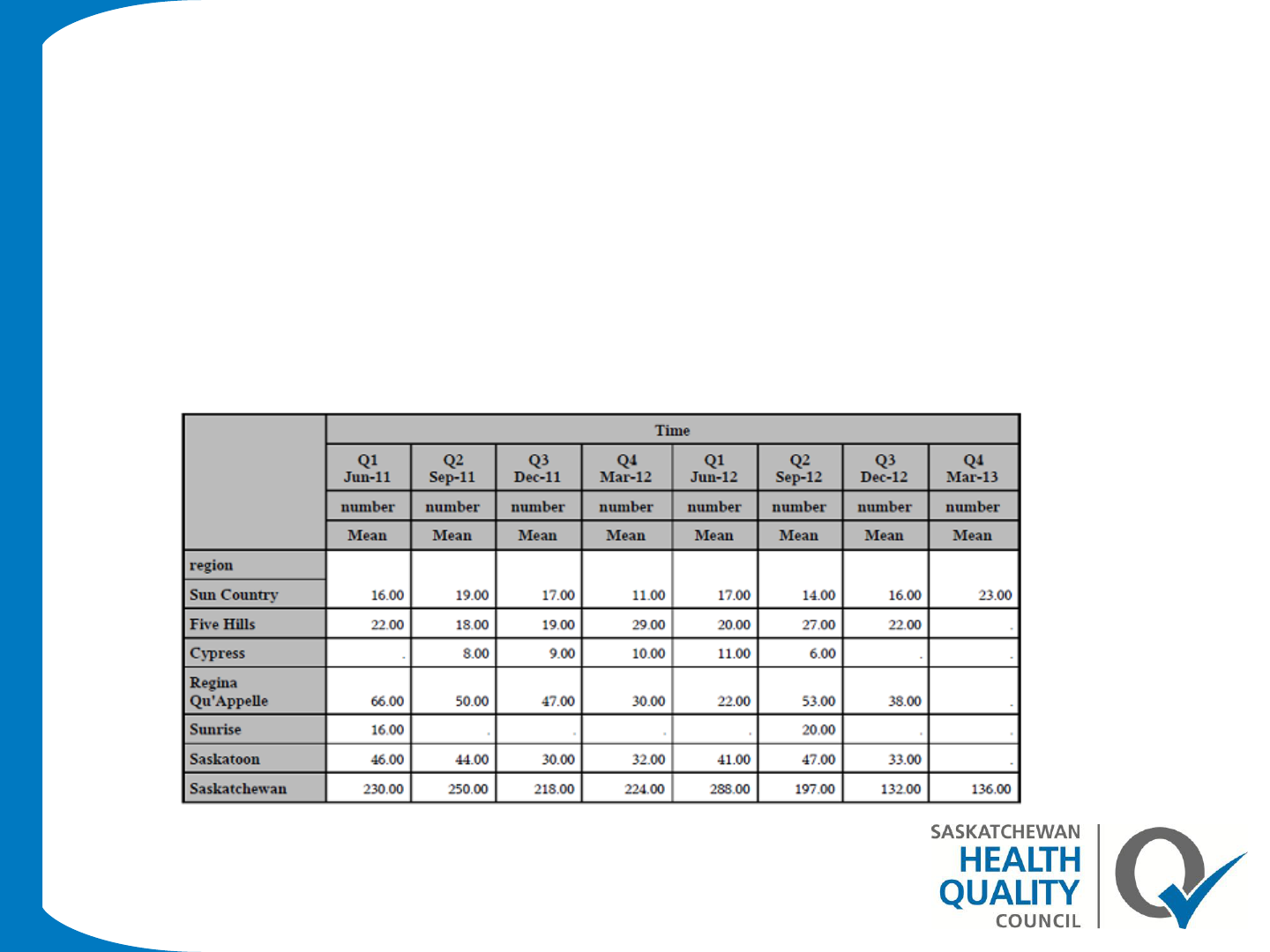
Proc tablulate-Example 4
proc tabulate data=asthma1 order=data ;
class region time;
var number ;
table region, number*mean*time ;
run;

Proc tablulate-Example 5
proc template;
define style styles.sty3;
parent=styles.printer;
style header/ font_size=0.7 font_weight=bold font_face="arial" ;
end;
run;
proc format;
value $backf
'Sun Country' = 'white'
'Five Hills' ='CX93D6FF'
'Cypress' = 'white'
"Regina Qu'Appelle "='CX93D6FF'
'Sunrise' = 'white'
'Saskatoon' ='CX93D6FF'
'Saskatchewan'='beige';
run;
options nodate nonumber orientation=portrait pagesize=max;
ods pdf file="U:/SAS/table/table1.pdf " style=sty3;

Proc tablulate-Example 5
title " Rate of Asthma related hospitalizations per 100,000 population
and count of hospitalizations ";
proc tabulate data=grap.obs_rate_asthma order=data;
class region reference time;
classlev time/style=[background=CX93D6FF];
classlev region / style=[background=$backf.];
classlev reference / style=<parent>;
var number ;
table (region *reference)*[style=<parent>[font_weight=medium
fontfamily="arial" foreground=black font_size=0.7]], time*number='
'*f=4./ misstext=[label="*"] box=[label="Baseline as Oct 31, 2011"
style=[font_weight=light fontfamily="arial" foreground=black
font_size=0.2]];
keylabel sum=' ';
keyword all/style=<parent> ;
run;


Proc report
The REPORT procedure combines features of the PRINT, MEANS, and TABULATE
procedures with features of the DATA step in a single report-writing tool that
can produce a variety of reports.
This procedure provides features as following:
Generating table easily
flexible to allow the calculation of a cumulative total and row
change.

Proc report
The general syntax
PROC REPORT <option(s)>;
BREAK location break-variable</ option(s)>;
BY <DESCENDING> variable-1 <…<DESCENDING> variable-n> <NOTSORTED>;
COLUMN column-specification(s);
COMPUTE location <target> </ STYLE=<style-element-name> <[style–attribute -specification(s)]>>;
LINE specification(s); . . . select SAS language elements . . .
ENDCOMP;
COMPUTE report-item </ type-specification>;
CALL DEFINE (column-id, ’attribute-name’, value); . . . select SAS language elements . . .
ENDCOMP;
DEFINE report-item / <usage> <attribute(s)> <option(s)> <justification> <COLOR=color> <’column-
header-1’ <…’column-header-n’>> <style>;
FREQ variable;
RBREAK location </ option(s)>;
WEIGHT variable;

Proc report-Example 1
Proc report data=asthma1 nowd;
column region number;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define number/"Mean" mean format=6.2 ;
run;
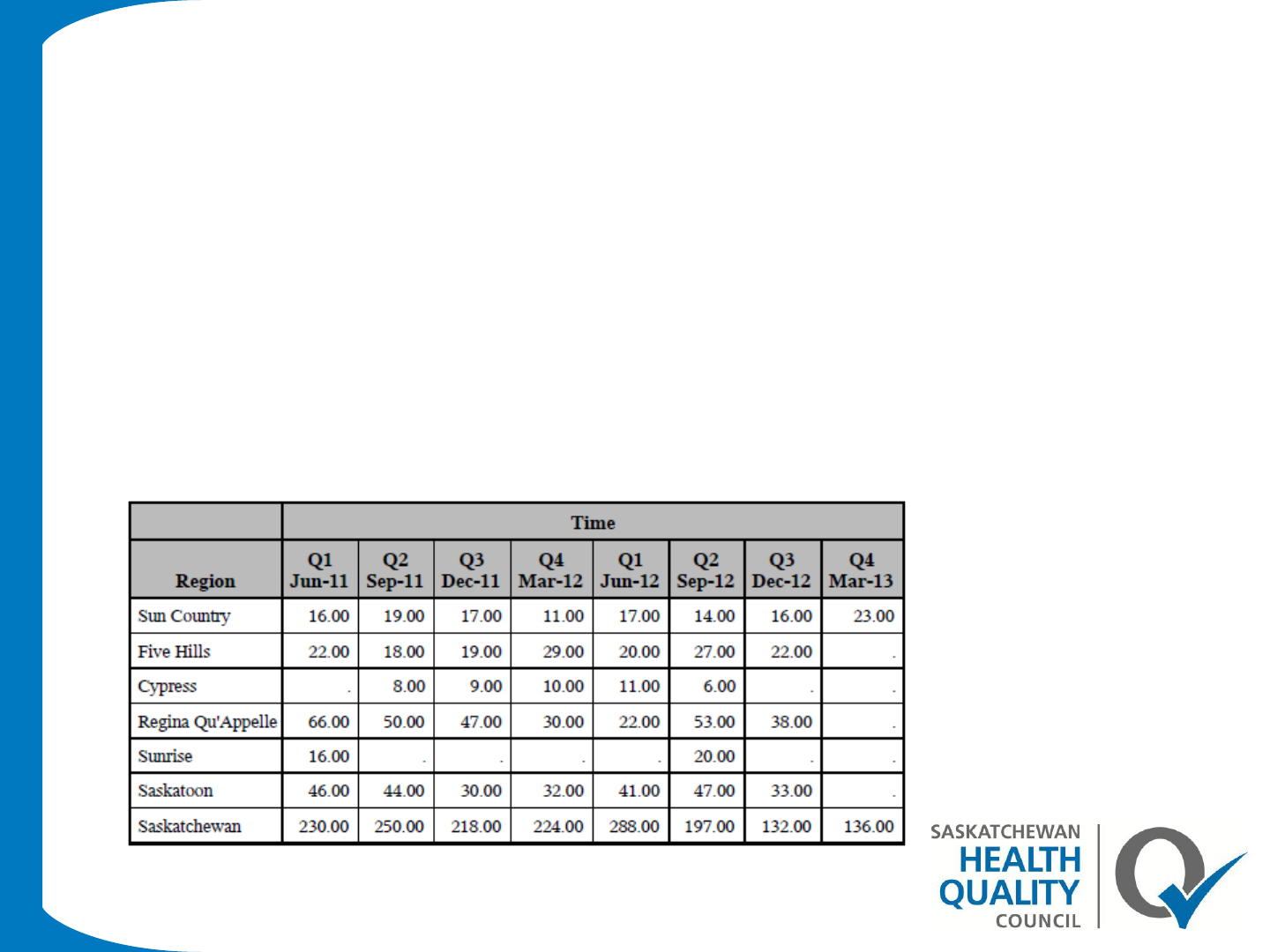
Proc report-Example 2
Proc report data=asthma1 nowd ;
column region number, time;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define time/ across order=data "Time" ;
define number/ "" analysis format=6.2 ;
run;

Proc report-Example 3
Proc report data=asthma1 nowd ;
column region time number;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define time/ order=data "Time" ;
define number/ "" sum analysis format=6.2 ;
break after region/ol skip summarize suppress;
rbreak after/ dol skip summarize;
run;

. . . . portions of the table not shown . . .

Proc report-Example 4
Proc report data=asthma nowd
style(header)=[background=CX93D6FF font_size=0.7 font_weight=bold
font_face="Arial"]
style(column)=[font_size=0.7 ];
column region reference number, time;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define reference/ "Reference" group;
define time/ across order=data "Time" ;
define number/ "" analysis format=6.0 ;
compute region;
if region='' then call define
(_row_,'STYLE','STYLE=[background=CX93D6FF]');
if region='Saskatchewan' then call define
(_row_,'STYLE','STYLE=[background=beige]');
endcomp;
run;


Proc report
Compute block
One of the unique features of the REPORT procedure is the Compute
Block.
• Unlike most other SAS procedures, PROC REPORT has the ability to modify values
within a column, to insert lines of text into the report, to create columns, and to control
the content of a column.
• Through compute blocks it is possible to use a number of SAS language elements,
many of which can otherwise only be used in the DATA step.
Compute <location> <report_item> </ options>;
one or more SAS language elements
Endcomp;
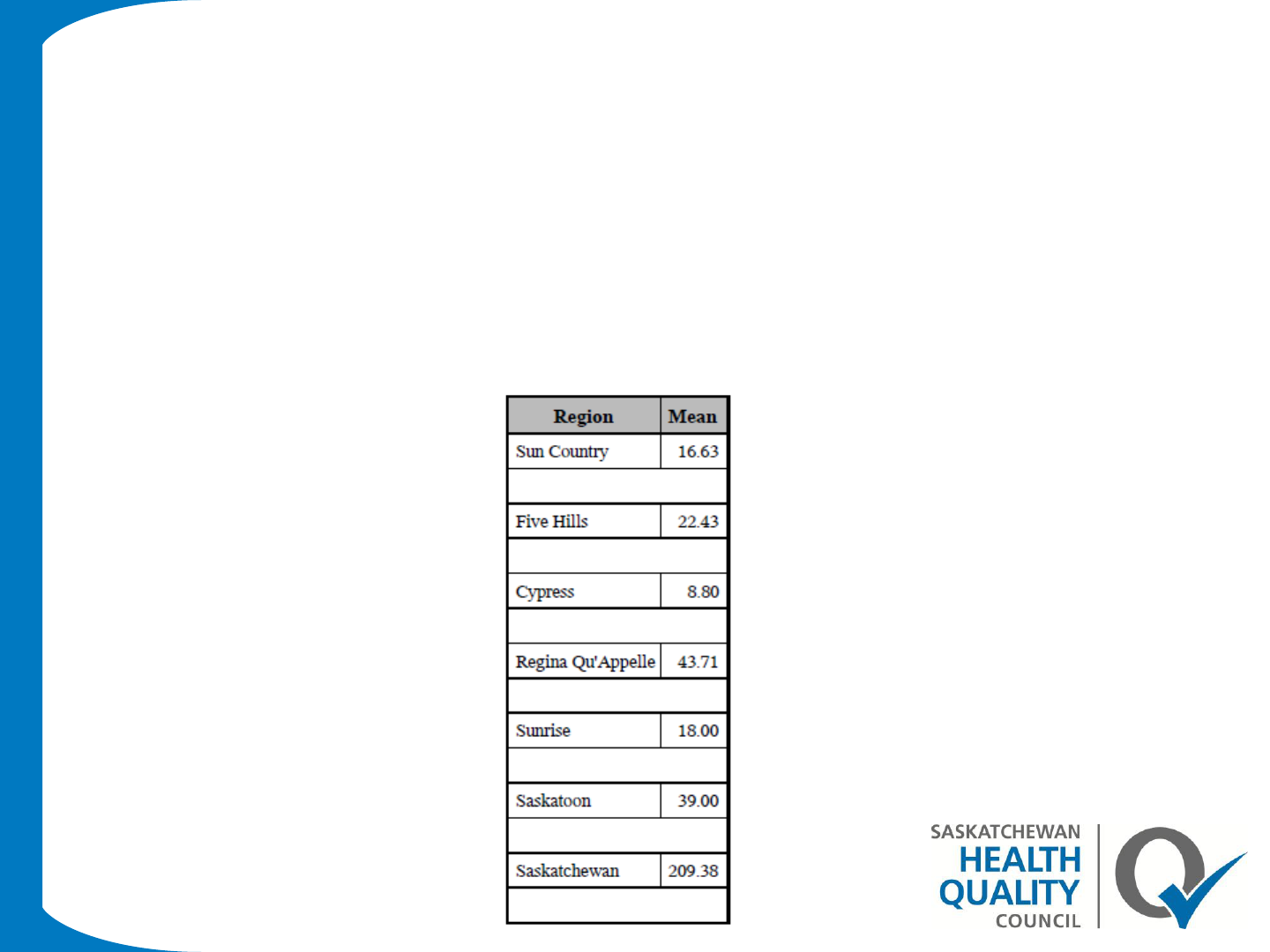
Proc report-Example 5
Proc report data=asthma1 nowd;
column region number;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define number/analysis "Mean" mean format=6.2 ;
compute after region;
line '';
endcomp;
run;
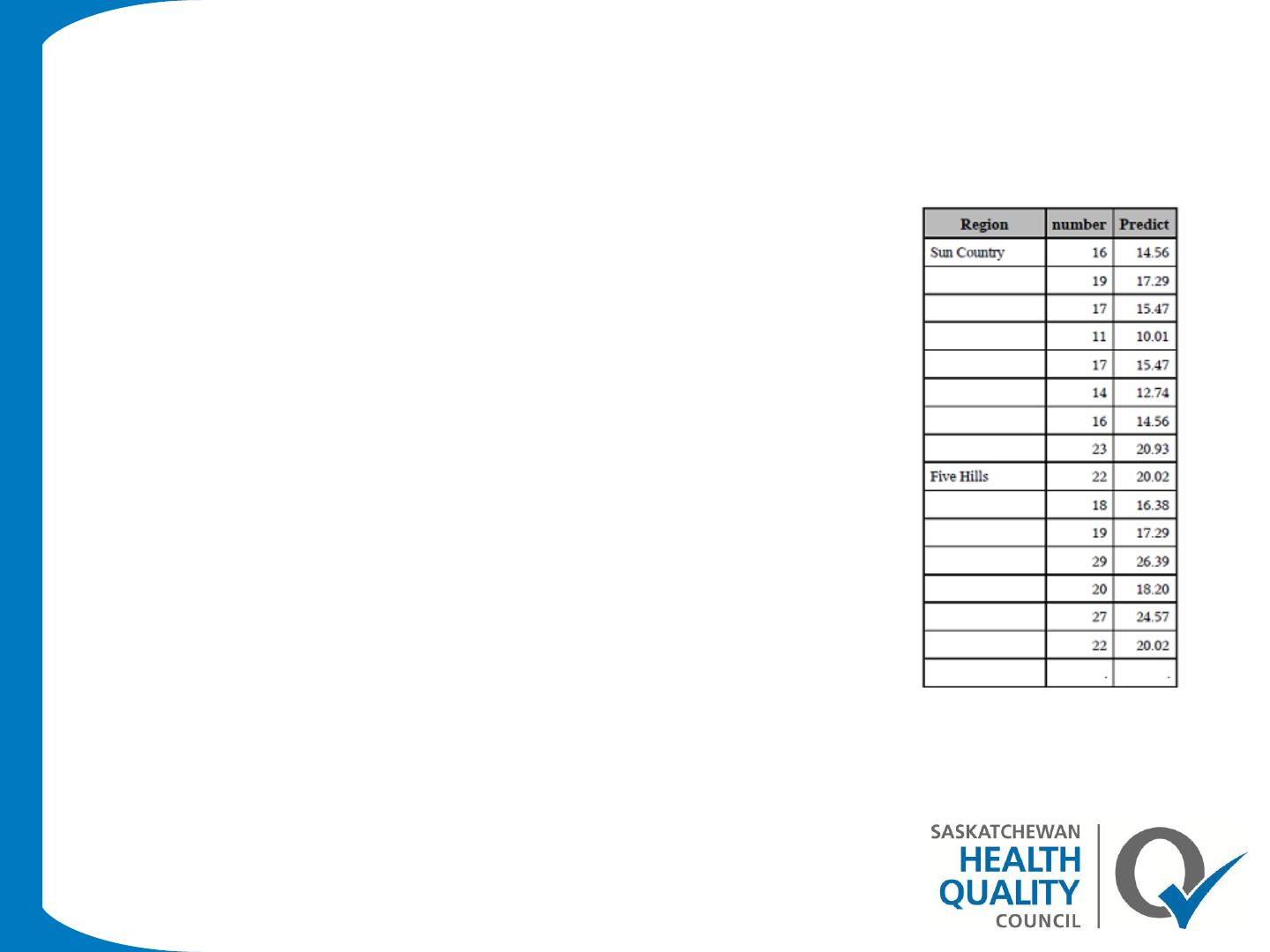
Proc report-Example 6
Proc report data=asthma1 nowd ;
column region number predict;
define region /"Region" group order=data ;
define number/disply ;
define predict/ computed "Predict" format=6.2 ;
compute predict;
predict=number*0.91;
endcomp;
run;
. . . portions of the table not shown . . .

Comparison of Proc tabulate with
Proc report
Proc tabulate
• Flexible table construction
• Supporting three-dimensional table.
Proc report
• Providing both detail and summary reports.
• Compute block.

Reference
1. Art Carpenter, Carpenter's Complete Guide to the SAS REPORT Procedure
2. Michele M.Burlew , SAS guide to report writing examples
3. Ray pass , PROC REPORT: Doin’ it in style
4. Arthur L. Carpenter PROC REPORT: Getting Started with the Primary Statements
5. Arthur L. Carpenter, PROC REPORT: Compute Block Basics – Part II Practicum
6. Lauren Haworth, Anyone Can Learn PROC TABULATE
7. Thomas J. Winn, Introduction to PROC TABULATE
8. Jonas V. Bilenas, Making Sense of PROC TABULATE (Updated for SAS9)

Thank you!
